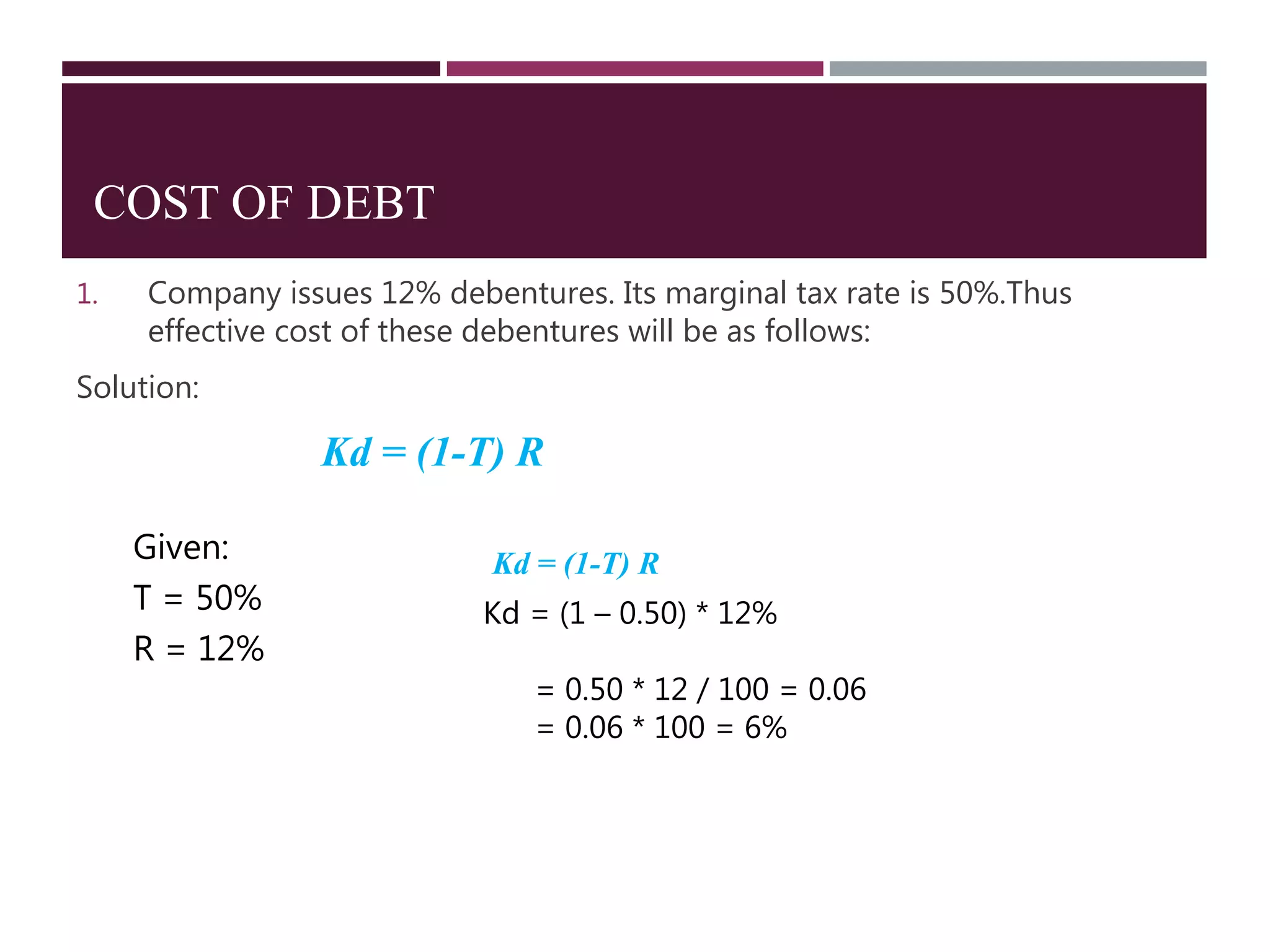
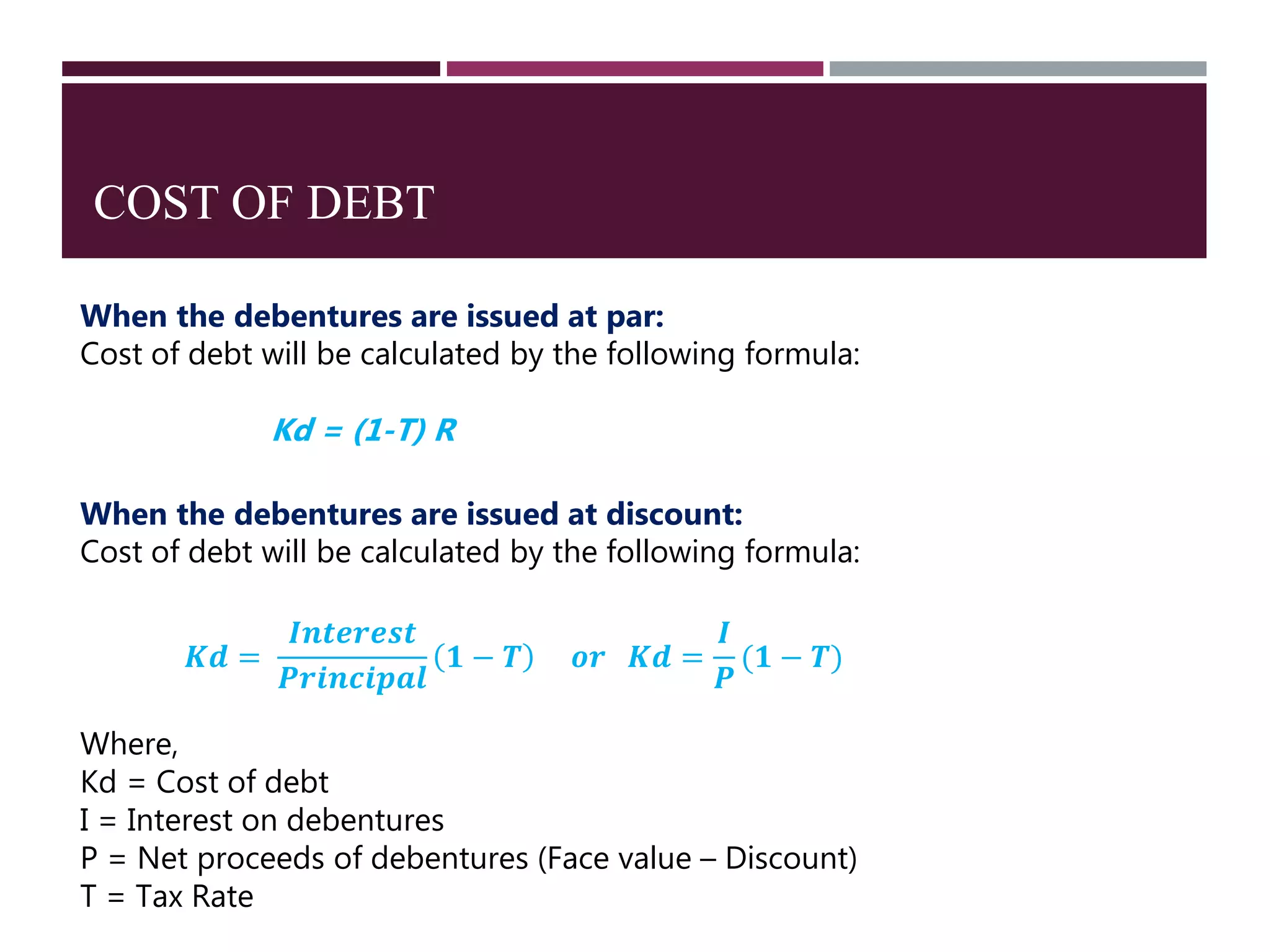
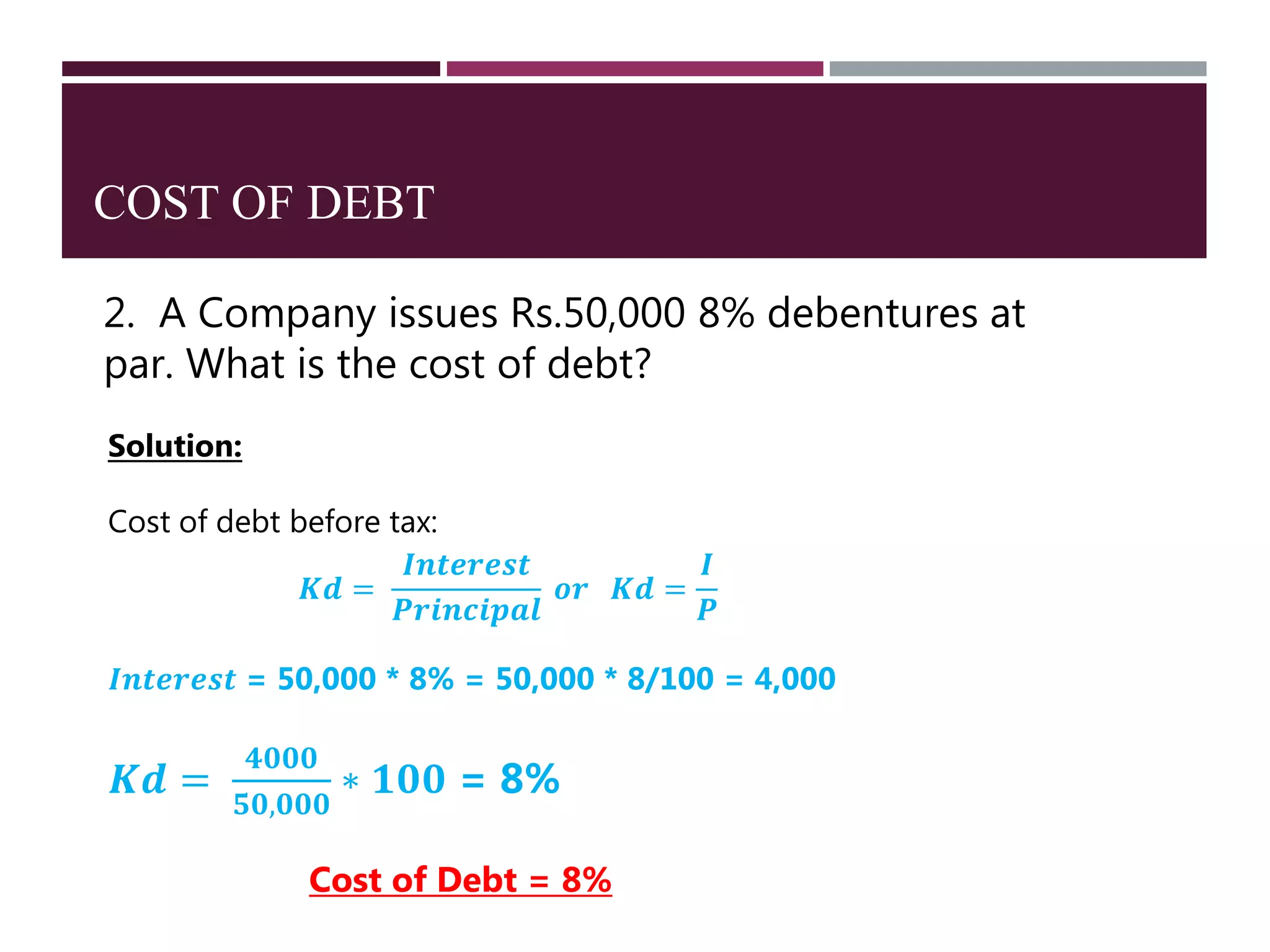
