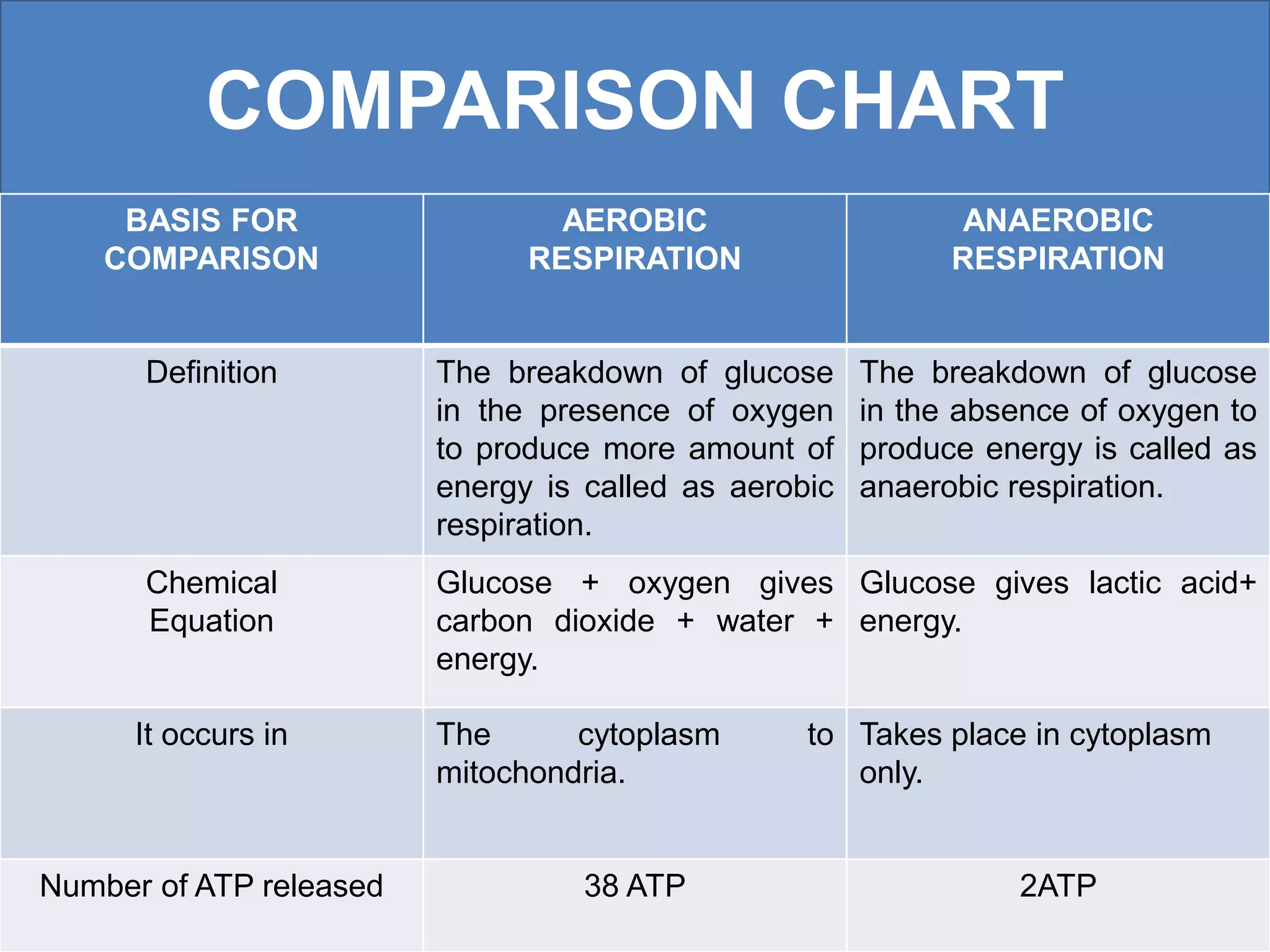
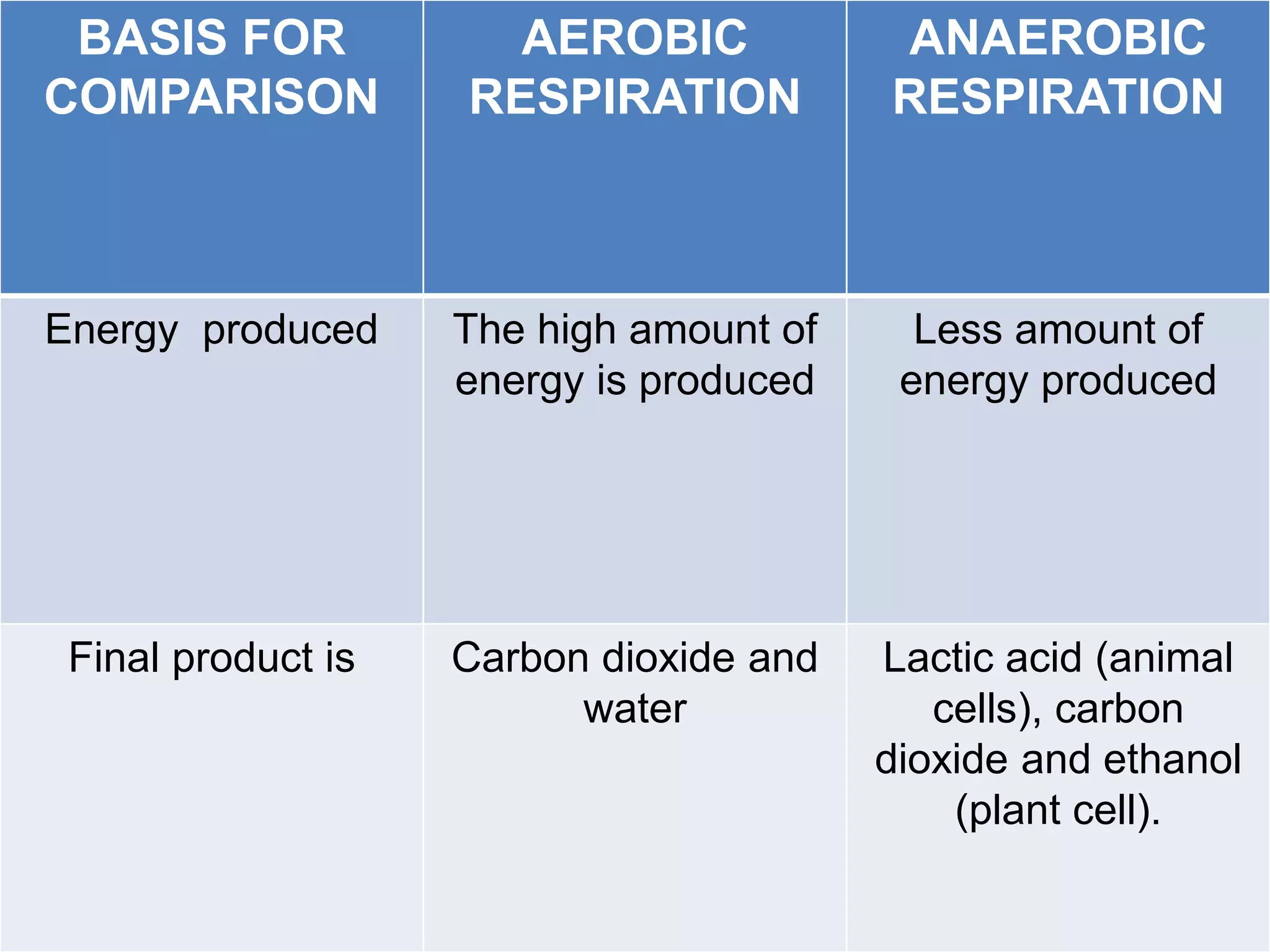
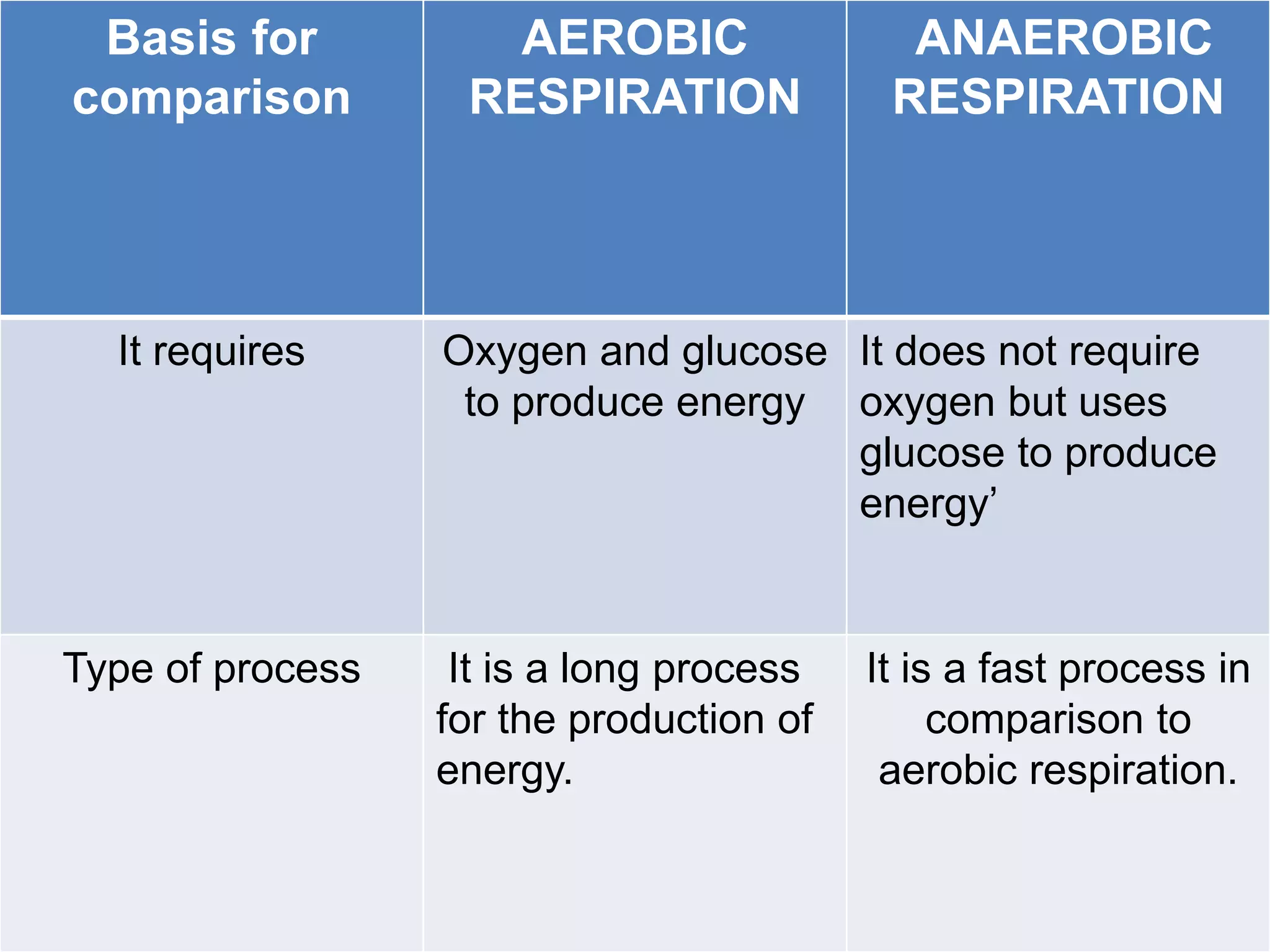
Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen and completely breaks down glucose to produce carbon dioxide, water, and a high amount of energy. Anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen and incompletely breaks down glucose to produce lactic acid or ethanol and less energy. The key differences are that aerobic respiration produces more energy through multiple pathways and requires oxygen, while anaerobic respiration is faster but produces less energy without using oxygen.