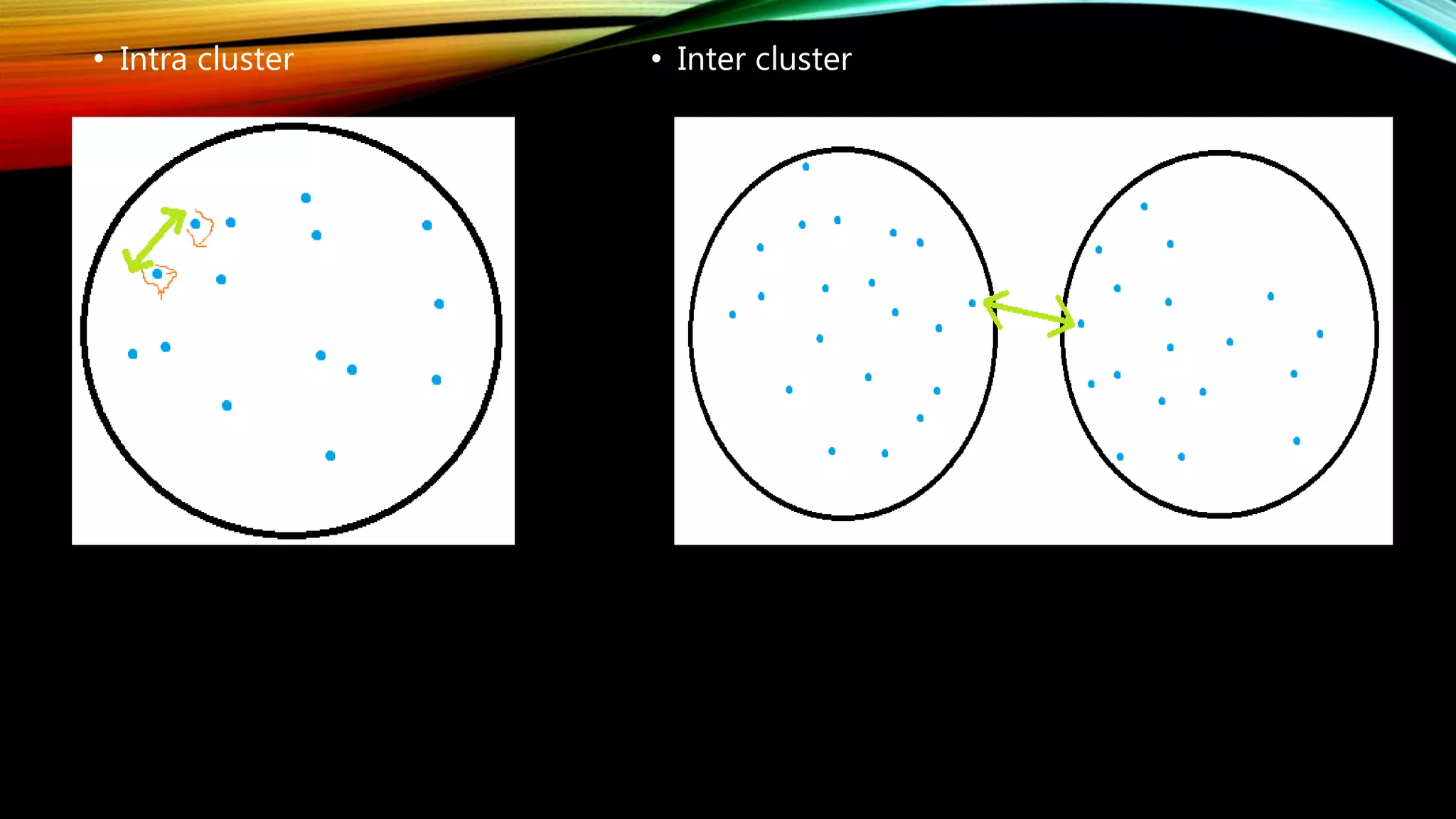
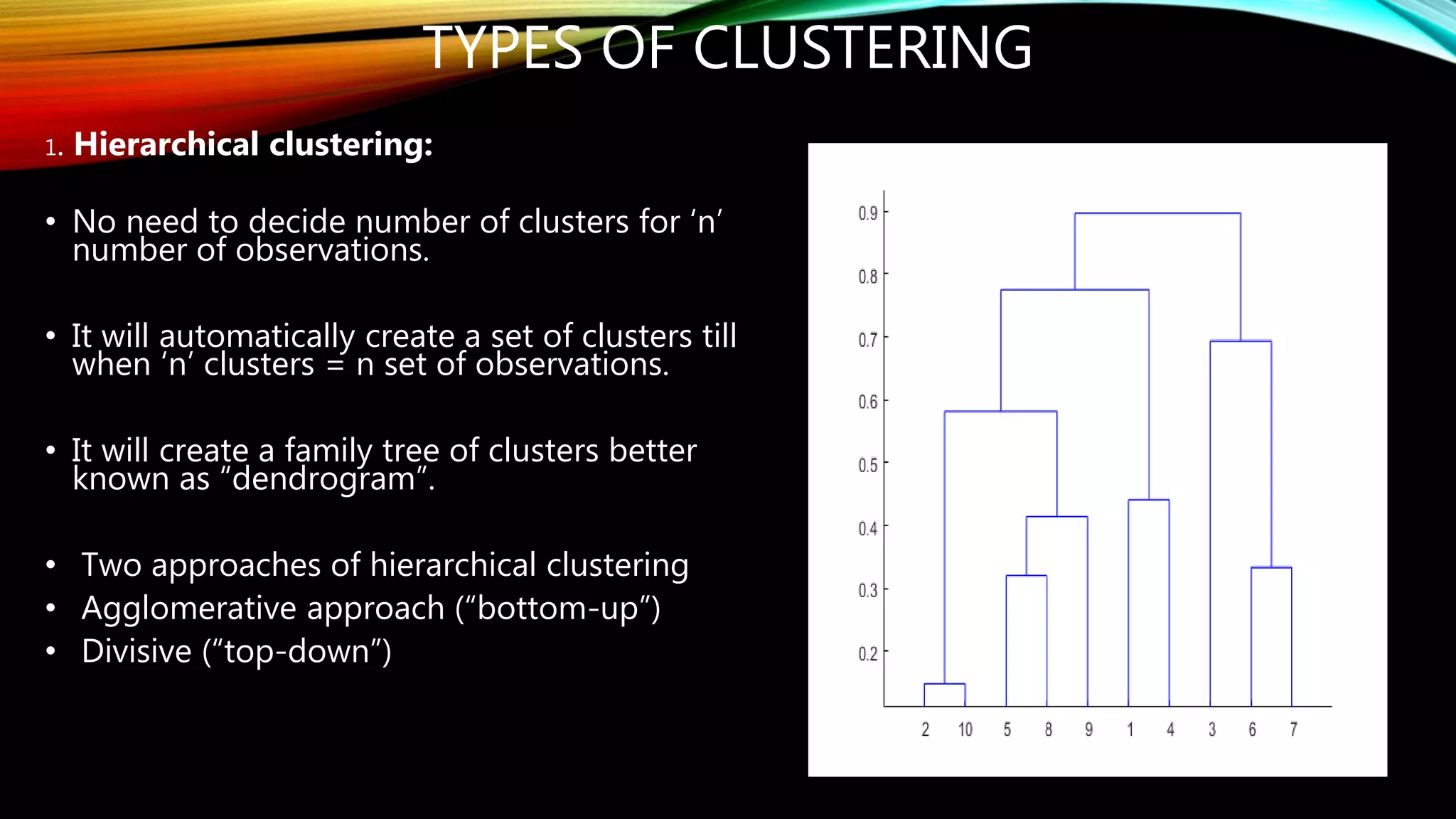
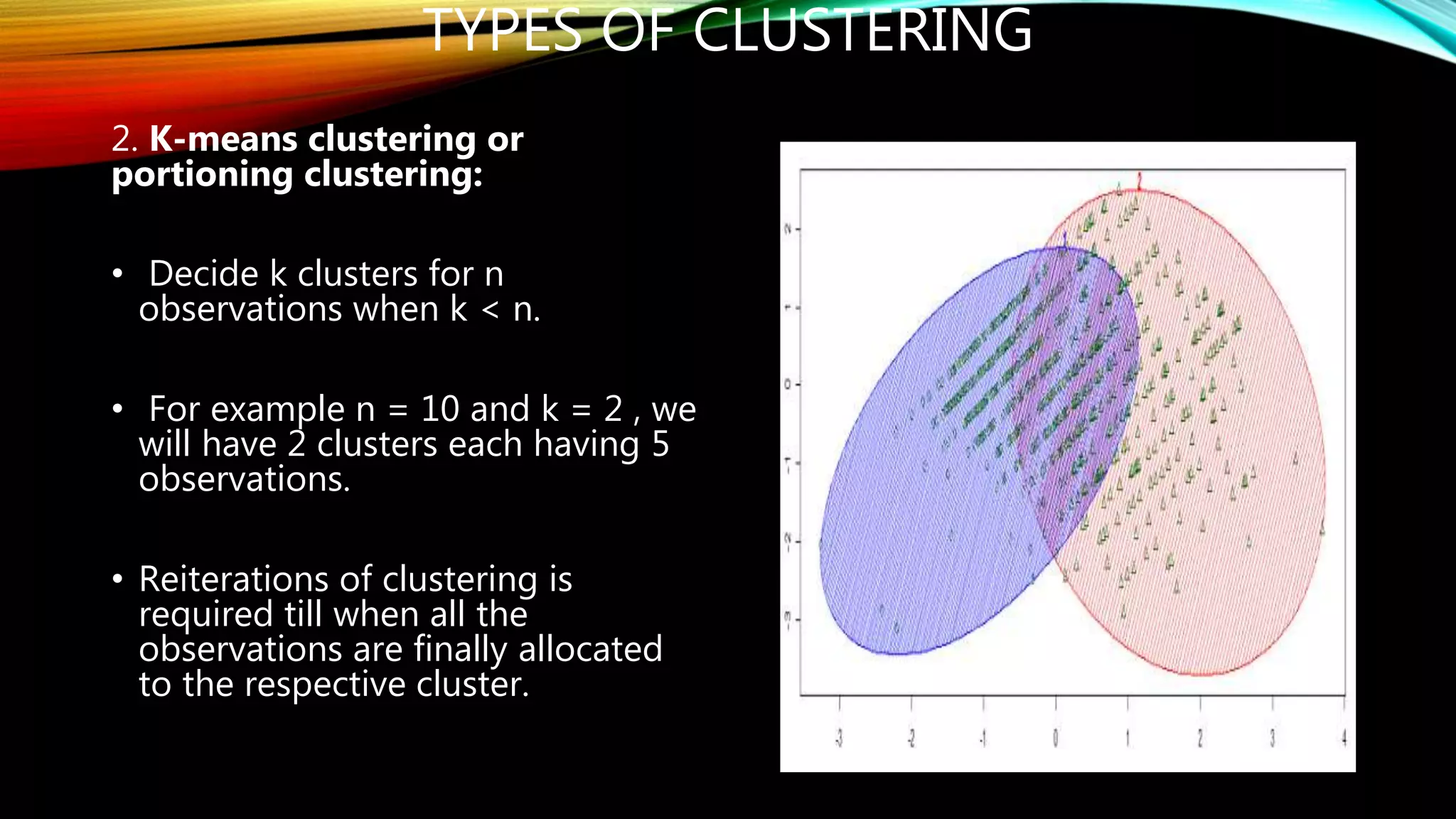