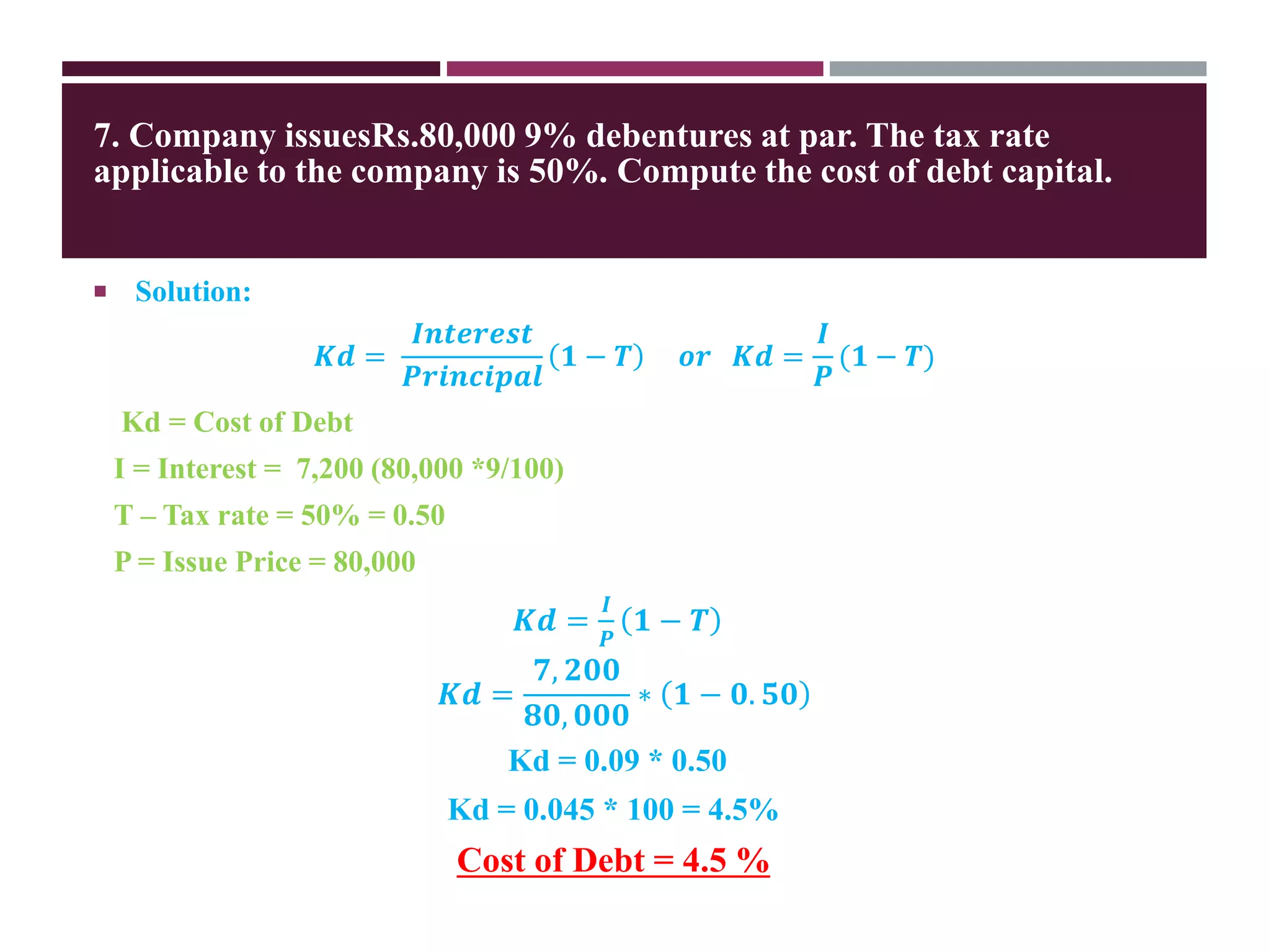
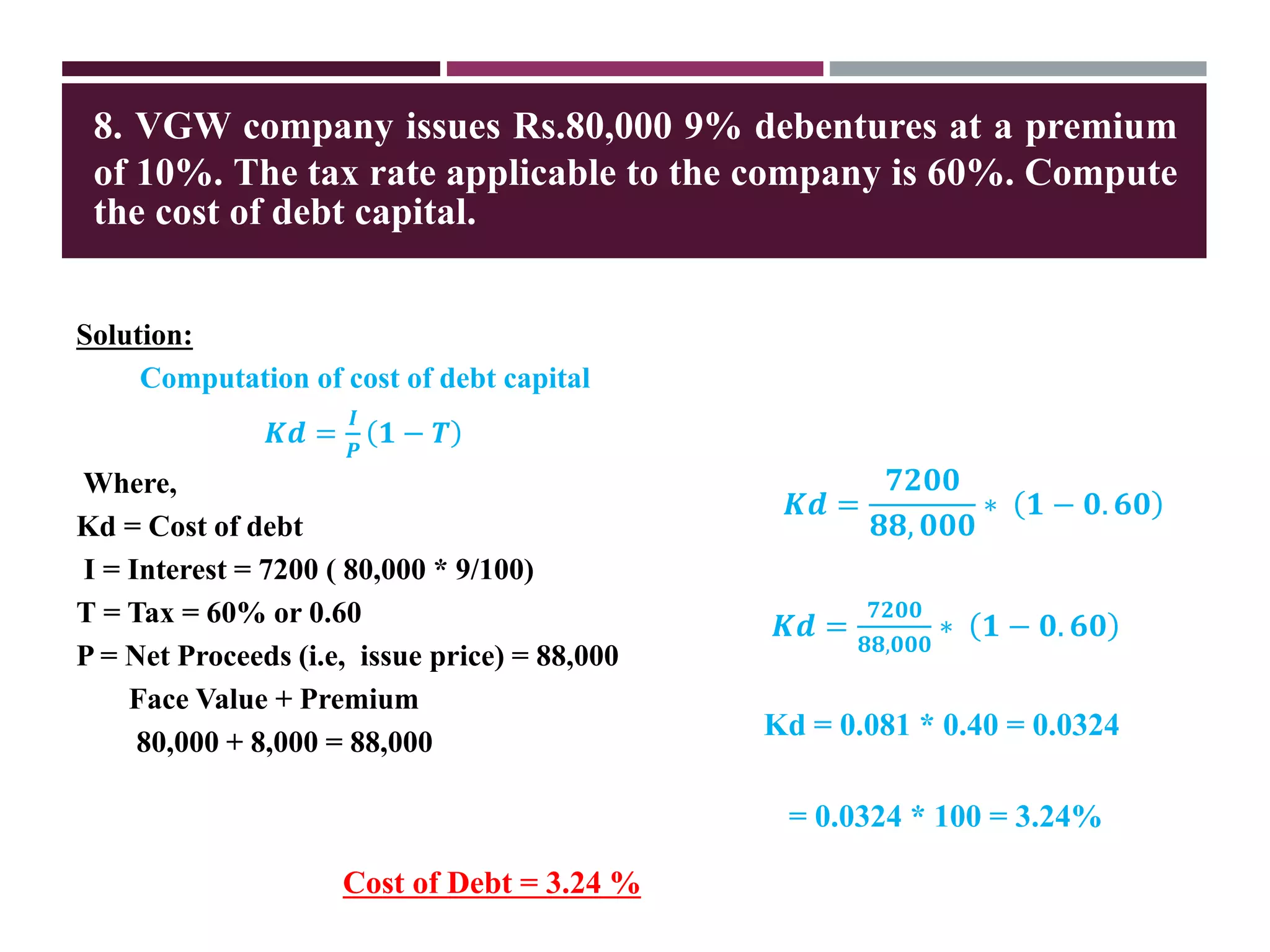
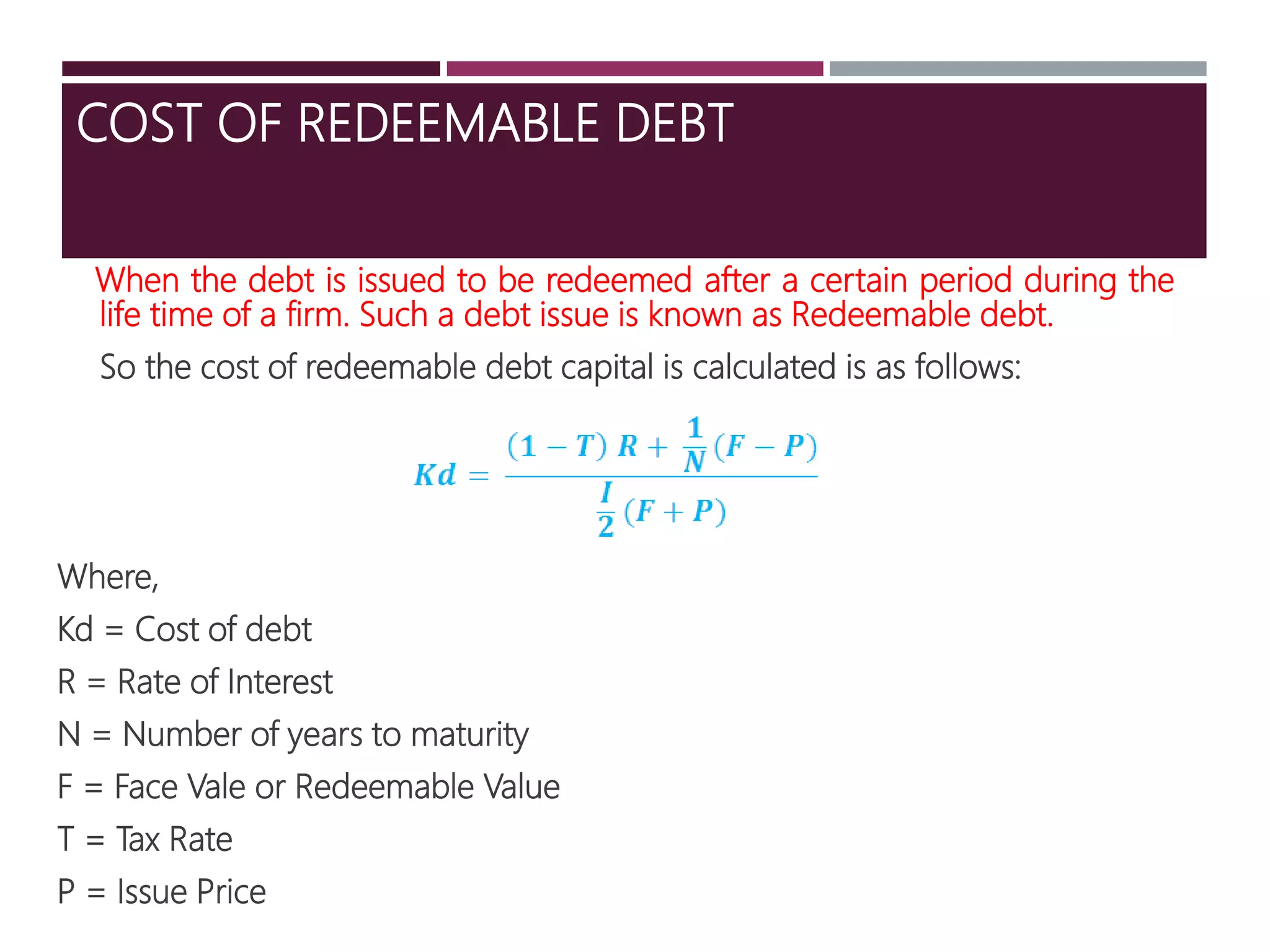
