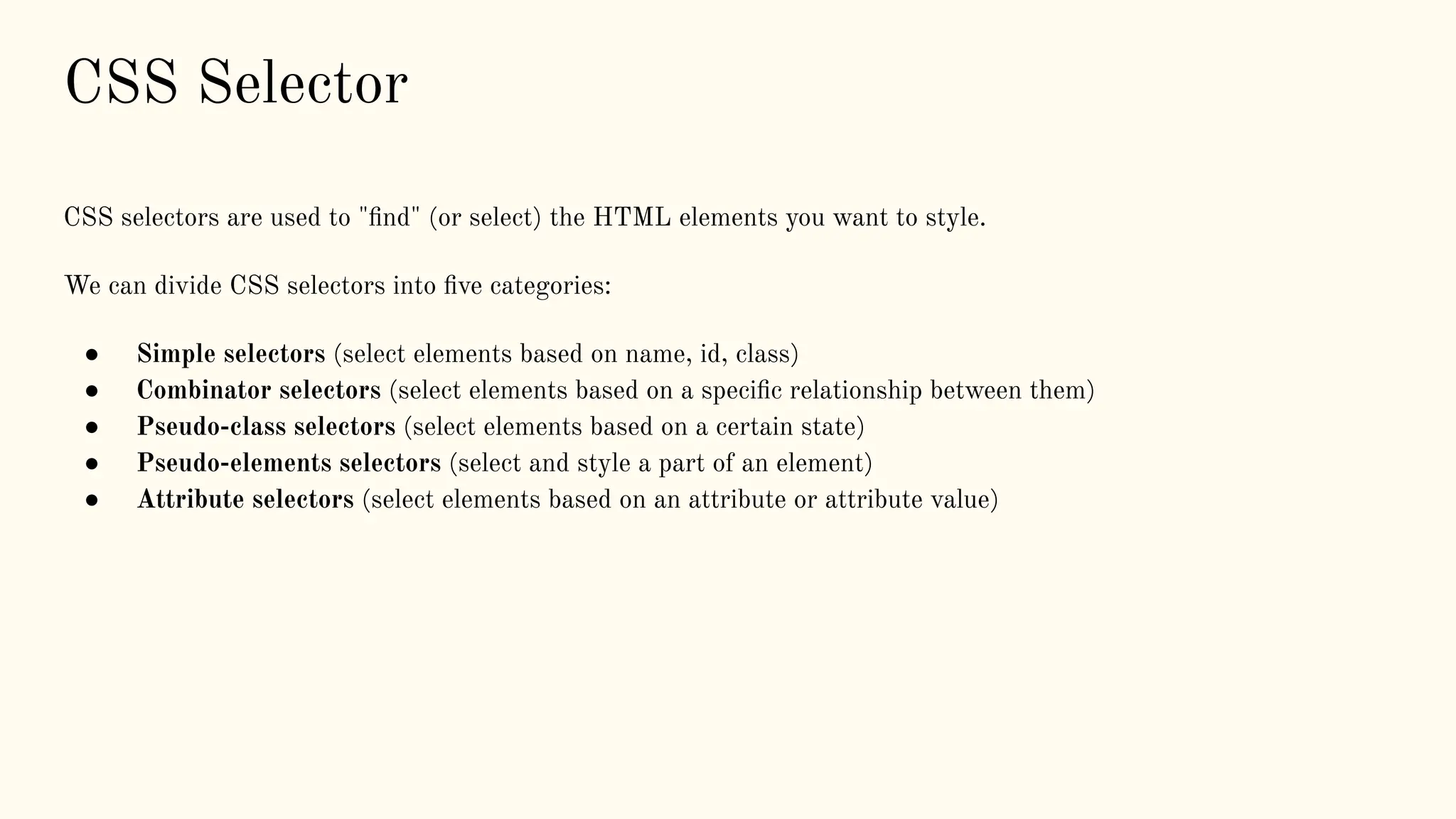
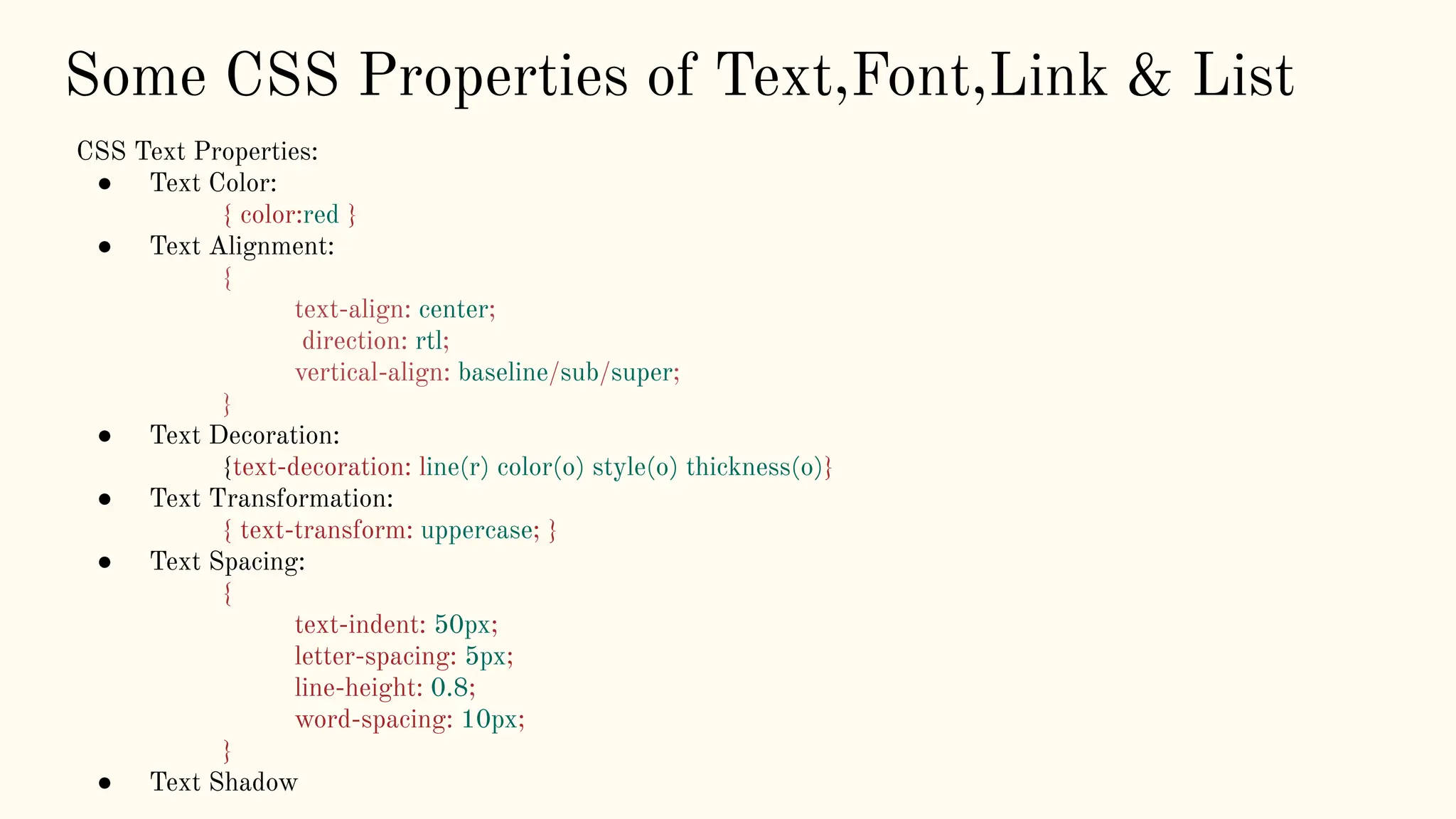
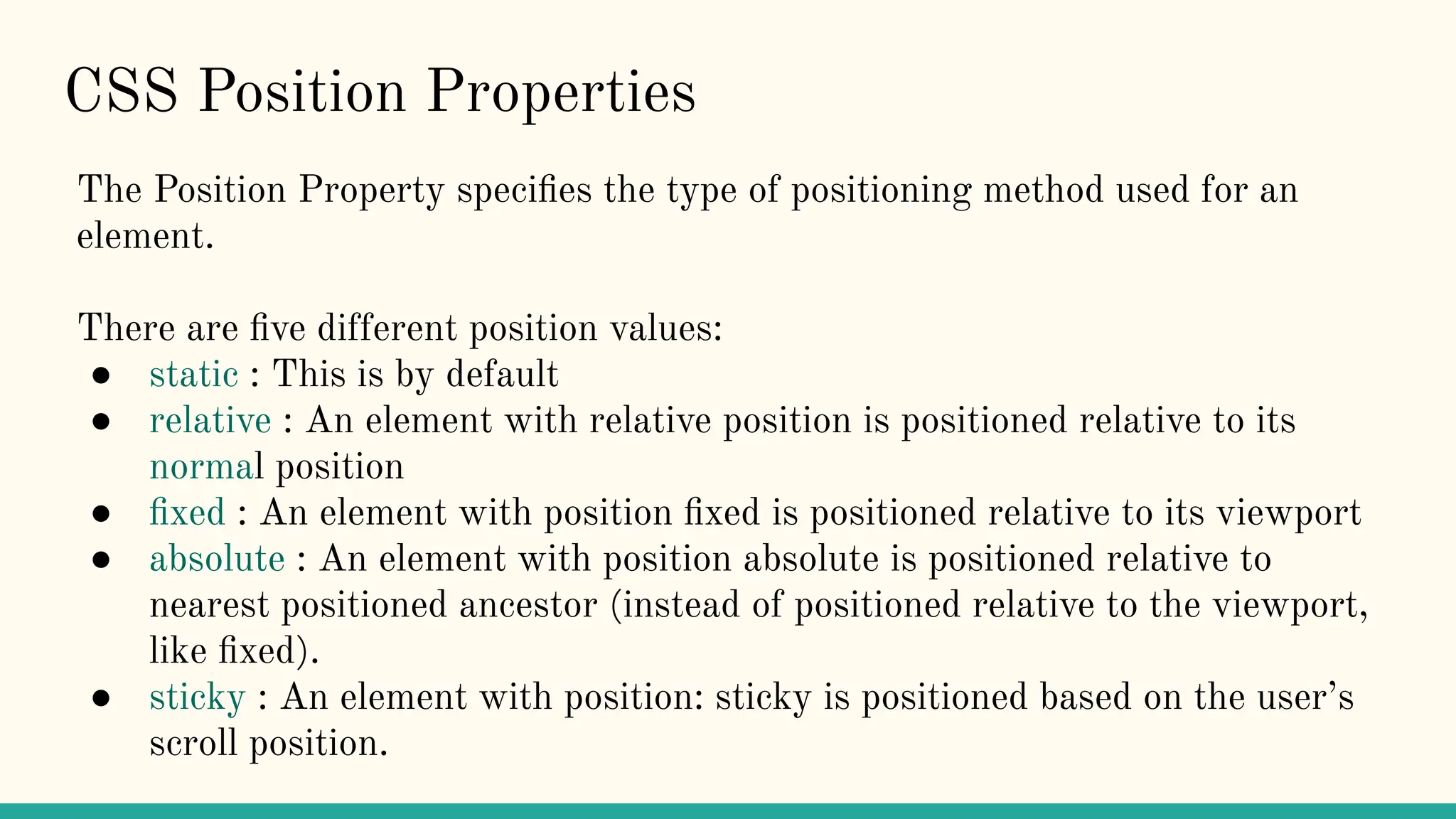
