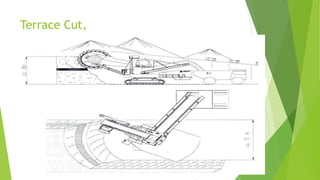
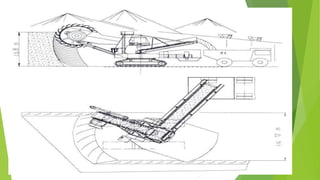
Bucket wheel excavators are large continuous mining machines used for soft to semi-hard materials like clay, sand, gravel, and coal. They have a large wheel with buckets that removes material in a continuous process. The largest bucket wheel excavators can be over 90 meters tall and 240 meters long, with a 21-meter diameter wheel. They are commonly used in strip mining and lignite mining to continuously remove overburden and deliver large volumes of material.