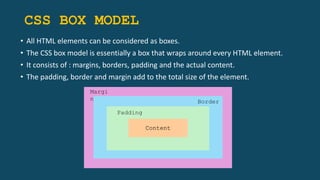
The document provides an extensive overview of CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), which is used to style HTML documents by controlling layout, colors, fonts, and more. It covers various selectors, types of CSS (inline, internal, and external), CSS properties for backgrounds, borders, and fonts, as well as advanced concepts like the box model, flexbox, and combinators. Additionally, it discusses the functionality of properties such as overflow, z-index, and float, along with practical examples.