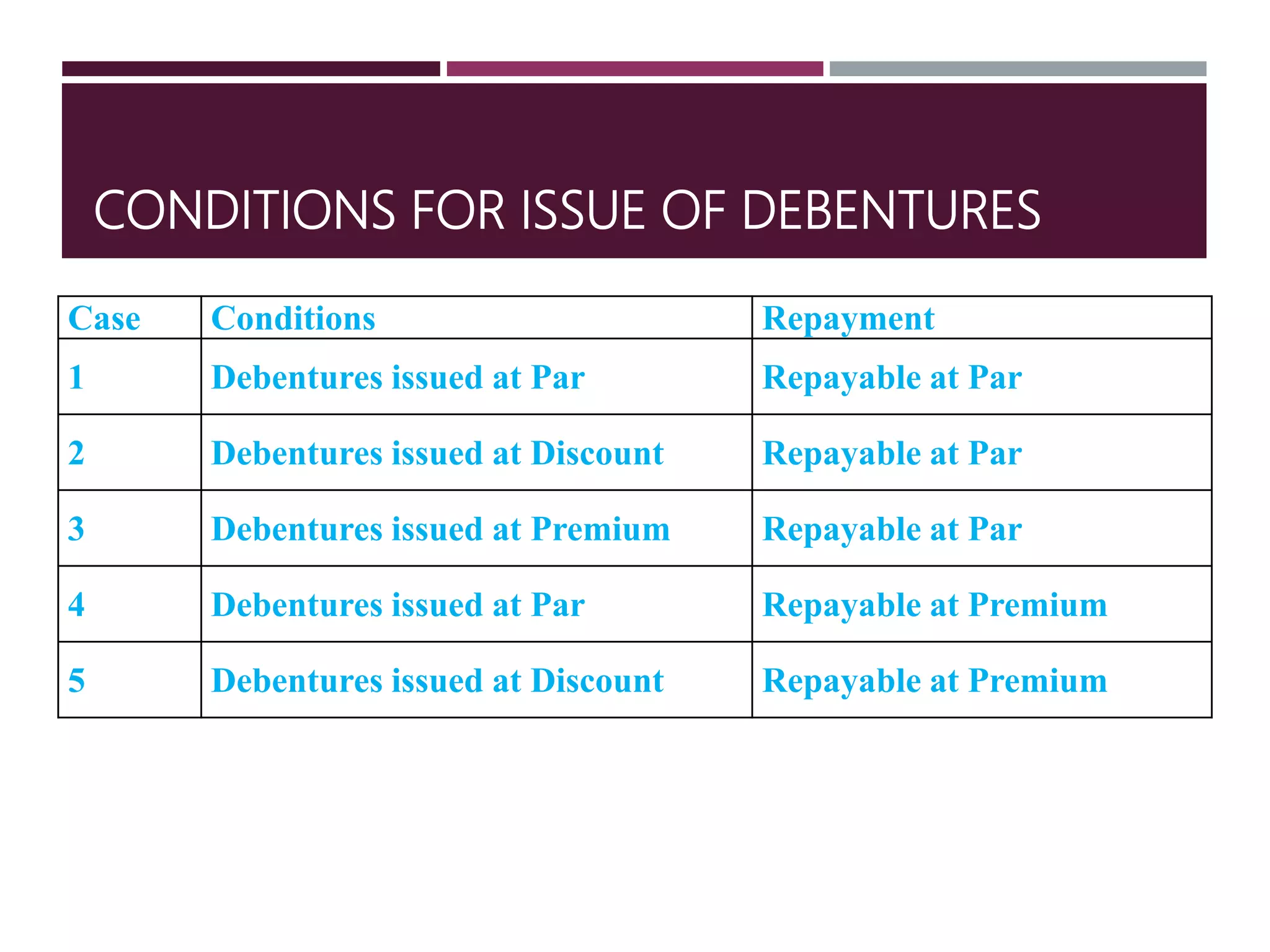
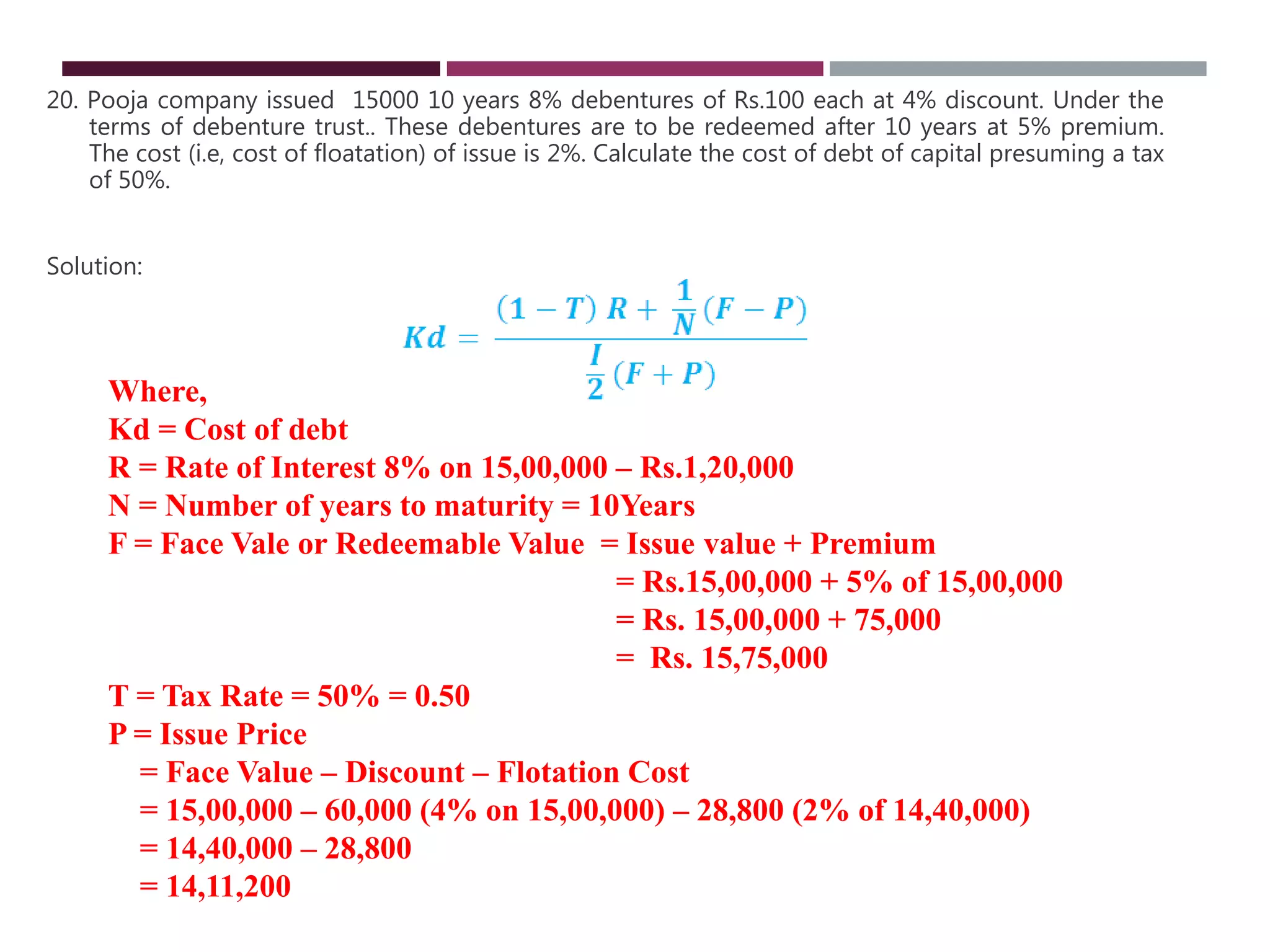
