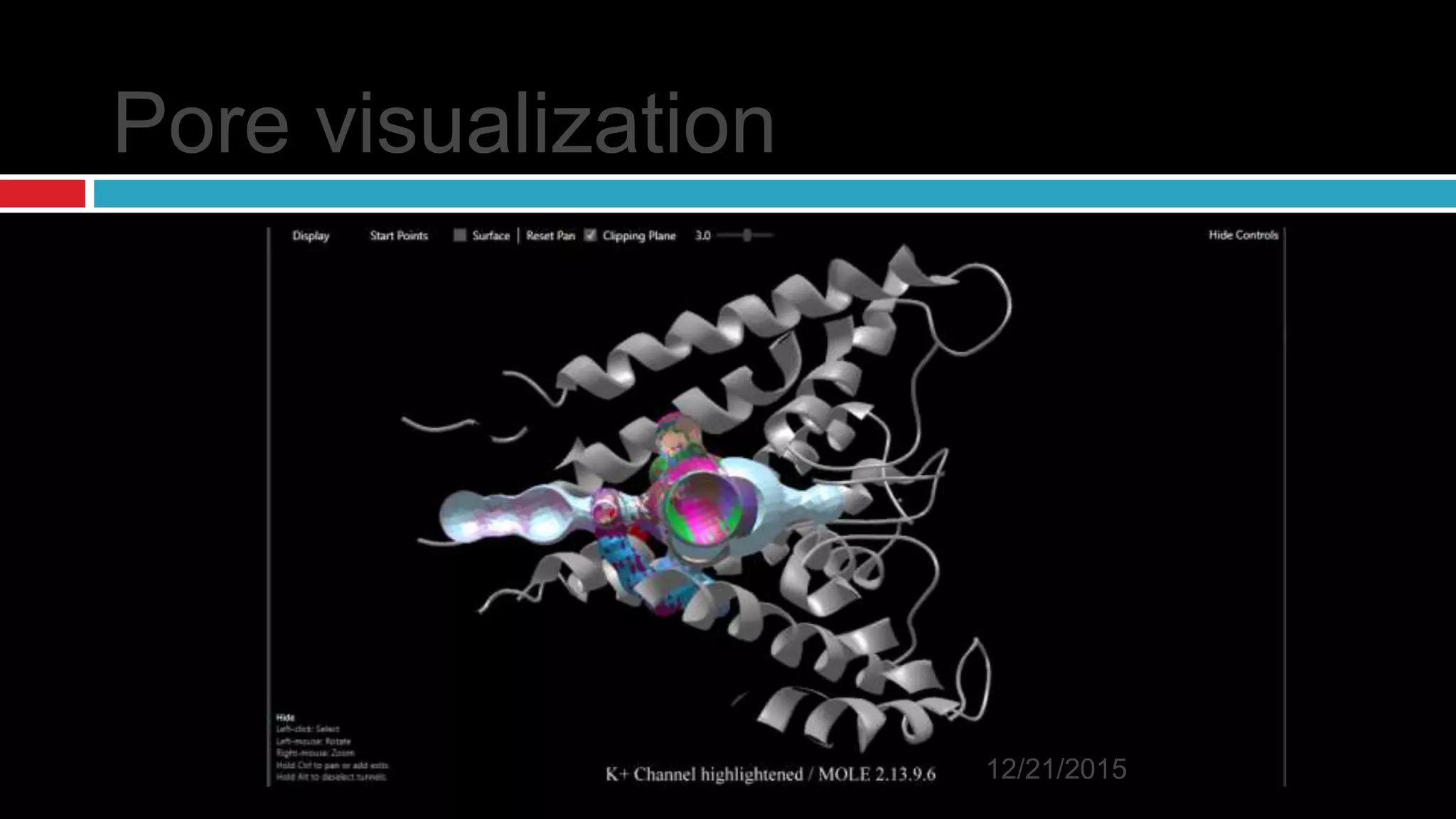
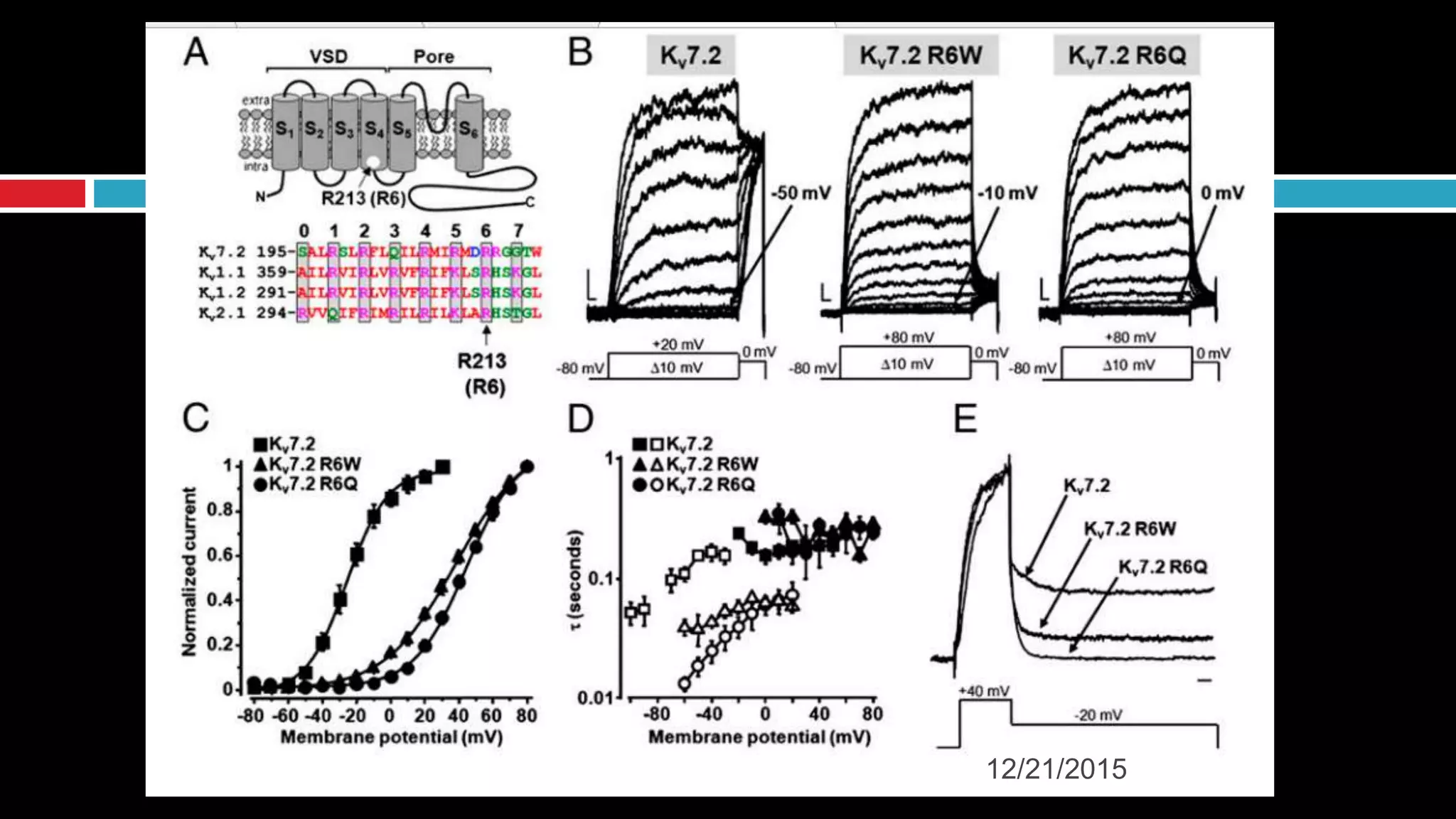
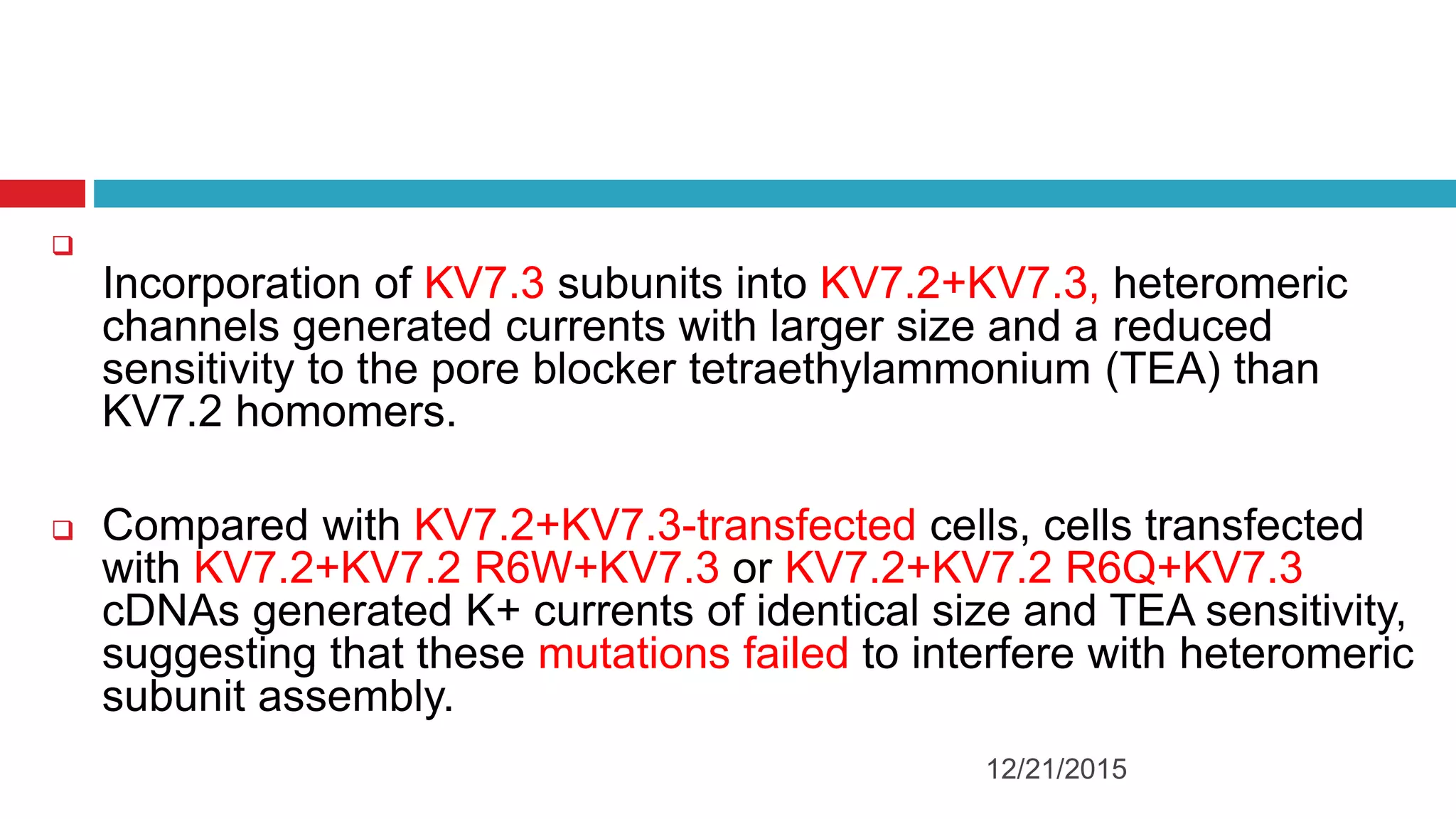
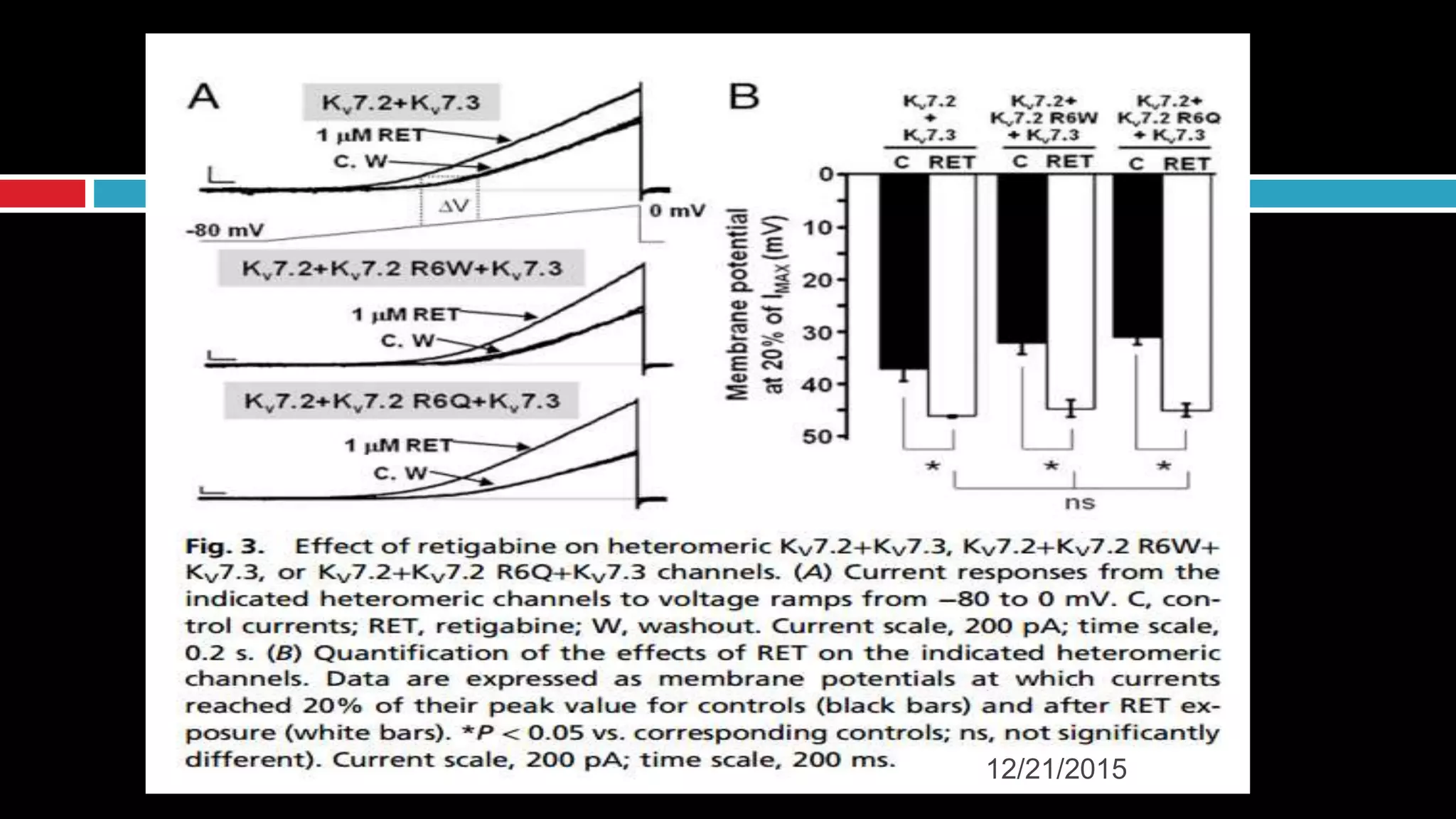
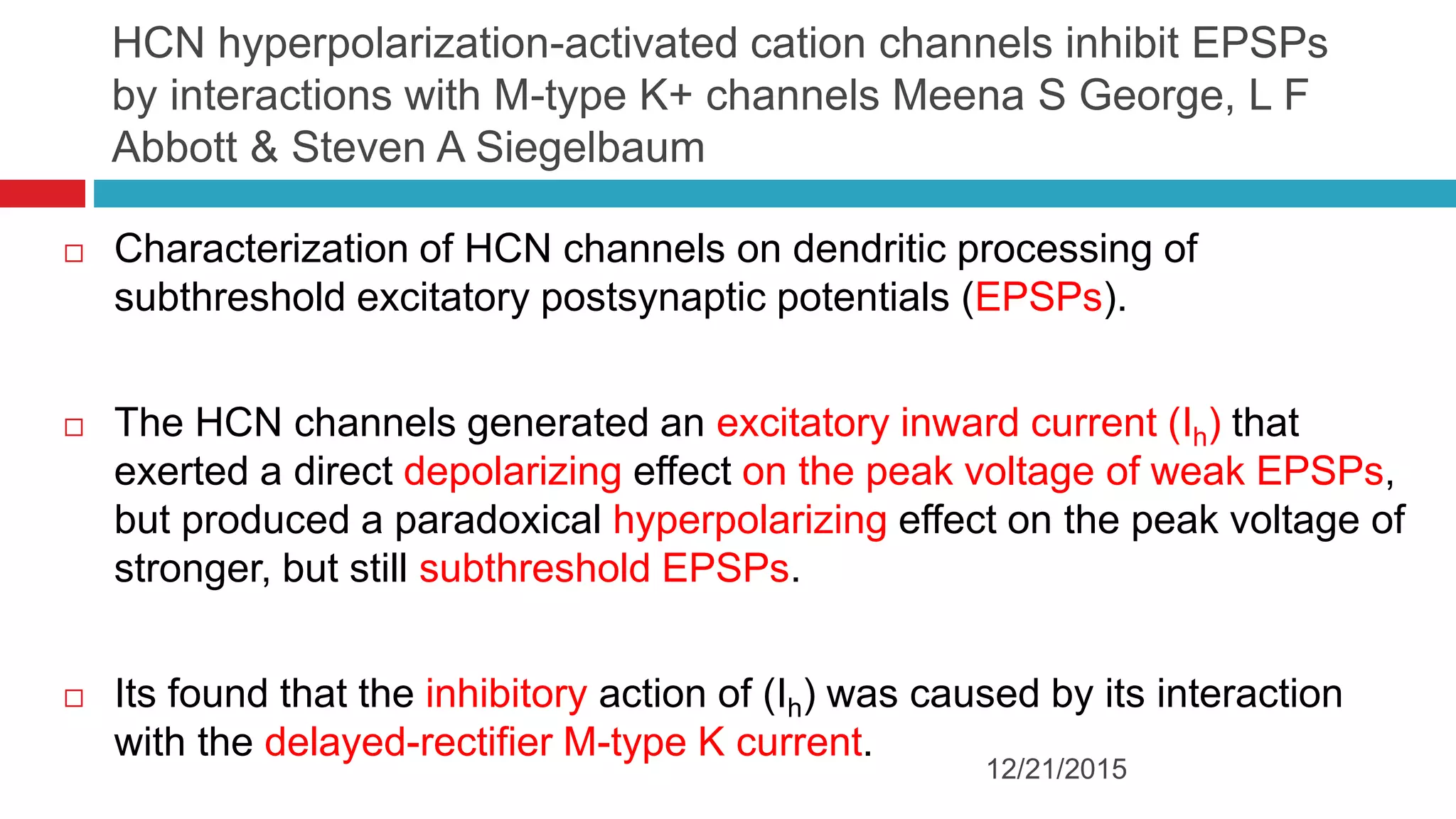
