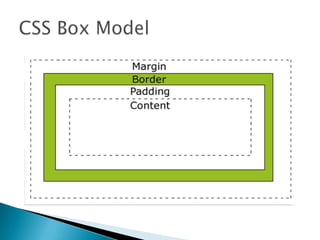
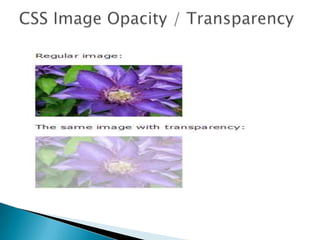
The document provides information on various CSS properties and selectors used to style HTML elements. It defines properties for styling text, links, lists, tables, boxes, borders, positioning and various other aspects of HTML elements. It also describes CSS pseudo-classes that can be used to select elements in certain states, like links that have been visited or the first child element.