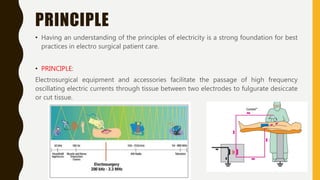
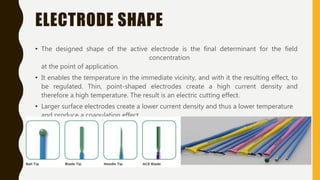
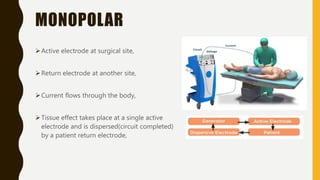
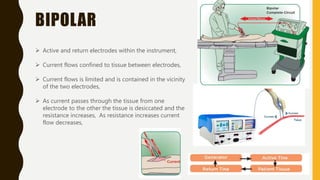
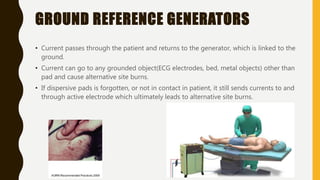
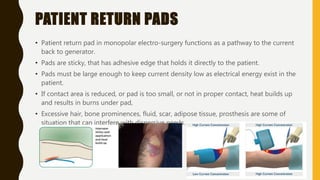
Electro-surgery uses high frequency electric current to cut, coagulate, desiccate, or fulgurate tissue. The generator converts electricity to high frequency waveforms over 30,000 cycles per second. Tissue effects are regulated by current, power, modulation level, electrode shape and condition, cutting speed, and tissue properties. Monopolar electro-surgery uses an active electrode at the surgical site and a return electrode elsewhere to complete the circuit. Bipolar electro-surgery contains active and return electrodes within the instrument to limit current flow. Proper use and maintenance of equipment, along with correct patient positioning and electrode application, are necessary to avoid risks like unintended burns.