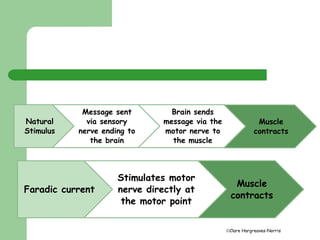
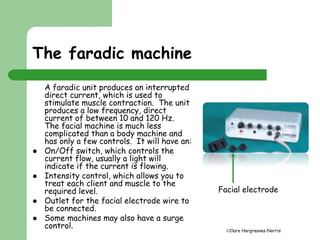
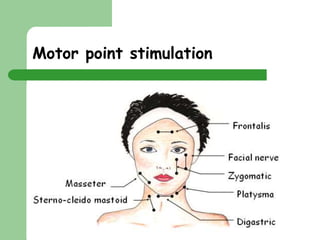
This document provides information about faradic facial treatments. It explains that faradic current uses electrical pulses to stimulate facial muscles and cause contraction, tightening and toning. Regular treatments over 4-6 weeks are needed, along with home care. The treatment works by directly stimulating motor nerves, bypassing the brain, to contract muscles. Sensations include tingling and muscle contractions. Precautions for the treatment are also outlined.