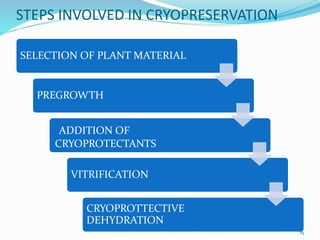
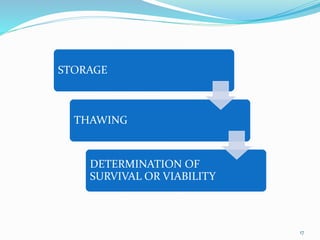
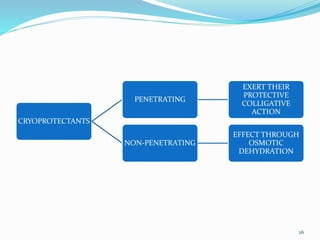
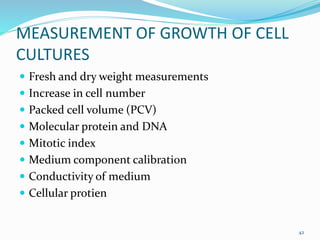
Cryopreservation is a process where biological materials like cells, tissues, and organs are preserved at very low temperatures, typically in liquid nitrogen at -196°C. This process stops all metabolic activities and allows long-term preservation. The key steps involve selection of suitable plant material, addition of cryoprotectants to prevent ice crystal formation, slow freezing or vitrification to solidify water in an amorphous glassy state without crystallization, storage in liquid nitrogen, and thawing for regeneration of plants. Cryopreservation has many applications in conservation of genetic resources, maintenance of disease-free stock, and long-term storage of cell cultures and germplasm in seed banks and gene banks.