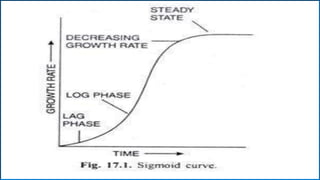
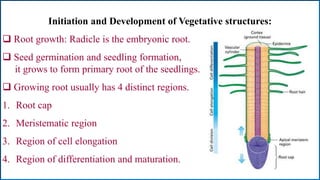
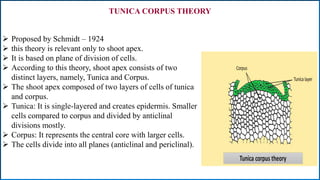
Growth and development are fundamental characteristics of living organisms. Growth involves an irreversible increase in size through metabolism and cell division, while development is a more qualitative change involving differentiation and specialization. Growth follows a sigmoid curve with lag, log, and steady state phases. It can be determinate, stopping at a fixed size, or indeterminate, continuing through overlapping vegetative and reproductive phases. Development involves ordered changes in organs and tissues through initiation, elongation, and differentiation of structures like roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits driven by hormones and genetic programs.