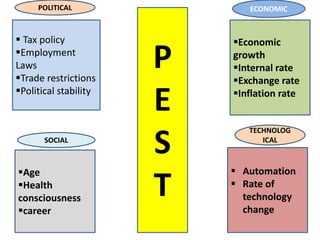
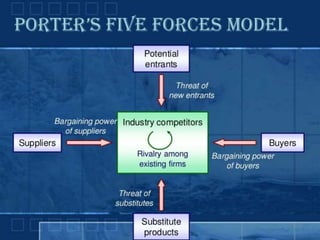
Environmental scanning is a critical process of gathering and analyzing information to identify internal strengths and weaknesses, and external opportunities and threats impacting an organization. Techniques such as SWOT analysis, PEST analysis, ETOP, QUEST, and Porter's Five Forces are employed to ensure optimal resource utilization and long-term strategic planning. This systematic analysis aids in effective decision-making, ensuring the survival and growth of businesses in a competitive landscape.