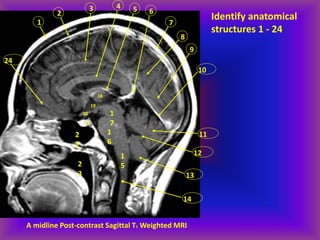
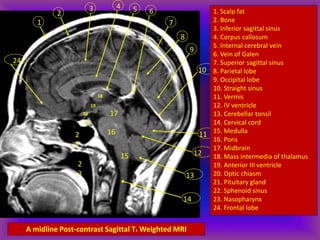
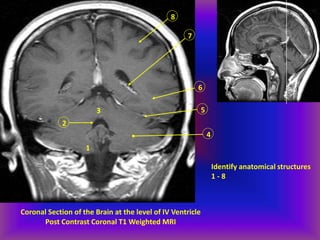
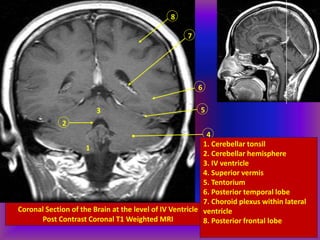
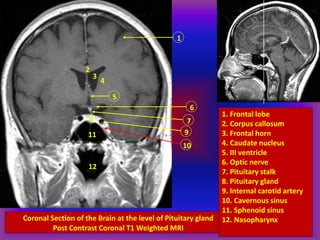
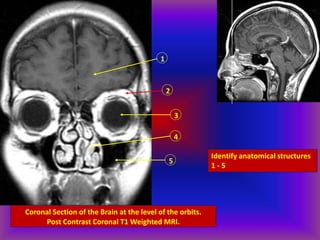
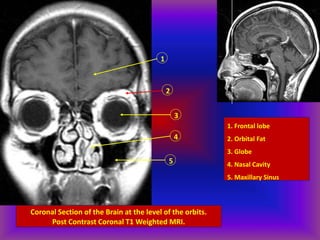
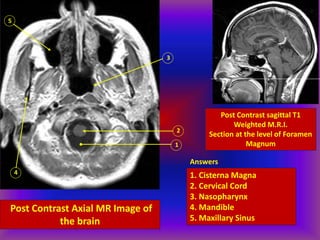
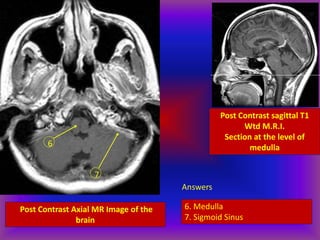
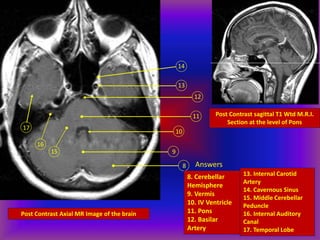
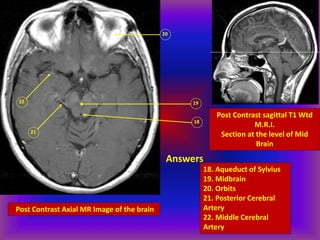
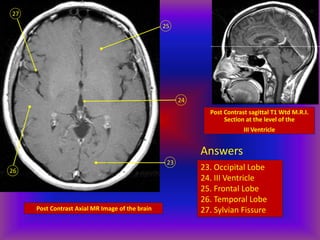
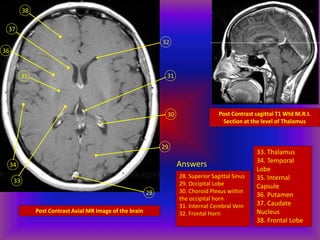
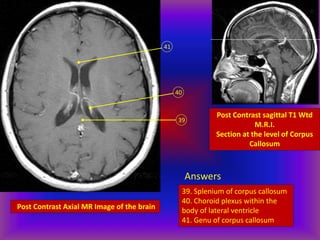
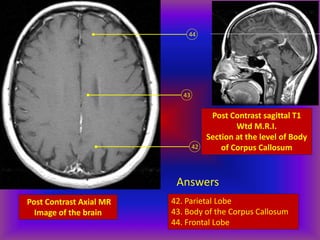
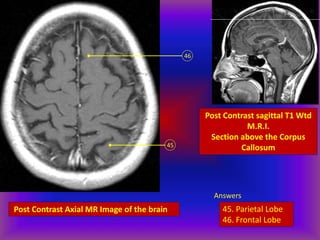
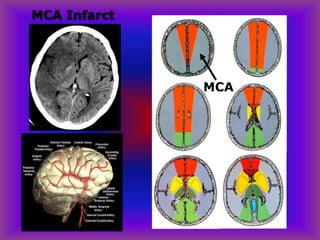
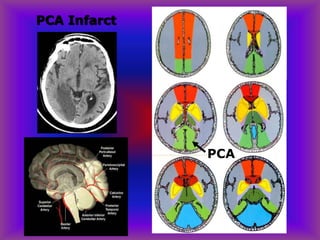
