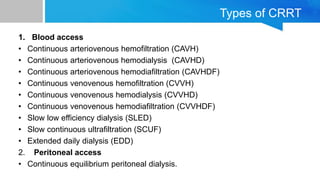
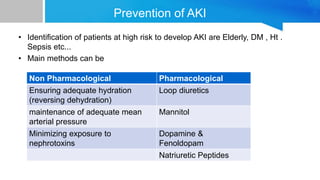
AKI is common in ICU patients and is associated with high mortality. It is defined based on changes in serum creatinine and urine output. The RIFLE criteria is commonly used for classification. Causes include prerenal, intrinsic renal and post renal factors. Treatment involves identifying and treating the underlying cause, fluid resuscitation, and renal replacement therapy like intermittent hemodialysis or continuous renal replacement therapy as needed. Prevention strategies focus on ensuring adequate perfusion and minimizing nephrotoxins. Outcomes remain poor despite treatment.