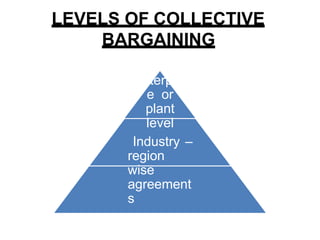
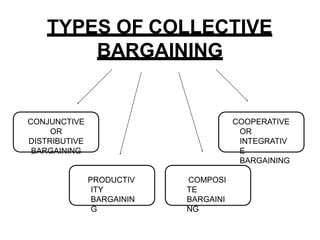
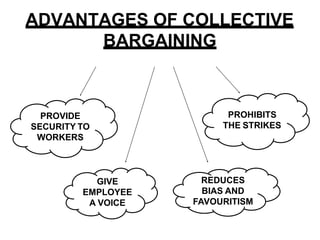
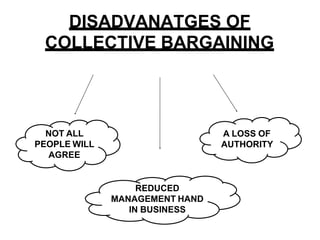
Collective bargaining is a process where labor union representatives and business management negotiate to create an agreement specifying the nature of the employee-employer relationship. It aims to settle disputes over wages and conditions, protect worker interests through collective action, and resolve differences through voluntary negotiations. Bargaining can occur at the enterprise, industry, or national level. The objectives, features, types (such as conjunctive, integrative, and productivity), issues discussed (like wages, benefits, grievances), and a 5-step process of collective bargaining are outlined in the document. Advantages include providing job security and giving employees a voice, while disadvantages include not all parties agreeing and reduced management authority. Careful preparation and understanding different viewpoints are