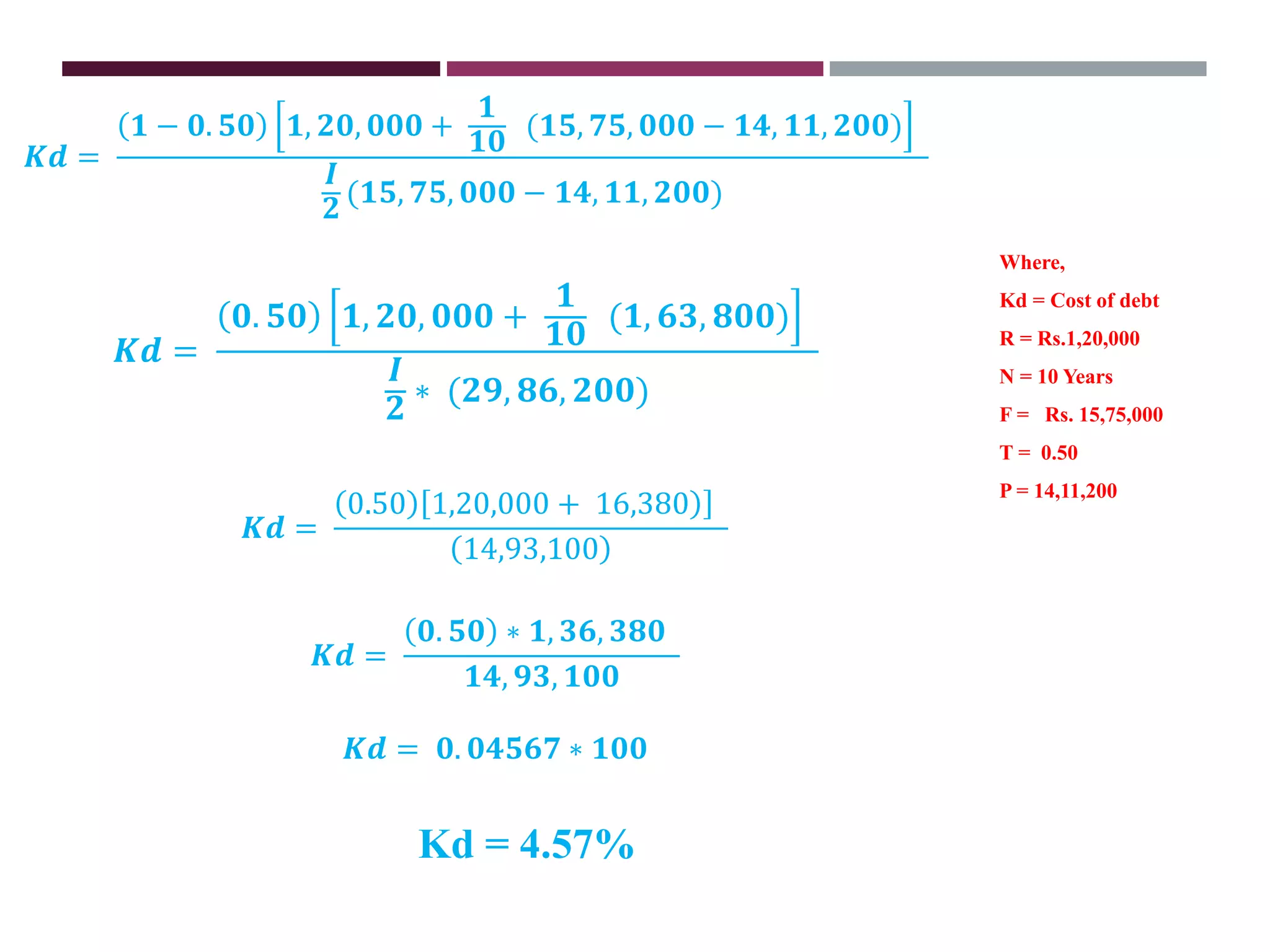
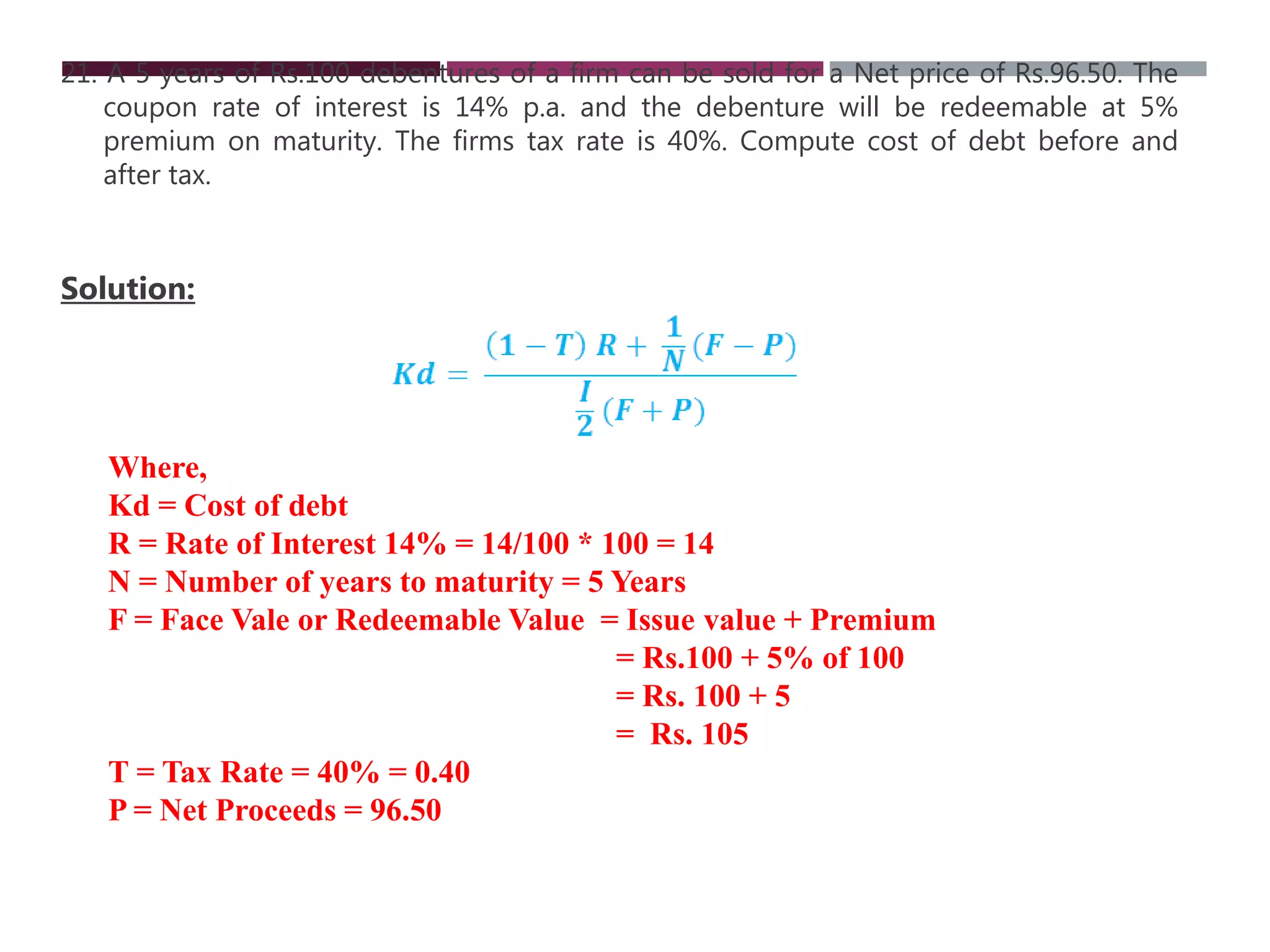
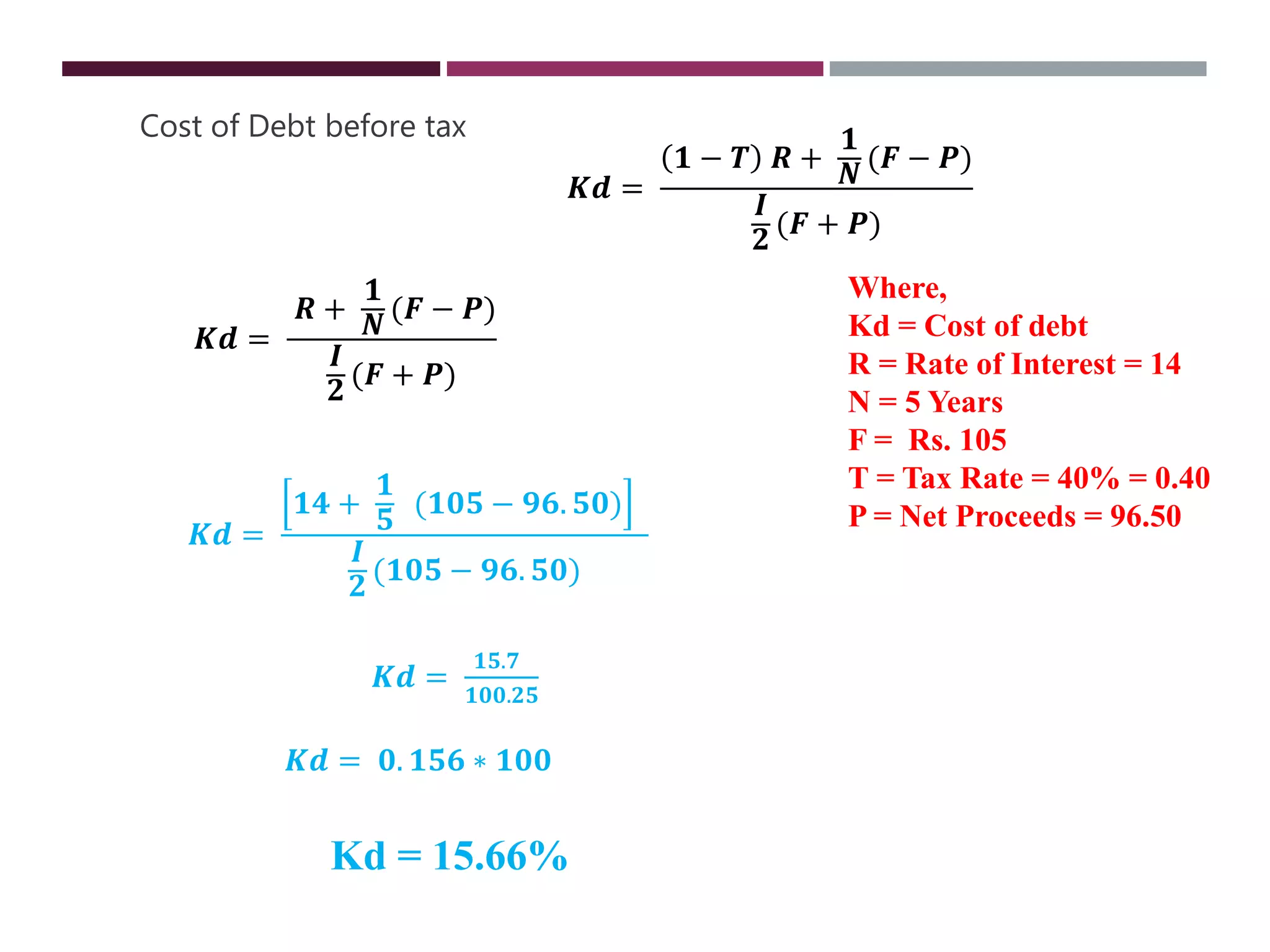
