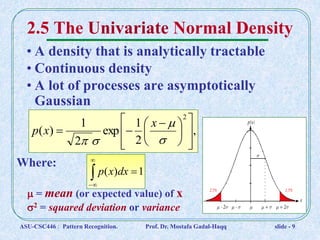
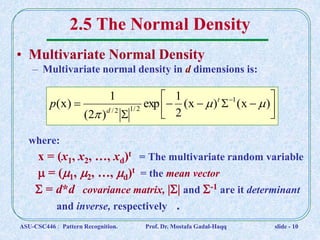
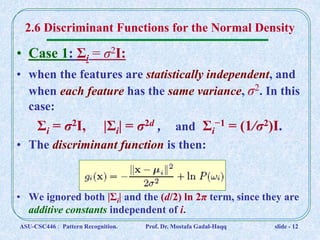
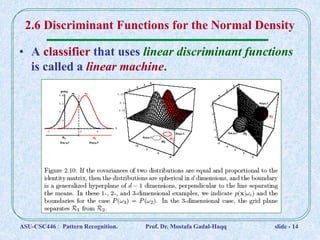
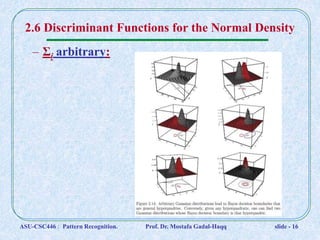
This document discusses Bayesian decision theory and classifiers that use discriminant functions. It covers several key topics:
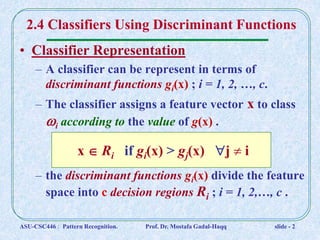
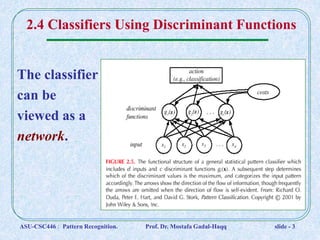
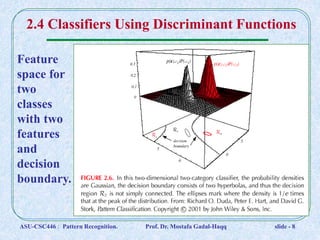
1. Classifiers can be represented by discriminant functions gi(x) that assign vectors x to classes based on their values. The functions divide the space into decision regions.
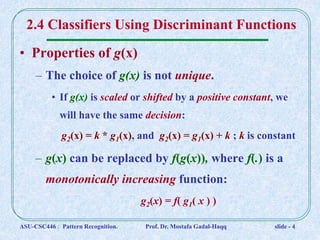
2. Discriminant functions gi(x) are not unique and can be scaled or shifted without changing decisions.
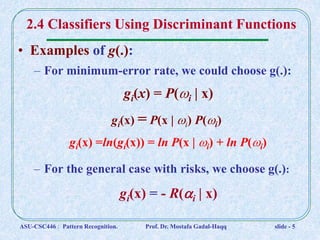
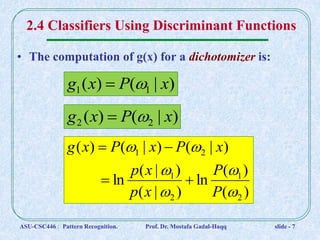
3. Examples of discriminant functions include posterior probabilities P(ωi | x), likelihood functions P(x | ωi)P(ωi), and risk functions.
4. The two-category case uses a single discriminant function g(x) = g1(x) - g2