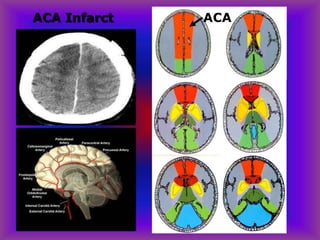
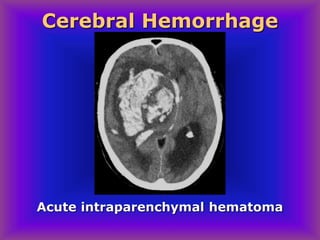
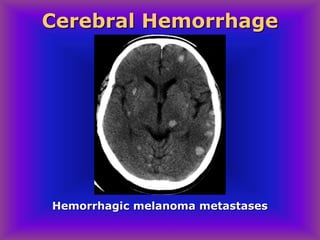
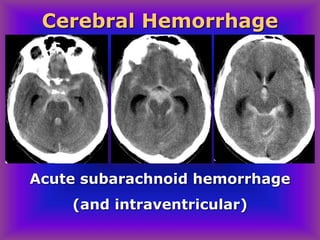
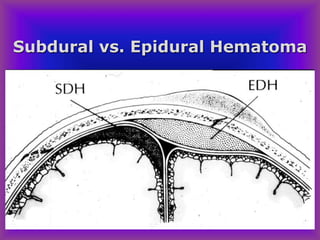
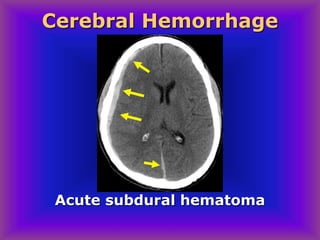
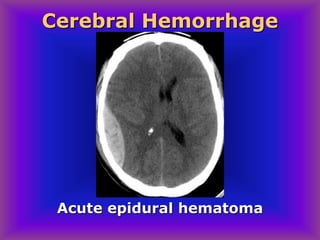
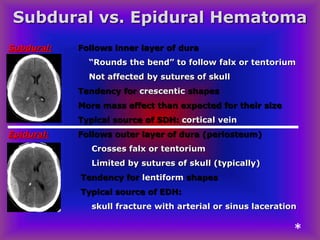
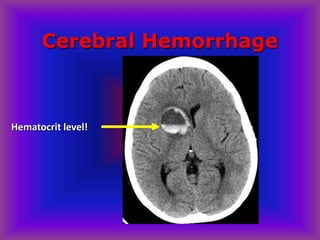
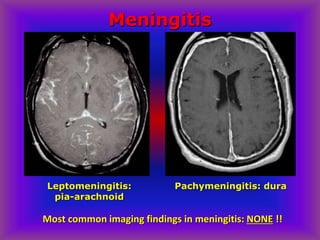
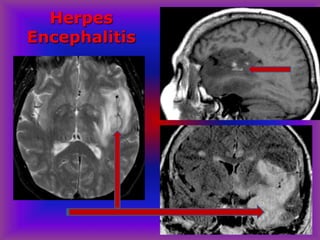
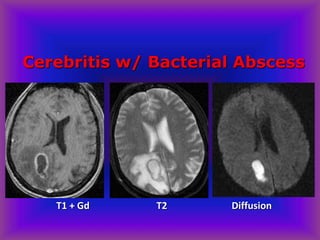
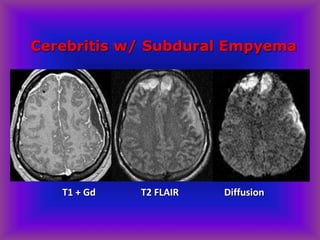
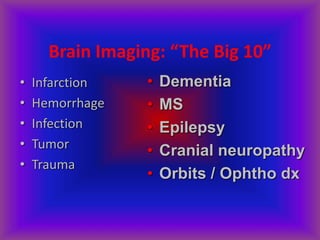
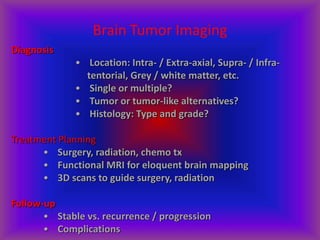
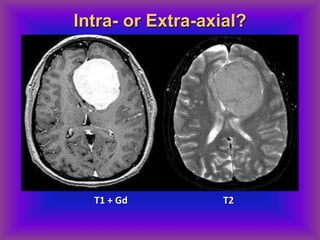
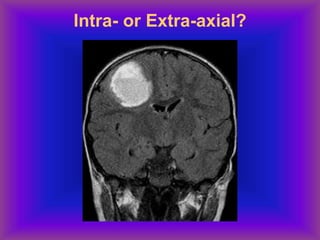
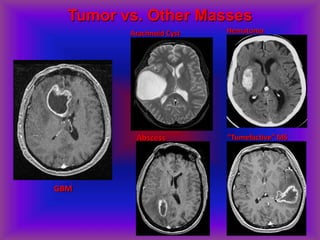
