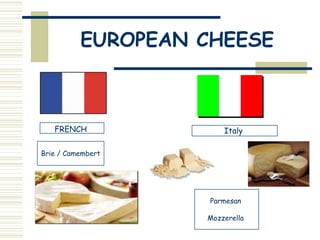
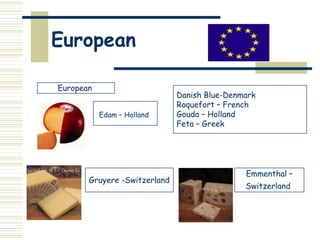
This document provides an overview of dairy products and milk. It discusses the main dairy foods such as milk, yogurt, cheese, cream, and ice cream. It describes different types of milk including pasteurized, UHT, flavored, dried, evaporated, and condensed. Specialist dairy products from sheep and goats are also outlined. The nutritional value of milk and why calcium is important is summarized. The document then discusses the production of cheese and lists common British and European cheeses. Other dairy foods like butter, yogurt, and ice cream are briefly described.