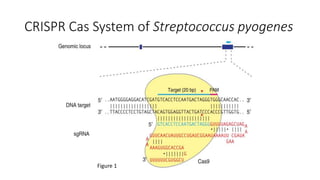
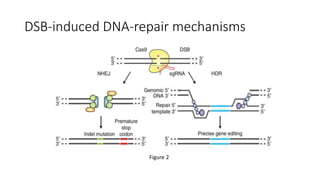
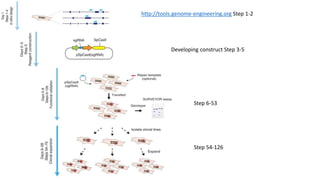
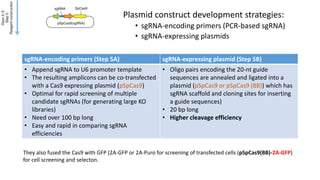
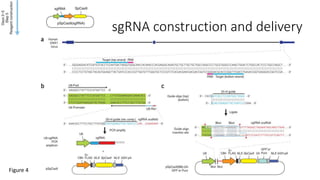
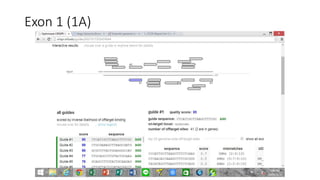
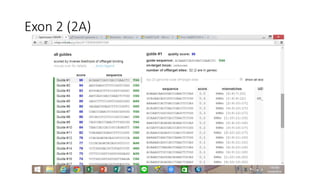
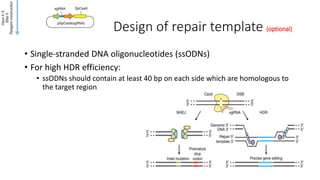
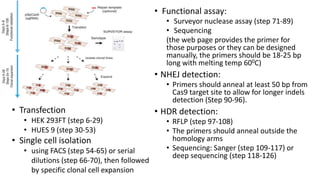
CRISPR-Cas9 is a powerful tool for genome engineering. The document provides guidance on using CRISPR-Cas9 to modify genomes. It describes: 1) Designing single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) to target specific gene loci using online tools; 2) Constructing plasmids expressing Cas9 and sgRNAs; 3) Validating plasmid function using assays like Surveyor nuclease; and 4) Transfecting cells, isolating clones, and further validating genome edits through sequencing. The goal is to use this method to precisely modify genomes for research applications.