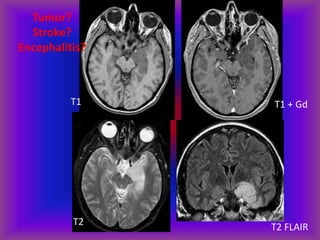
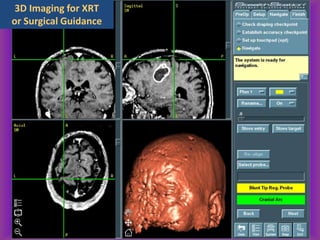
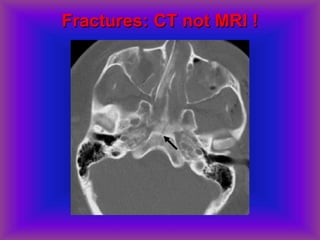
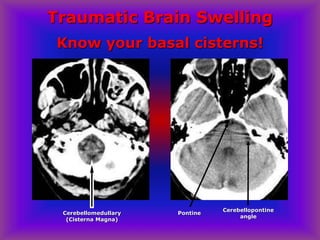
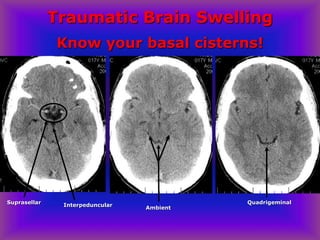
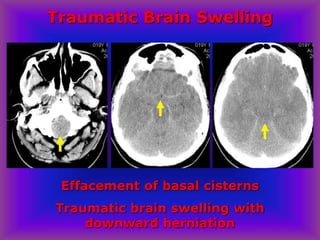
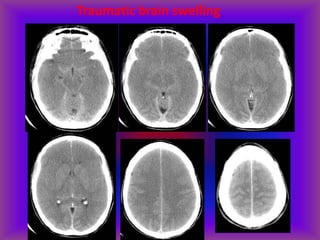
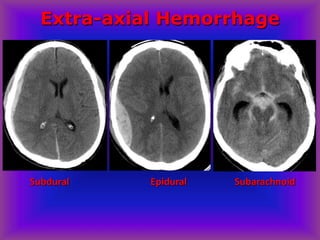
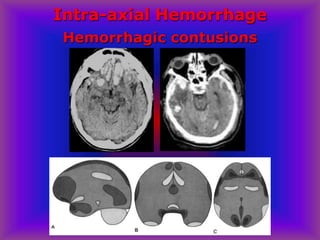
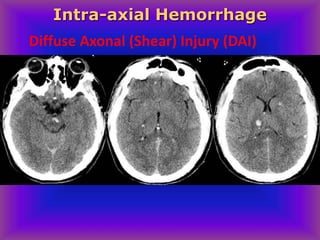
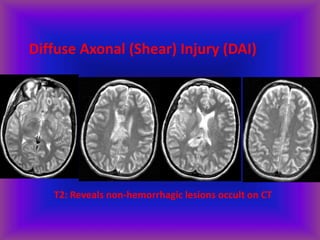
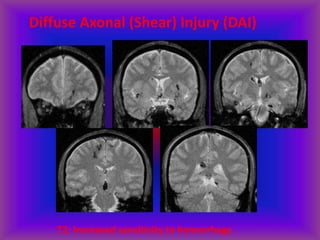
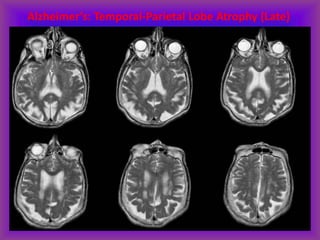
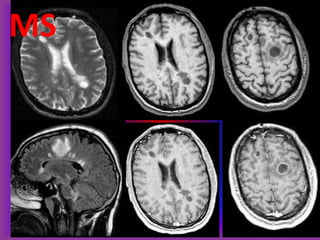
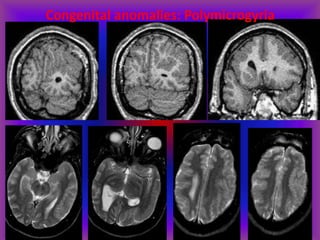
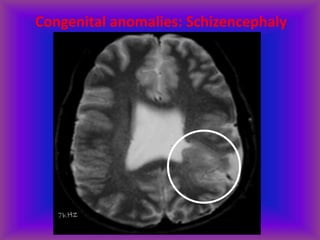
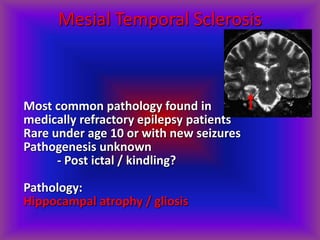
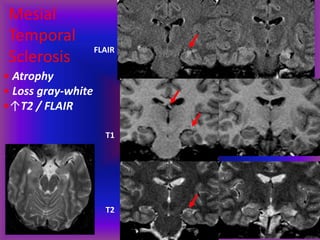
