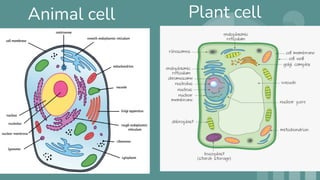
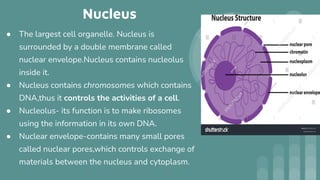
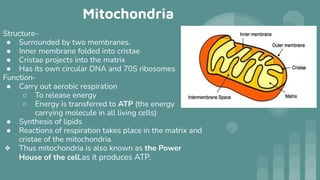
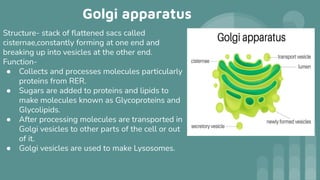
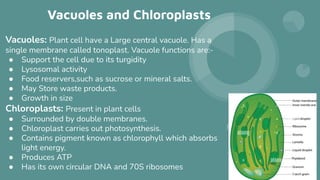
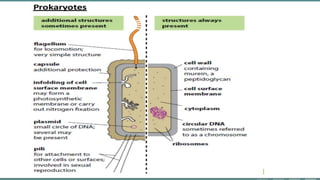
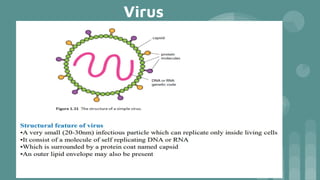
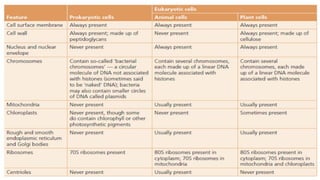
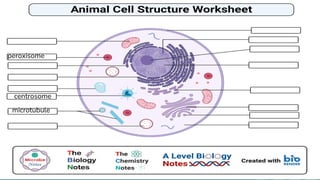
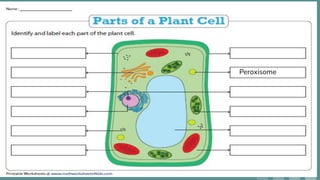
Cells are the basic unit of all living organisms. There are two main types of cells - complex cells with a nucleus and organelles, and simple cells without a nucleus. Complex cells are known as eukaryotes and include animal, plant, and fungi cells. Simple cells are prokaryotes like bacteria. Key cellular components include the cell membrane, nucleus containing DNA, mitochondria which produces energy, and chloroplasts which perform photosynthesis in plant cells. Organelles are either membrane-bound like the nucleus and mitochondria, or non-membrane bound like ribosomes.