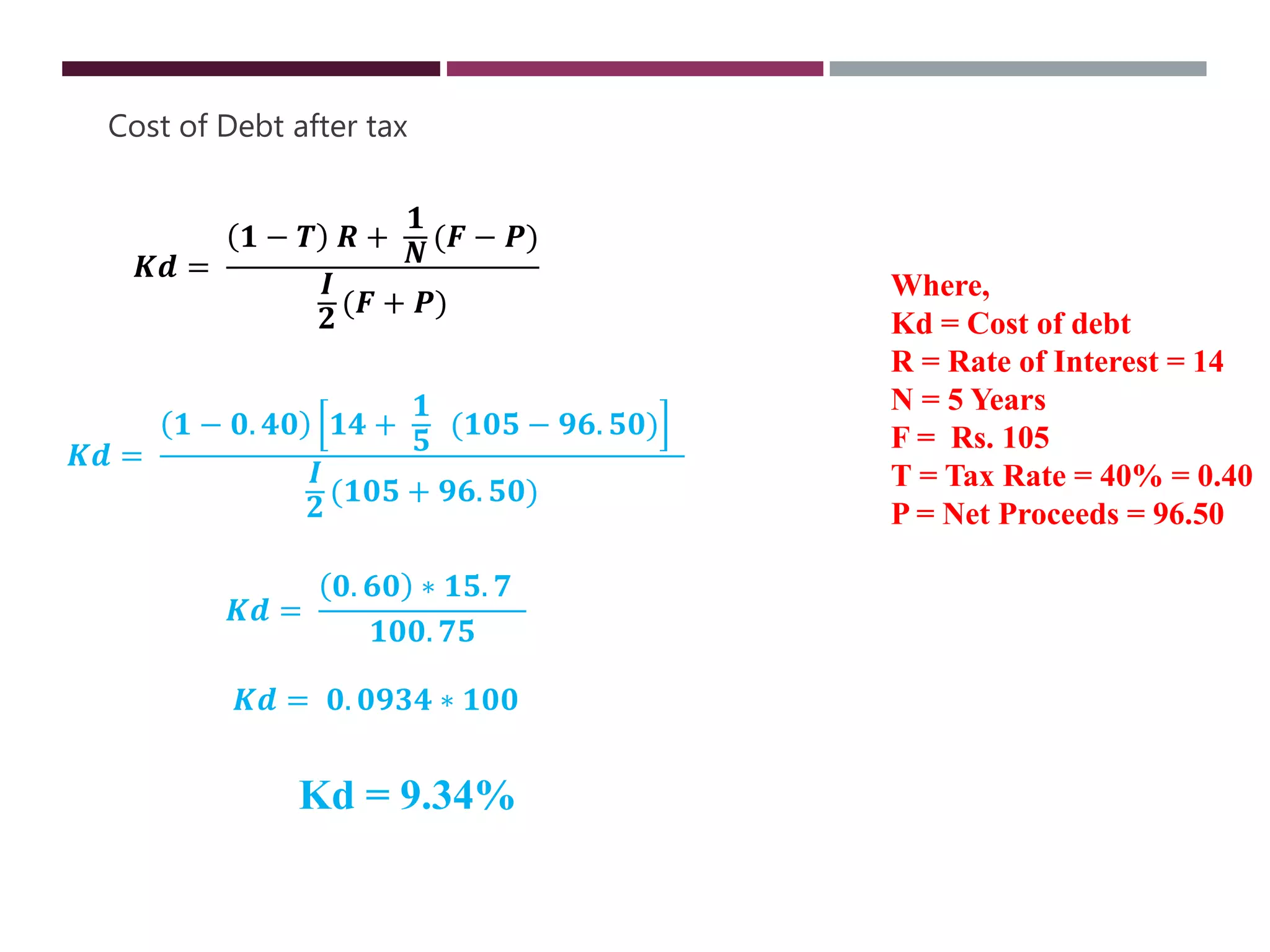
The document discusses financial management related to the cost of capital, specifically focusing on the computation of the cost of debt. It outlines formulas for calculating the cost depending on whether debentures are issued at par, premium, or discount, as well as providing various examples to illustrate these calculations. Additional details about taxes and their impact on the cost of debt are also included.