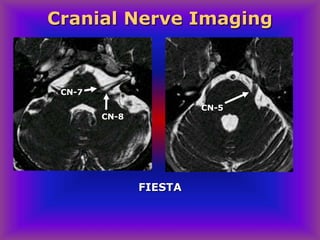
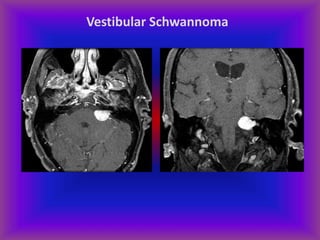
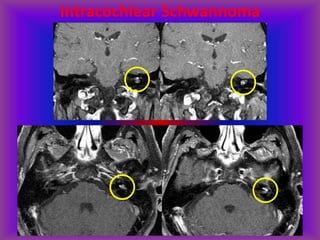
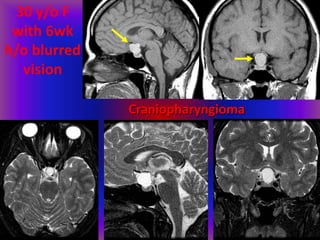
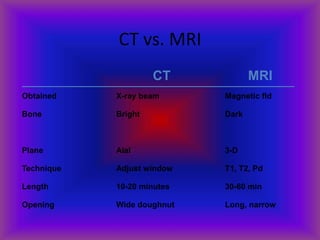
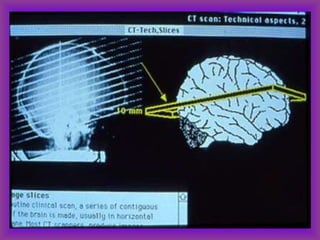
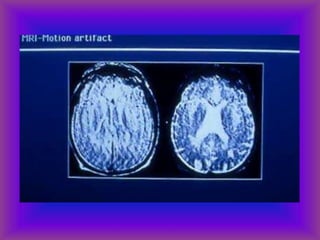
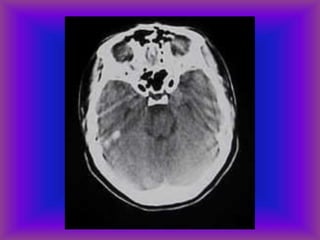
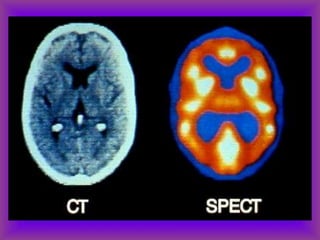
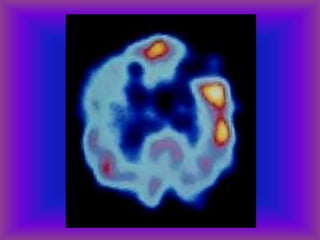
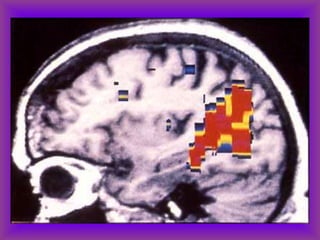
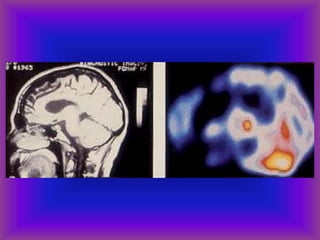
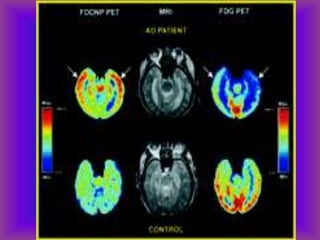
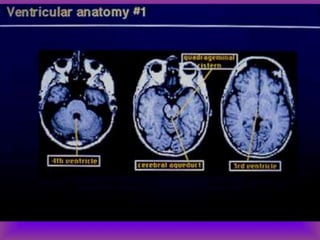
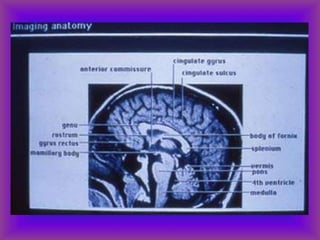
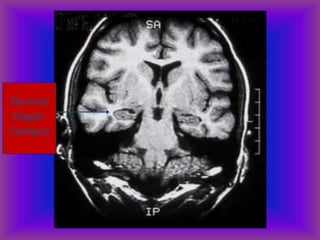
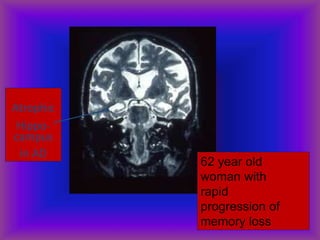
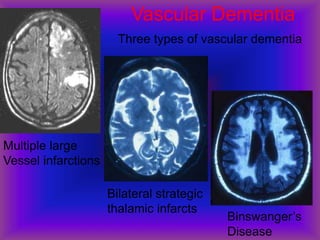
