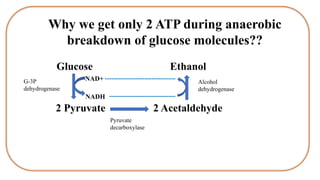
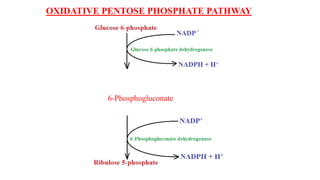
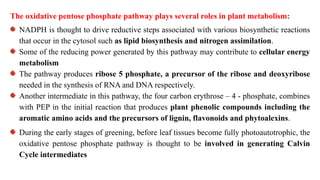
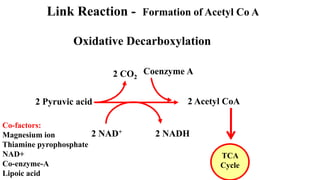
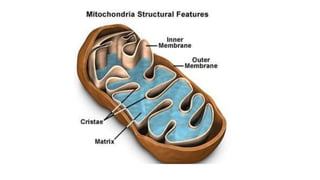
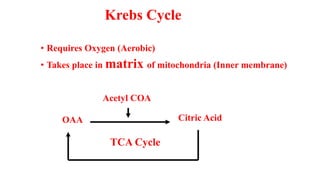
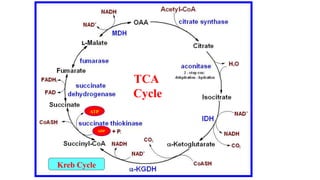
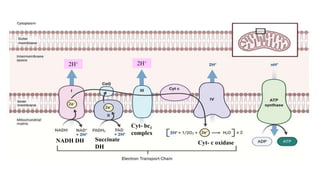
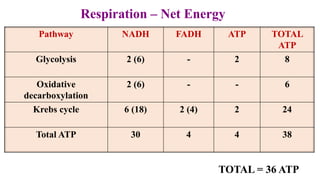
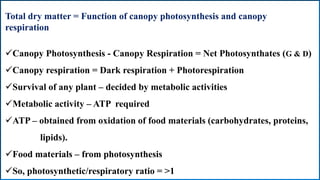
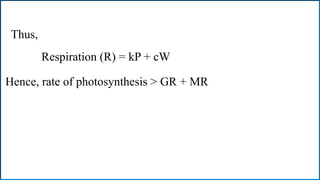
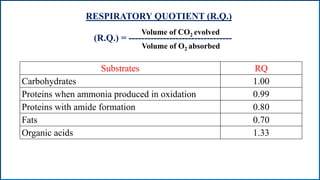
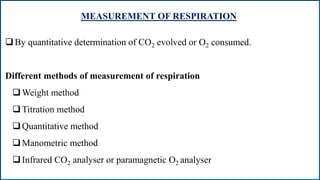
Respiration is the process by which plants release energy stored during photosynthesis. There are two types of respiration - aerobic respiration which requires oxygen and occurs in the mitochondria, and anaerobic respiration which does not require oxygen. Respiration involves several stages including glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain, which ultimately generate ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. Respiration is essential for plant growth and metabolism as it provides energy for cellular processes and converts stored energy into usable form.




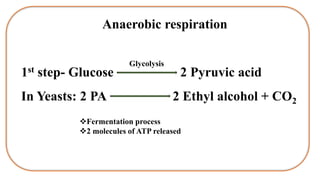


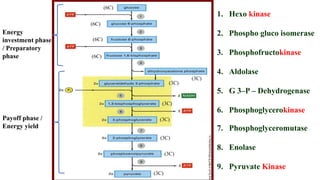
![Glucose
2 Pyruvic acid
4 ATP
2 ATP
2 NADH
NET GAIN = 2 ATP & 2 NADH
Gross ATP = 8 ATP [1 NADH=3ATP]
Glycolysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cphy-161lec-10respirationglyimp-210921150227/85/RESPIRATION-9-320.jpg)