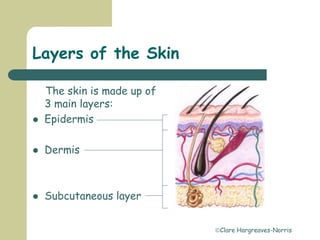
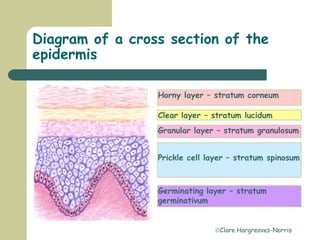
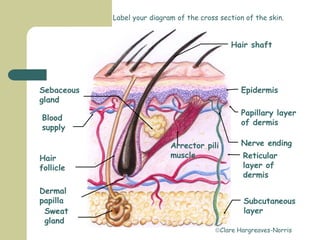
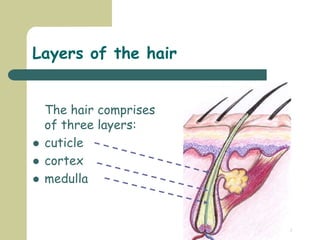
The skin has three main layers - the epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous layer. The epidermis has five layers and does not have its own blood supply. The dermis lies below and has two layers, the papillary and reticular layers. It contains collagen, elastin and fibroblasts. Below this is the subcutaneous layer made of fat. The skin has seven main functions - sensation, heat regulation, absorption, protection, excretion, secretion and vitamin D production.