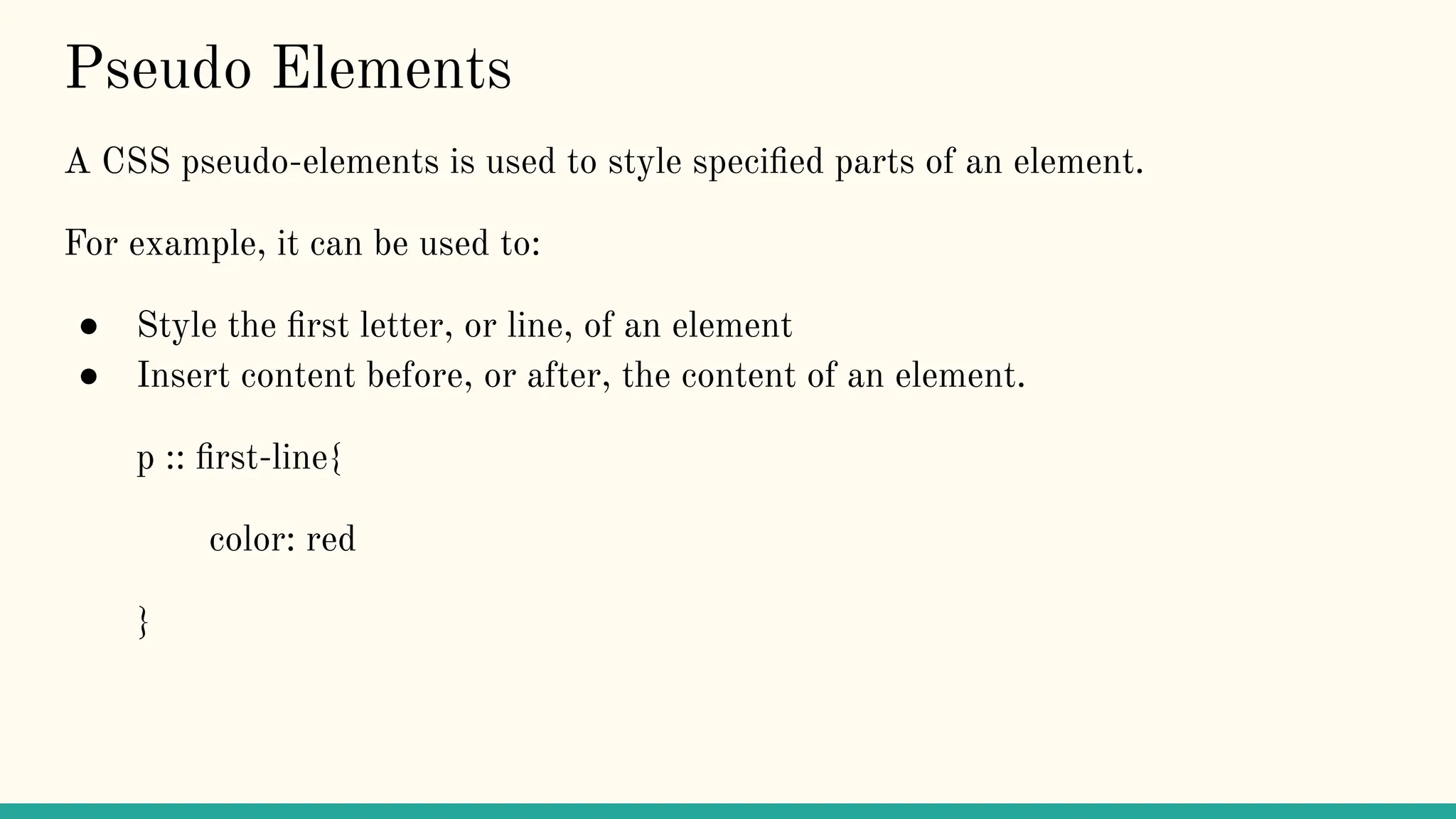
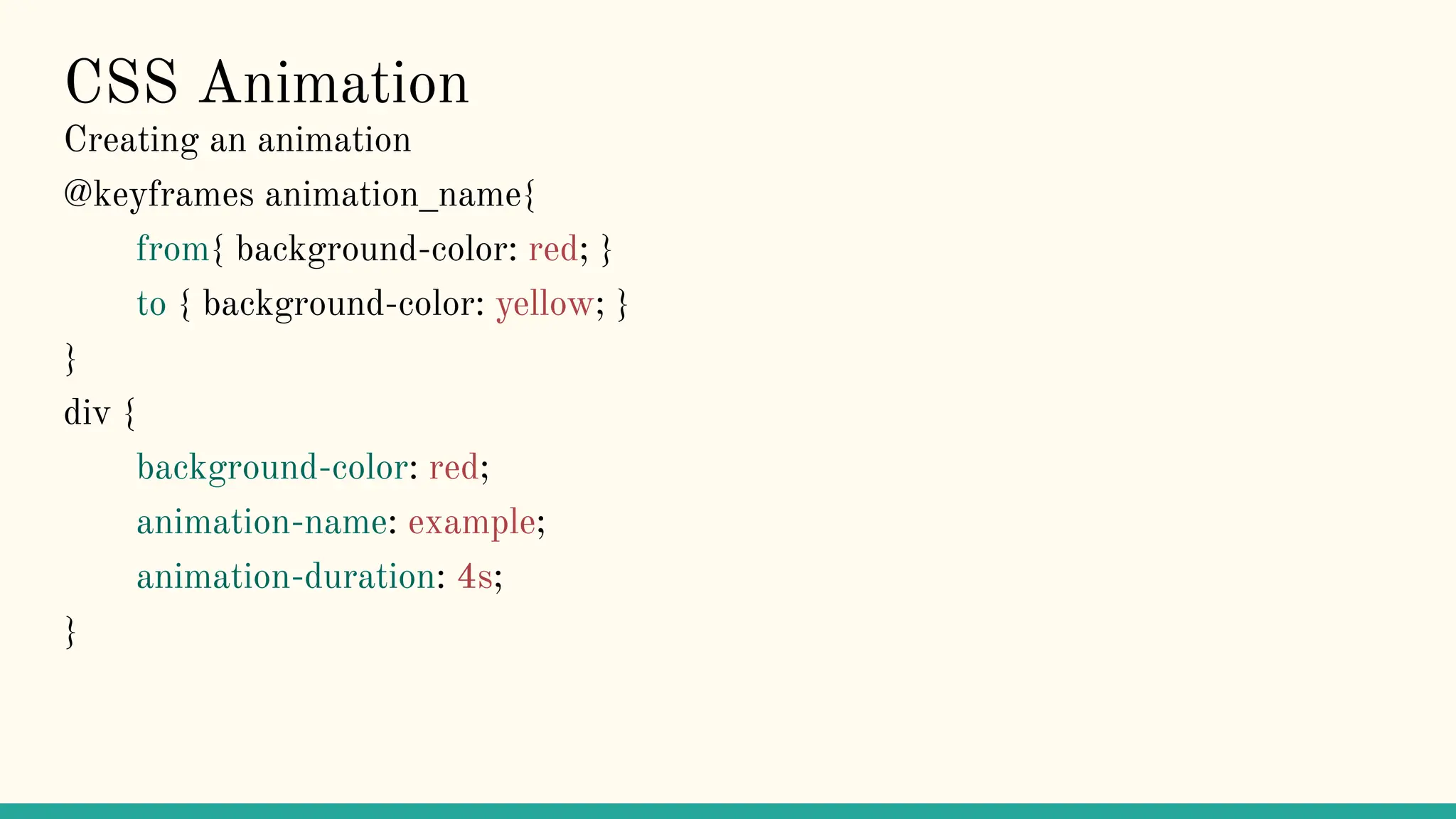
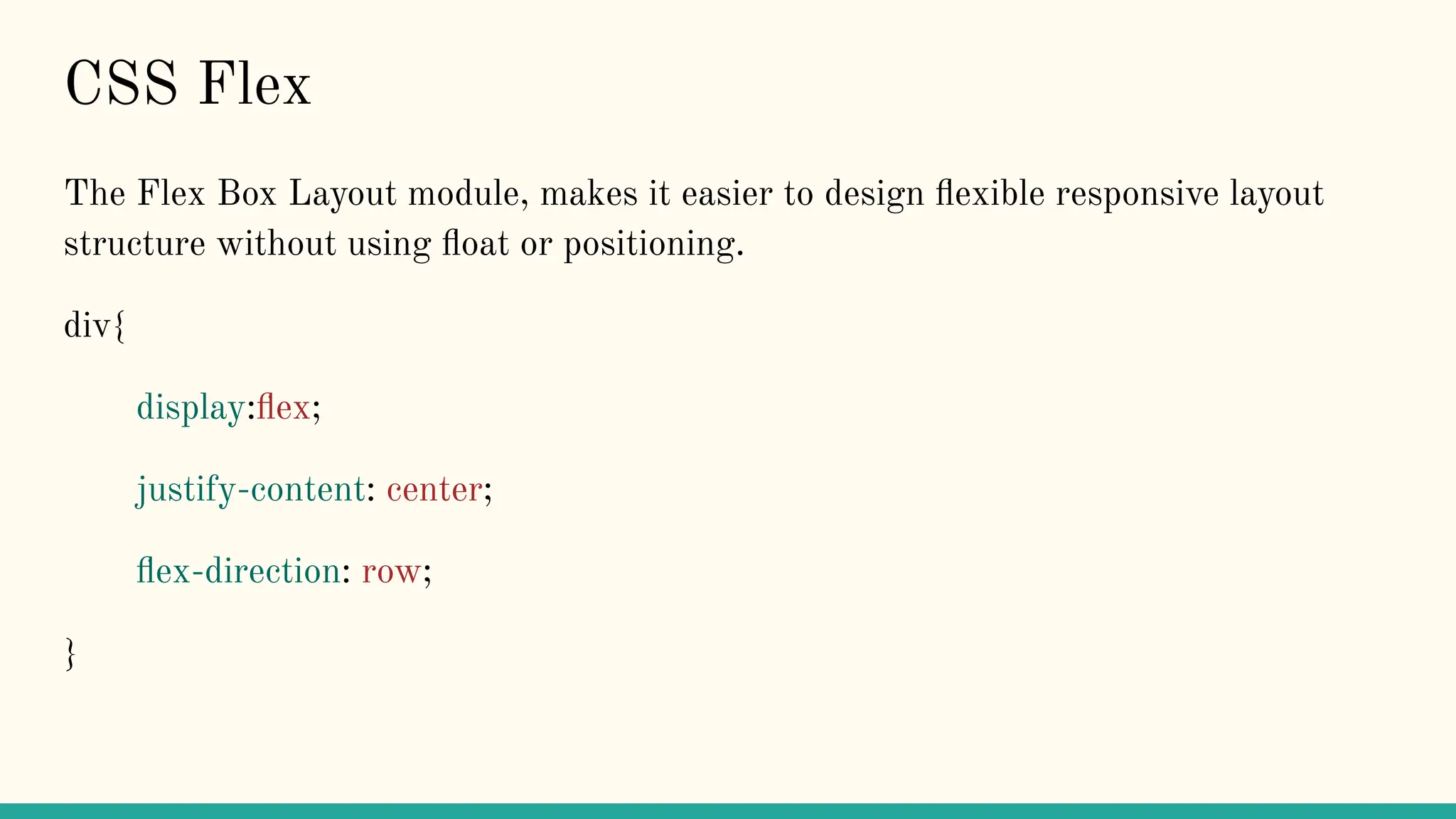
The document is a comprehensive tutorial on CSS, covering its fundamental concepts such as selectors, syntax, variables, and properties related to colors, backgrounds, borders, and box models. It explains how to link CSS to HTML, the importance of CSS for enhancing user experience through animations, and details on text, font, and layout properties including flexbox and grid. The tutorial includes examples and explanations of advanced topics like pseudo-classes, pseudo-elements, and animations.