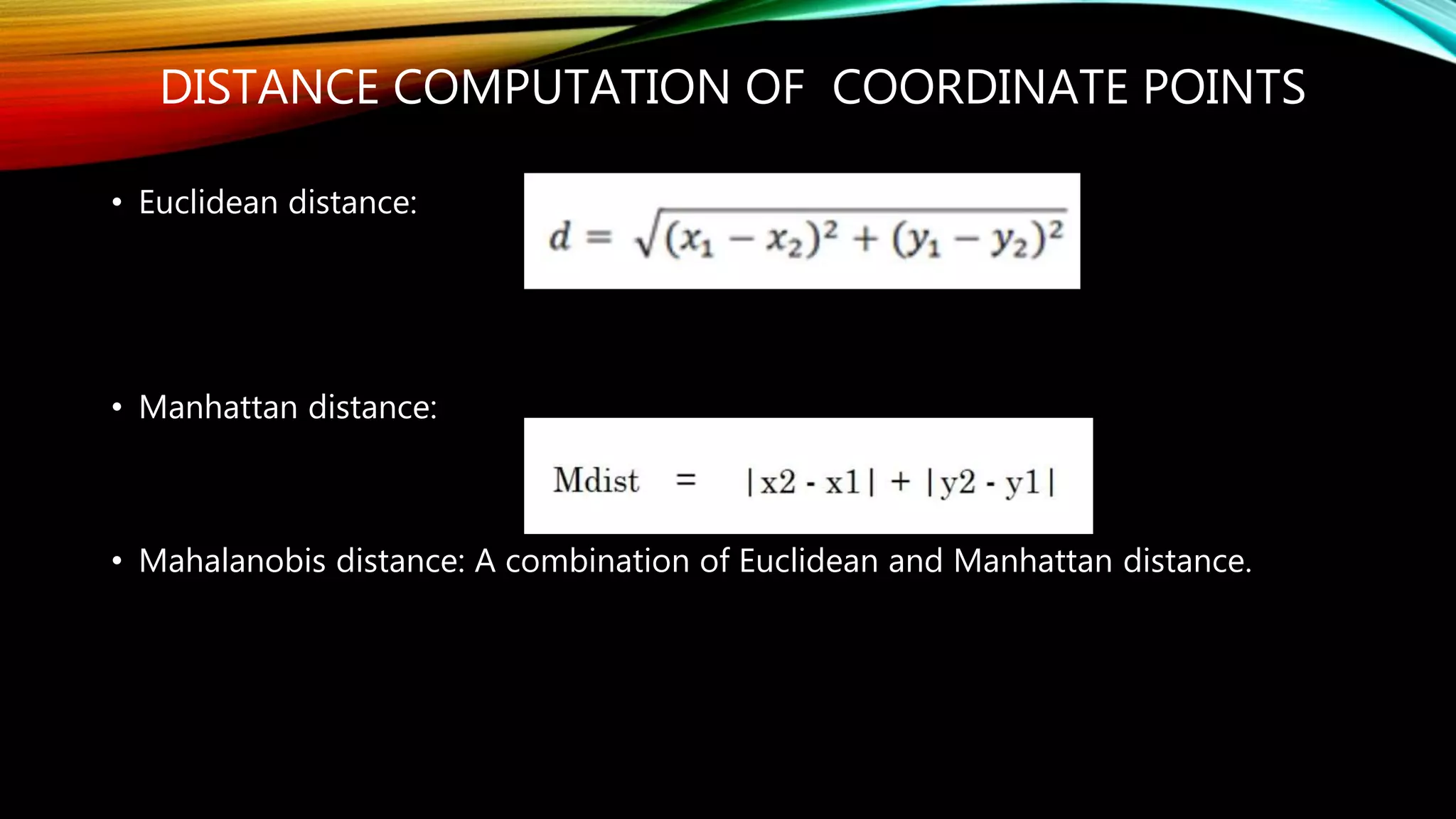
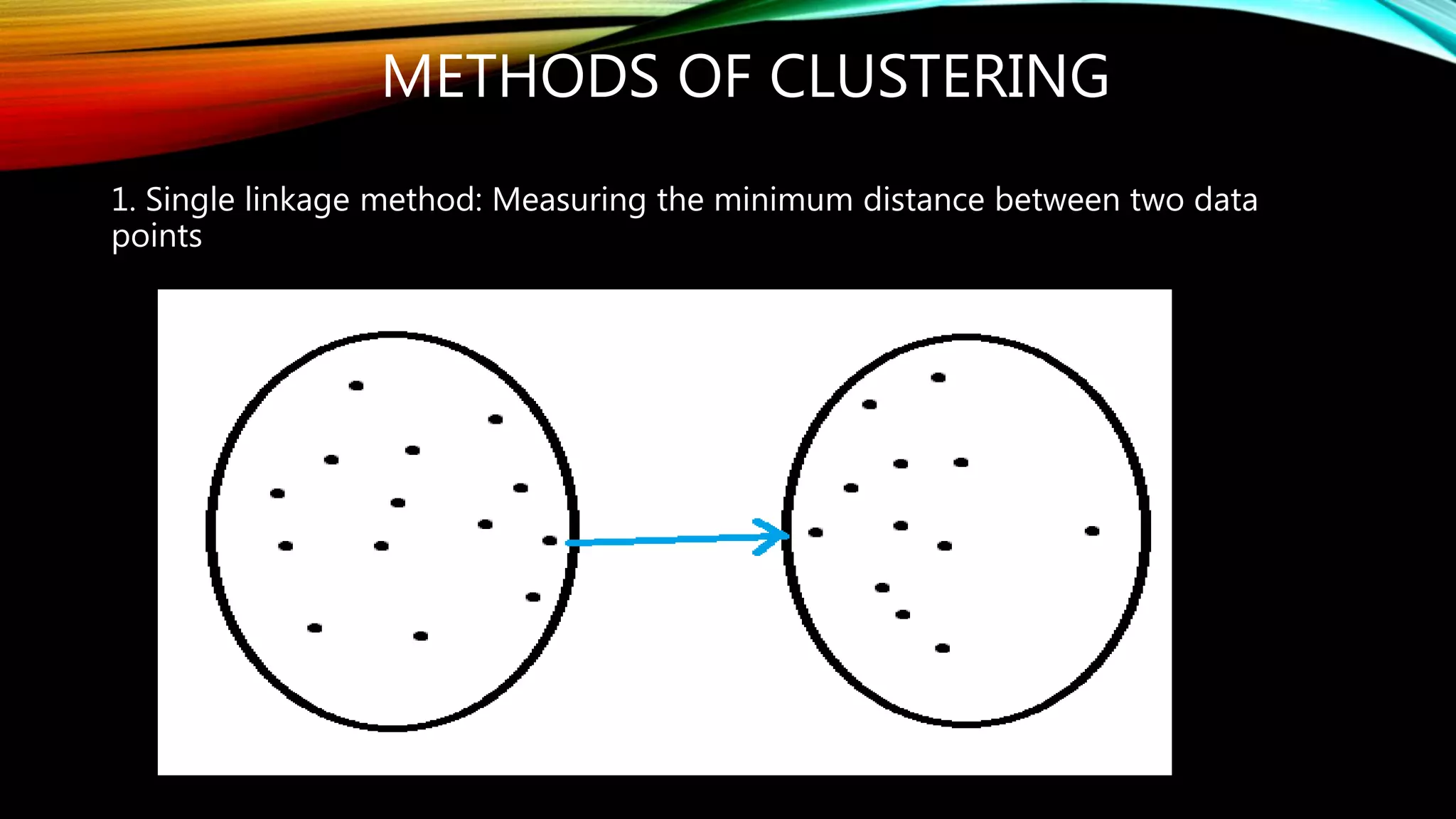
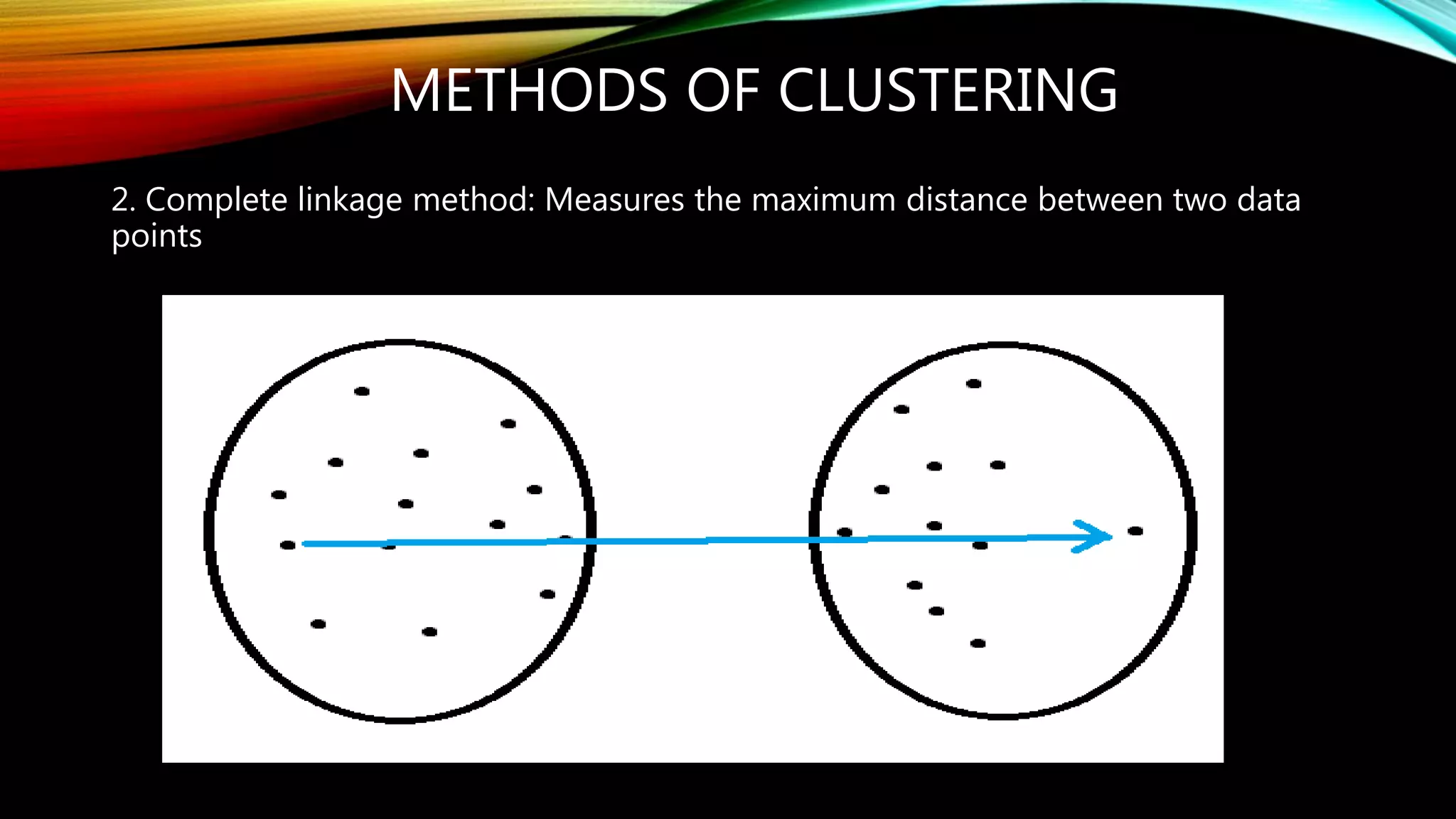