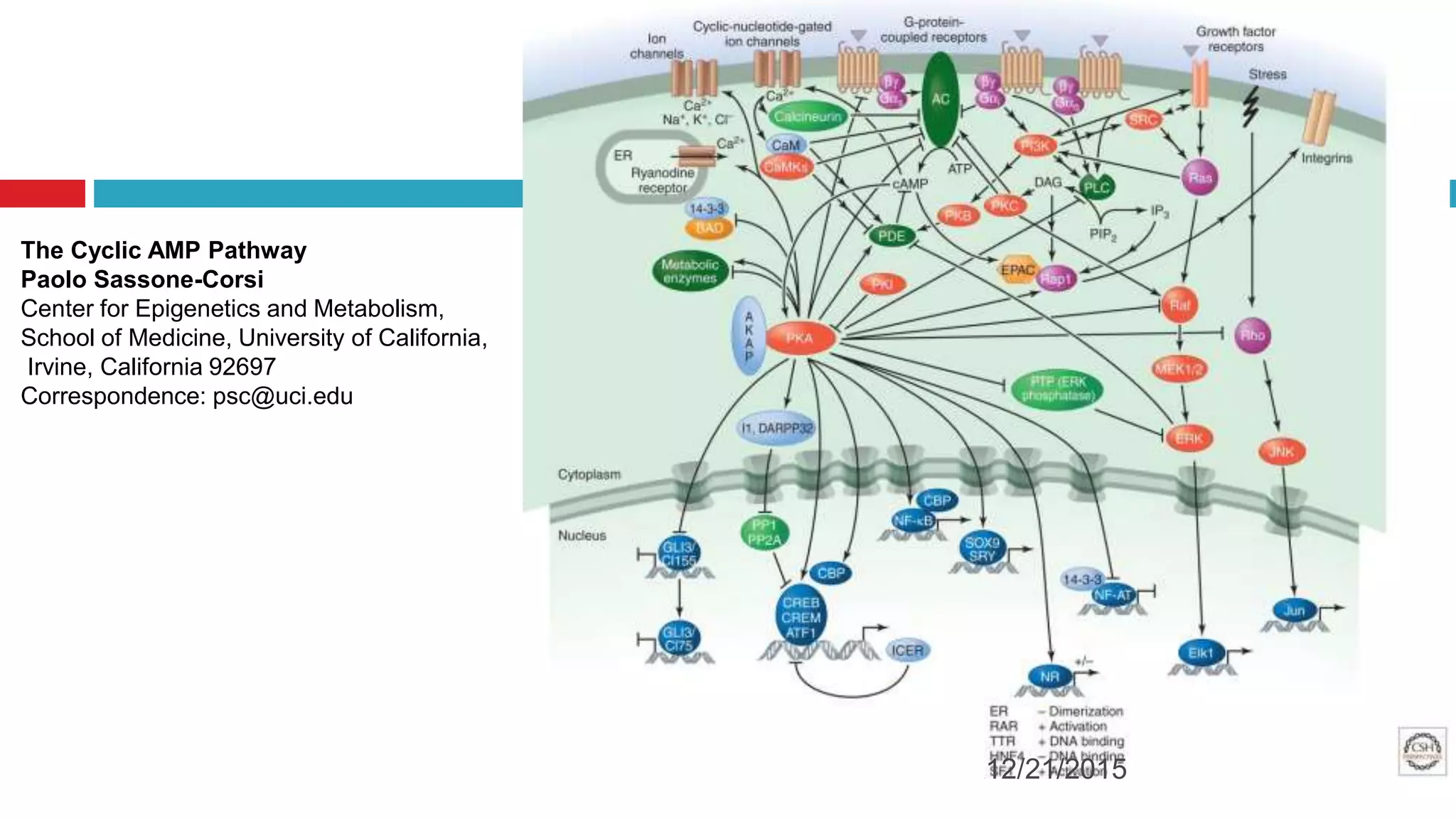
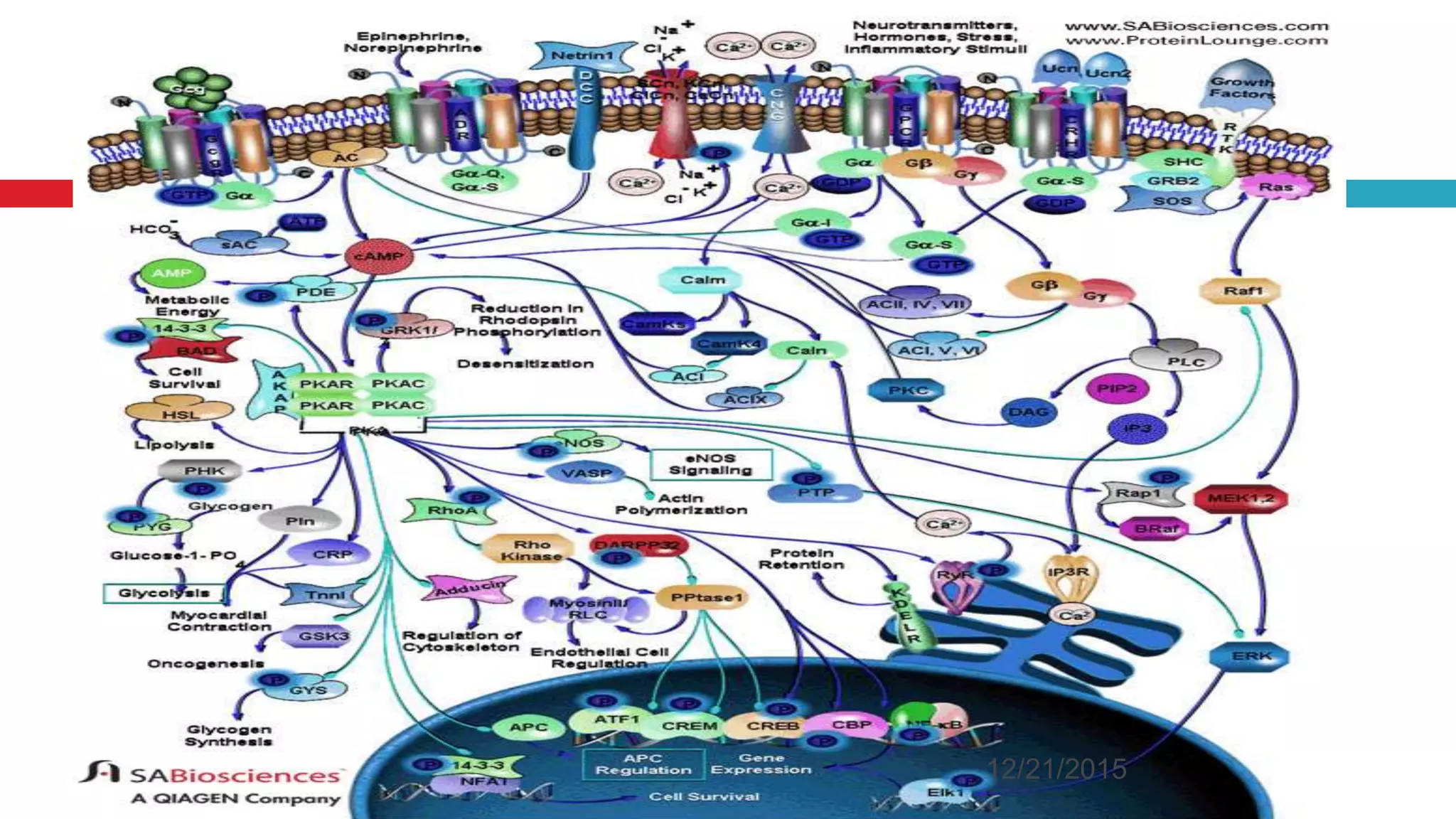
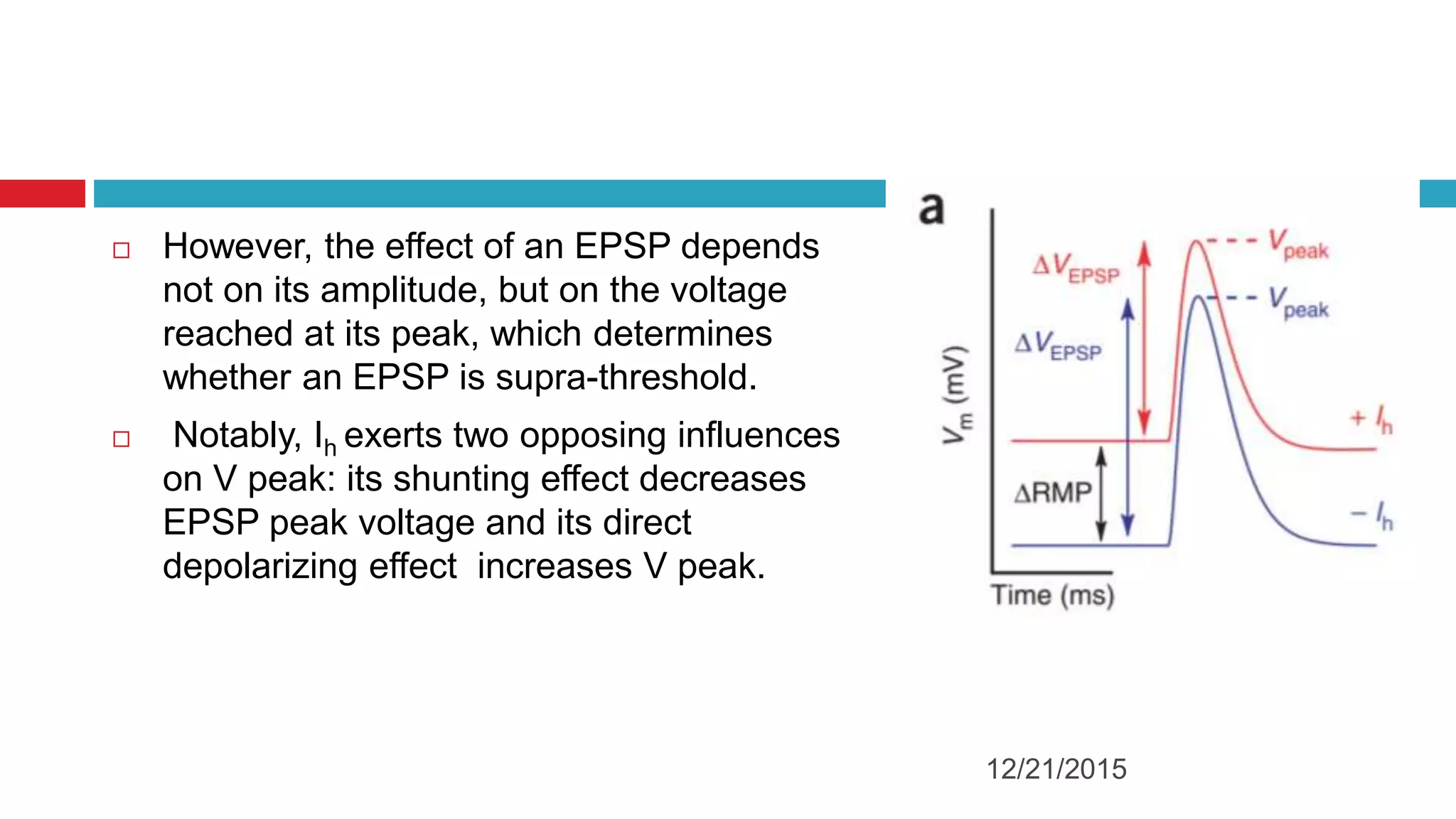
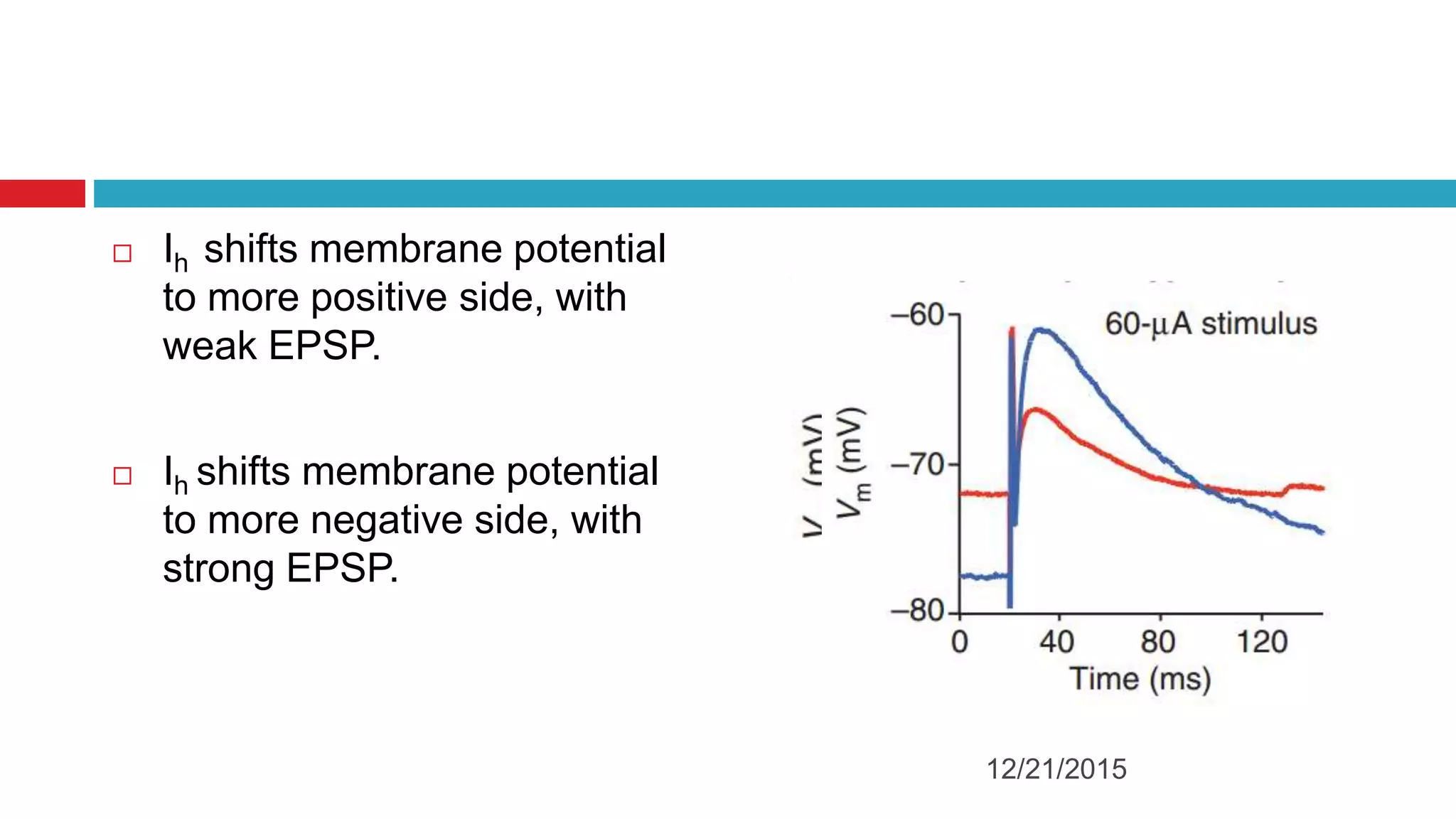
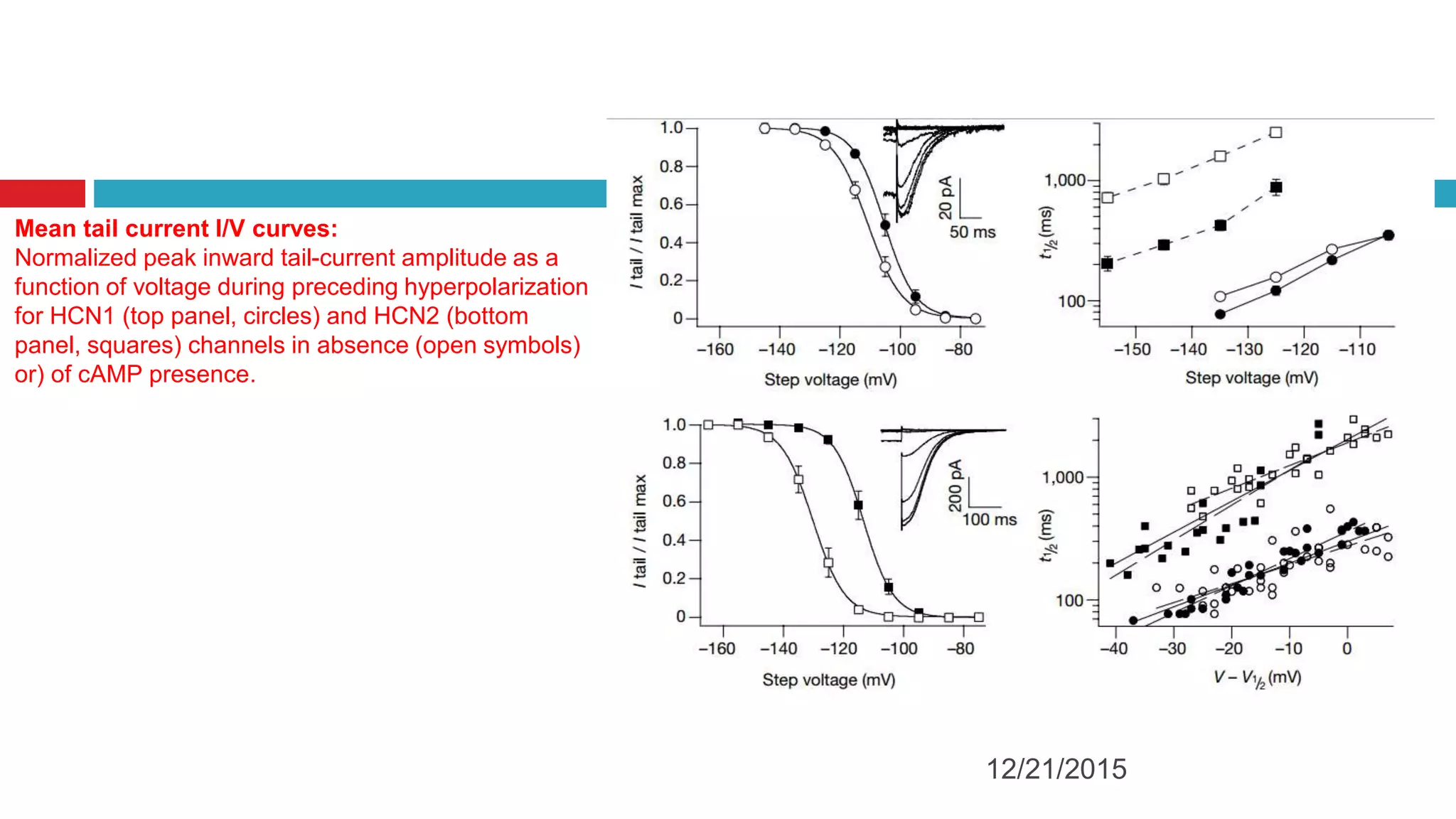