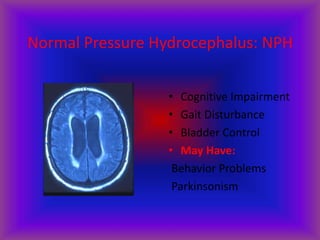
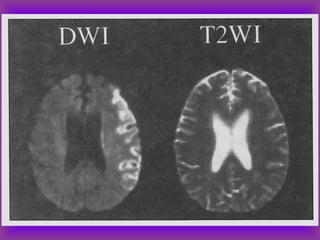
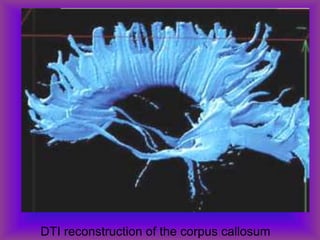
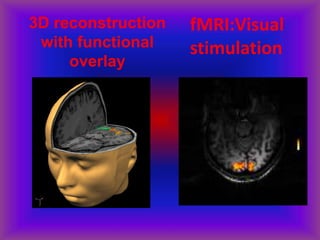
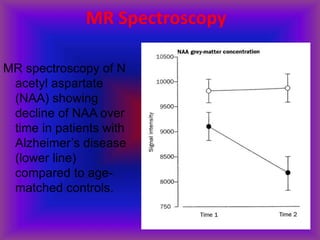
This document provides an overview of CT and MRI interpretation for various neurological conditions. It includes labeled images showing normal anatomical structures and examples of: stroke demonstrated on perfusion and diffusion MRI; hemorrhage on CT and MRI; brain infection; tumors; traumatic brain injuries; dementia; multiple sclerosis lesions; and epileptic foci. The document serves as an educational guide for medical students and residents to learn cross-sectional brain anatomy and recognize key imaging findings for common neurological disorders.