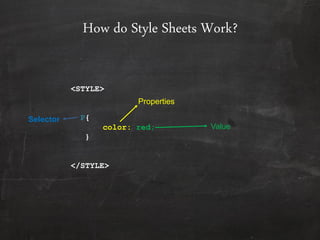
This document provides an overview of Cascading Style Sheets (CSS), including what they are, their features and advantages, how they work, different types of selectors, and common style properties. CSS allows separation of document content from presentation through stylesheets, providing control over fonts, colors, spacing and more. Styles can be applied inline, internally via <style> tags, or externally via linked CSS files for consistency across pages. Selectors target specific elements to which declarations applying various properties and values are made. This allows presentation to be customized while keeping markup semantic.