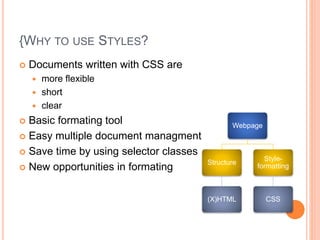
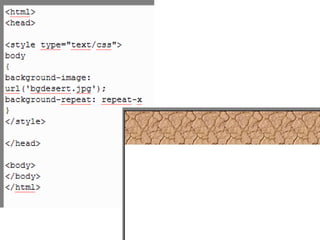
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) allows styling and formatting of HTML documents. CSS syntax uses selectors to target HTML elements and applies properties that define visual styles like color, font, size and layout. Styles can be defined internally, in an external stylesheet, or inline. When multiple conflicting styles apply, there is a cascading order that determines which styles take precedence. CSS properties control various aspects of text formatting, backgrounds, lists and dimensions. While CSS provides flexibility, there are some limitations in browser support and functionality.