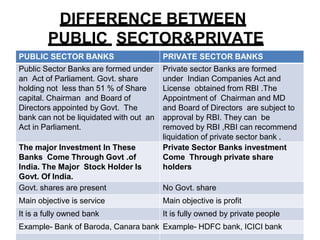
The document compares the service quality between public and private sector banks in India. It finds that the service quality gap, being the difference between customer expectations and satisfaction, is lower for private sector banks. Specifically, private bank customers are more satisfied with physical facilities, product offerings, promptness, and employee courtesy. However, public sector banks perform equally well in terms of transaction security and staff knowledge. Overall, private banks provide better quality services across most dimensions and have successfully retained more customers as a result. Both types of banks can improve by addressing their respective weaknesses.