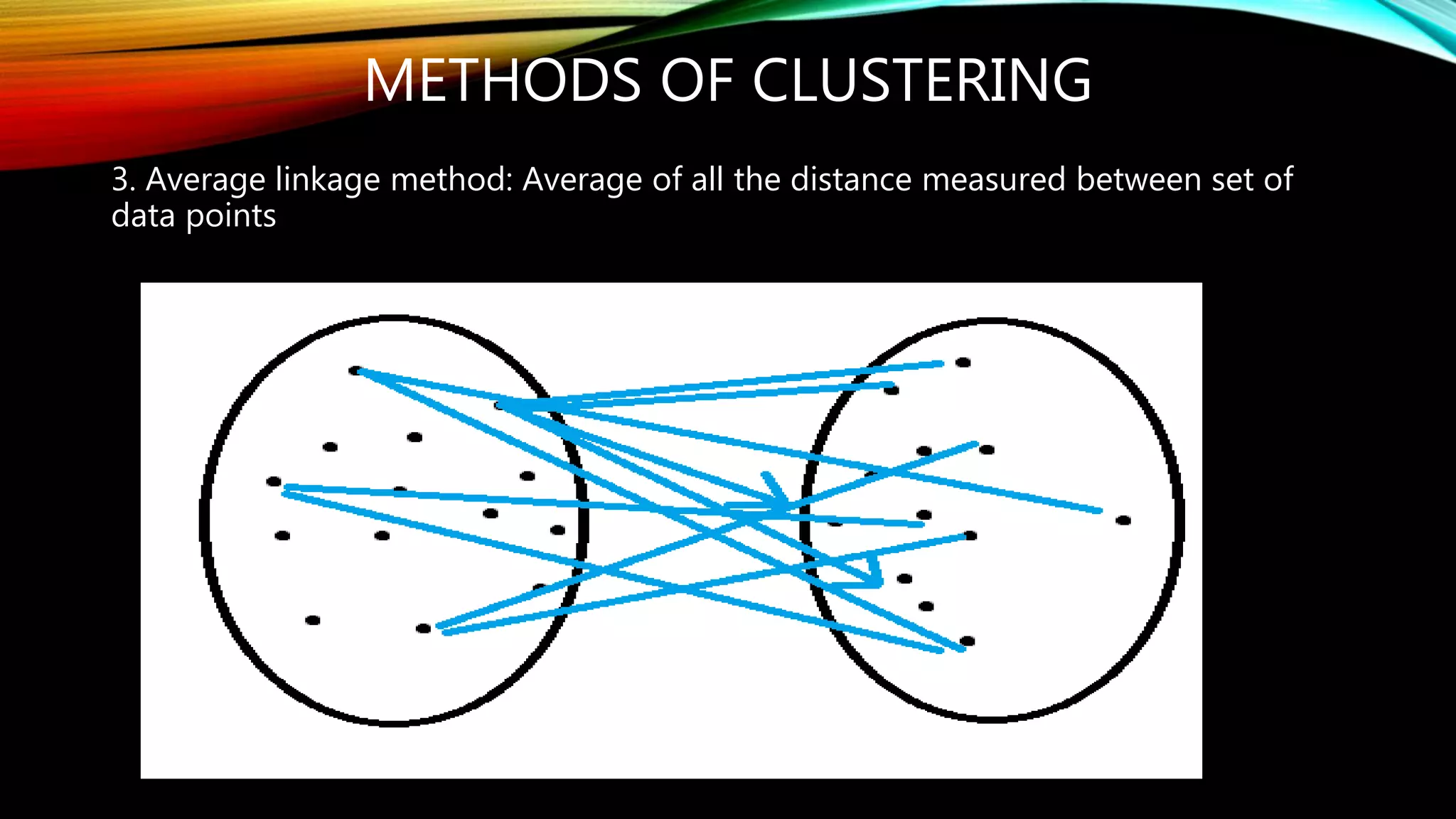
Clustering is the grouping of objects based on their similarities. It can involve initially separating objects into groups and then further dividing those groups based on additional homogeneous features. The goal of cluster analysis is to maximize intra-cluster similarity (objects within the same cluster are very similar) while minimizing inter-cluster similarity (objects from different clusters are very dissimilar). There are two main types of clustering - hierarchical, which creates nested clusters without predefined numbers, and k-means, which partitions objects into k mutually exclusive clusters through iterative reassignment.