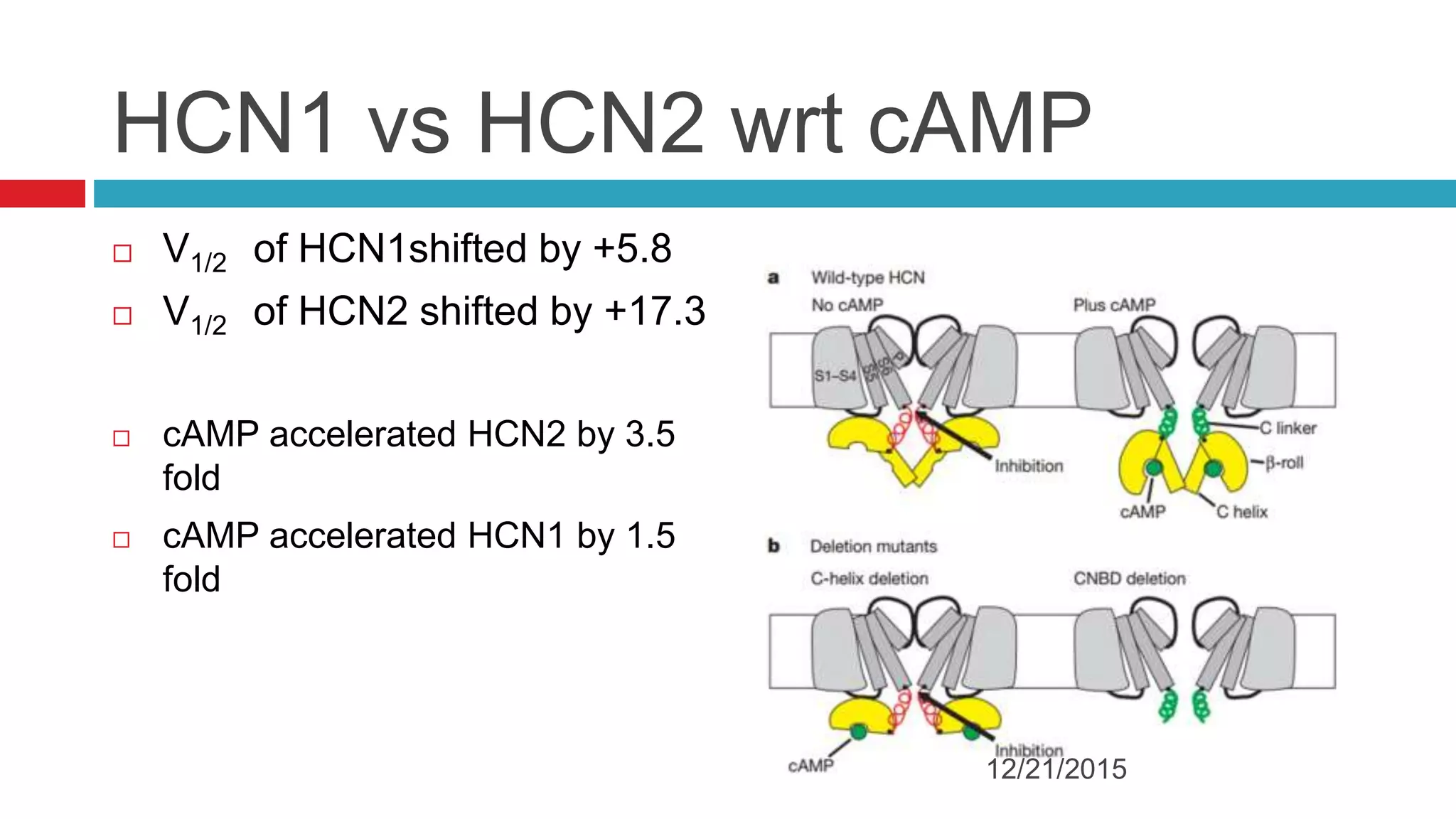
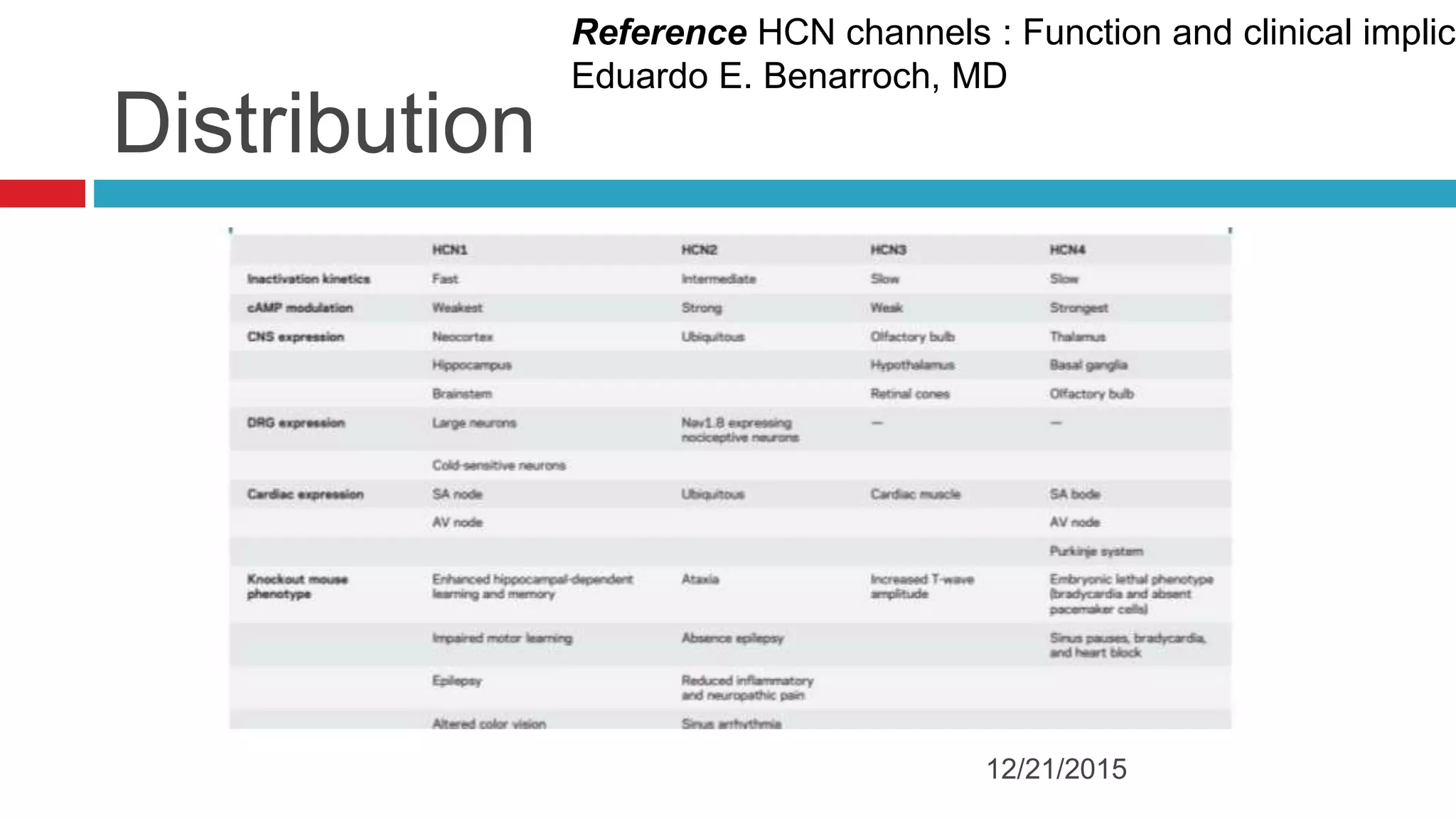
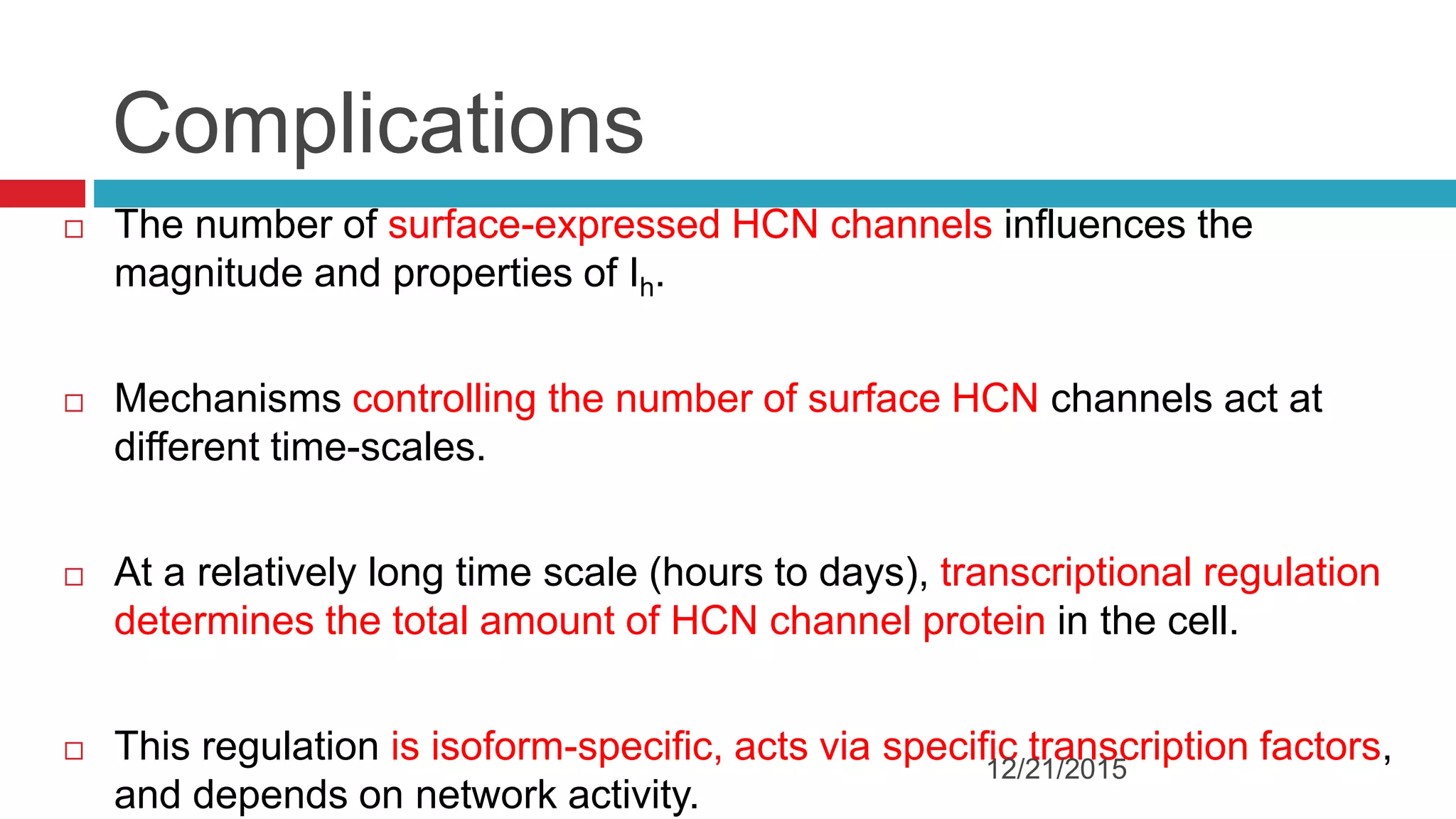
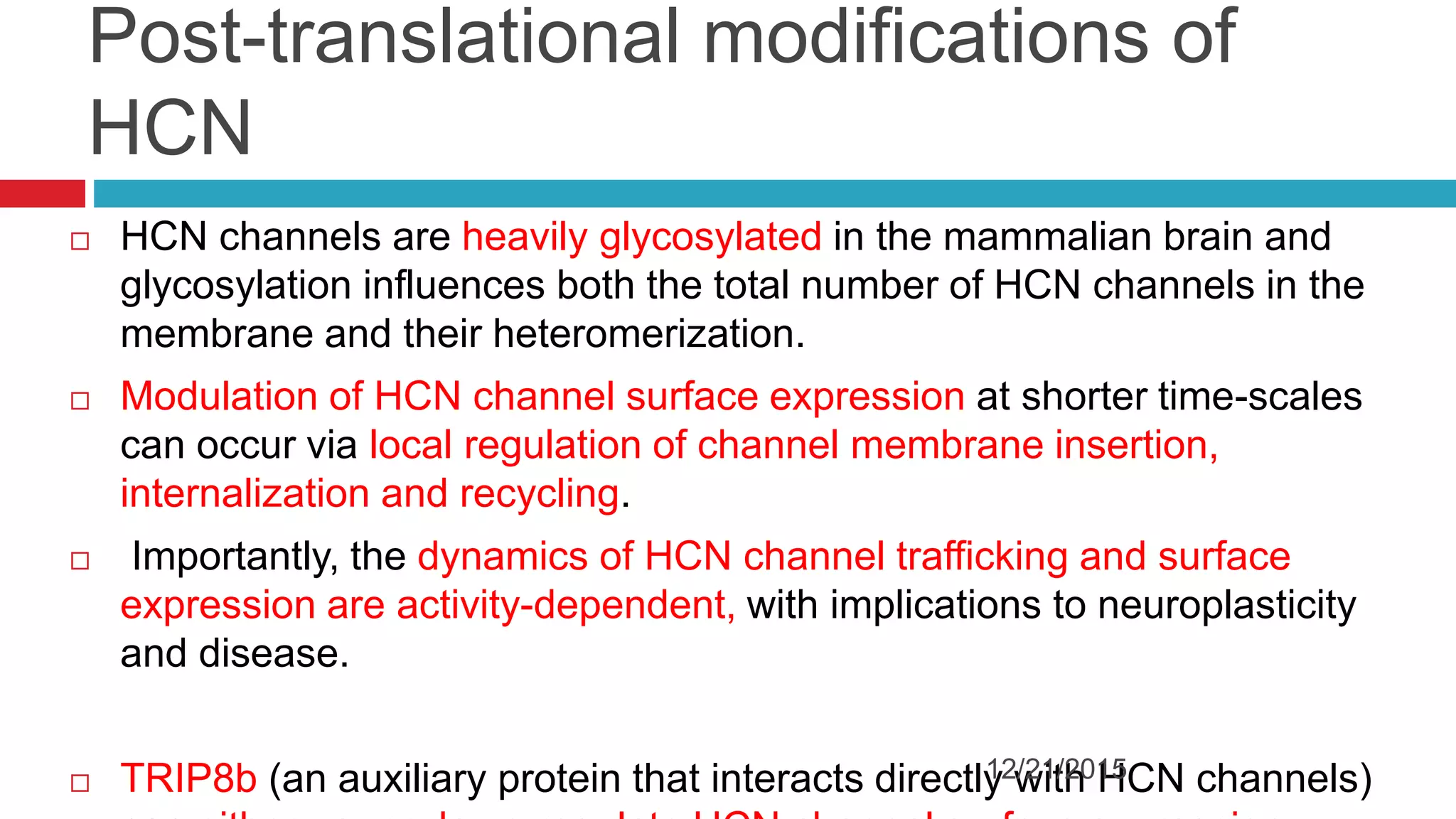
The document discusses the complex role of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide (HCN) channels in epilepsy, noting that abnormal regulation can contribute to seizure activity through both upregulation and downregulation mechanisms. It highlights specific mutations in HCN channels that influence neuronal excitability and synaptic transmission, as well as the paradoxical effects of HCN currents on excitatory postsynaptic potentials in various contexts. Additionally, the document explores the interplay between HCN channels and other ion channels, with implications for understanding seizure dynamics and potential therapeutic strategies.











![REFERENCE: Jasper's Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies [Internet]. 4th
edition, Noebels JL, Avoli M, Rogawski MA, et al., editors. Bethesda (MD):
National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2012.
12/21/2015](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/epilepsy-151221062603/75/Epilepsy-15-2048.jpg)