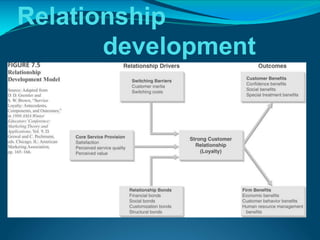
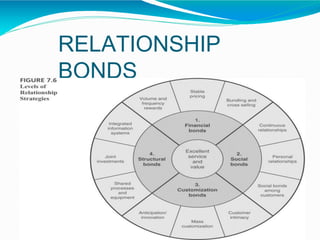
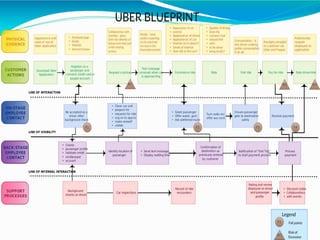
The document discusses customer relationship management and strategy, focusing on the shift from acquisition to retention in marketing, emphasizing that maintaining relationships with current customers is more cost-effective than acquiring new ones. It compares the marketing and service design strategies of Ola and Uber, highlighting their differing brand positioning, promotional tactics, and customer engagement efforts, with Ola aiming for broader accessibility and Uber branding itself as a premium service. Additionally, it touches on relationship stages, switching barriers, and the importance of establishing strong service quality for long-term customer loyalty.