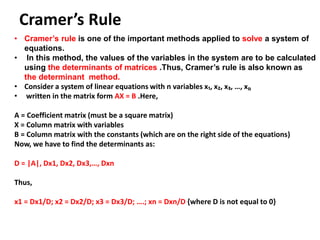
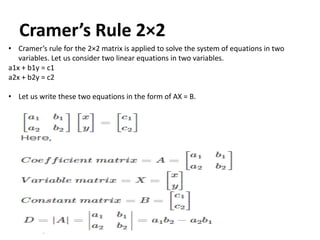
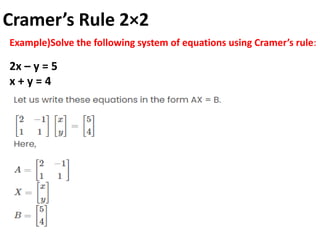
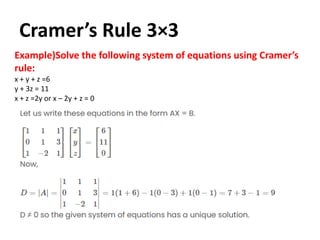
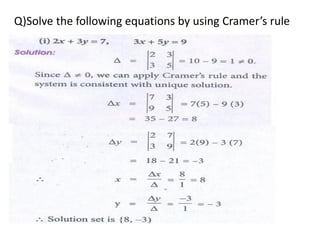
Cramer's rule is a method for solving systems of linear equations. It involves calculating the determinants of matrices. For a system of n variables (x1, x2, ..., xn) written in matrix form AX = B, the value of each variable is calculated as the determinant of the coefficient matrix with one column replaced by the constants column, divided by the determinant of the coefficient matrix. For a 2x2 system, Cramer's rule involves calculating the determinants D, Dx1, and Dx2. For a 3x3 system, the determinants are D, Dx1, Dx2, and Dx3. An example of applying Cramer's rule to a 2x