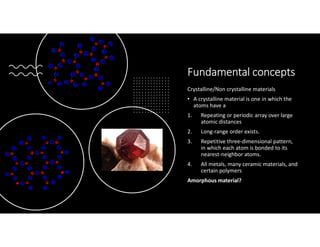
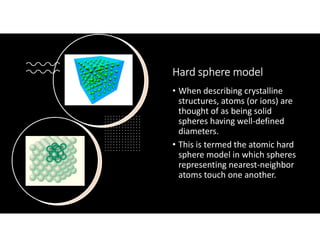
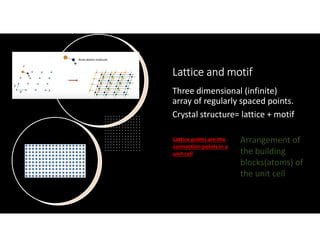
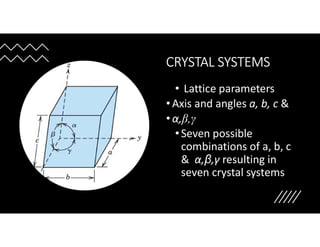
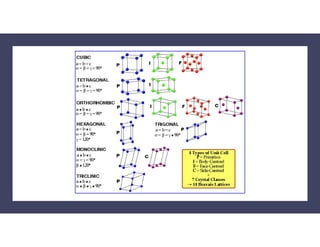
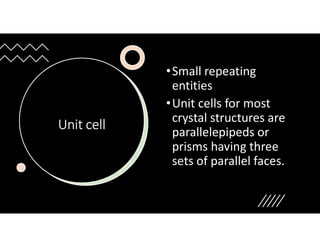
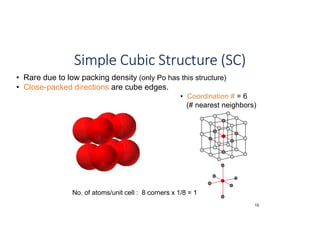
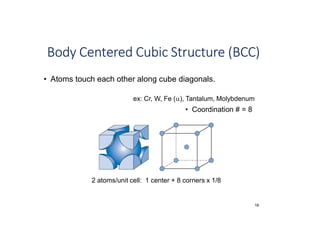
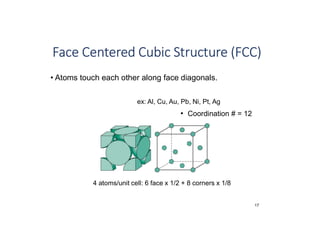
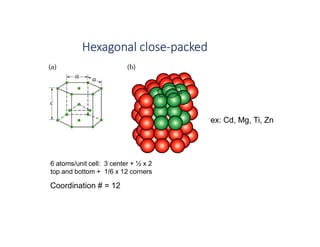
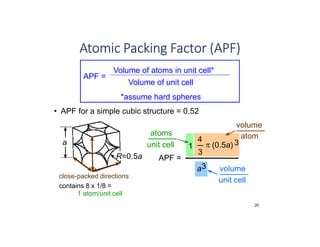
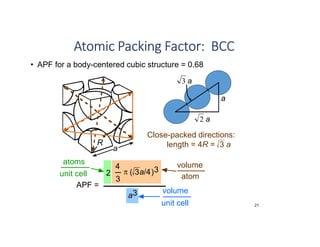
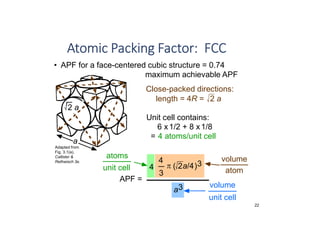
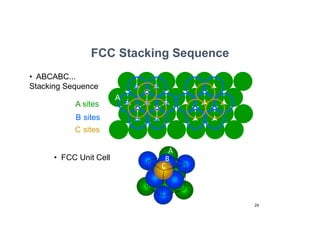
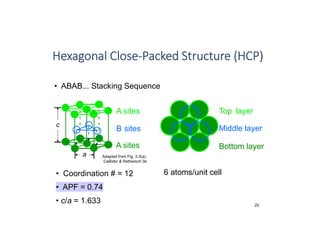
The document serves as a basic introduction to crystallography, covering essential concepts including crystal systems, lattice structures, unit cells, coordination numbers, and atomic packing factors. It details the characteristics of crystalline materials, such as their long-range order and repetitive patterns, and explores various cubic structures like simple cubic (sc), body-centered cubic (bcc), and face-centered cubic (fcc). Additionally, it discusses the atomic packing factor and stacking sequences relevant to these structures.