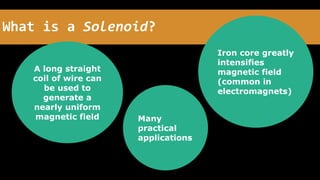
A solenoid is a coil of wire that generates a nearly uniform magnetic field when electric current passes through it. The magnetic field is greatly intensified when an iron core is placed inside the coil. When current flows through the coil, it produces a magnetic field that travels in a doughnut shape around the coil and through its center, and this magnetic field can be used to move or attract the iron core or other ferromagnetic materials.