The document discusses different types of costs including:
1. Accounting costs include expenses incurred during production adjusted for depreciation, while economic costs include explicit payments to factors of production as well as implicit opportunity costs.
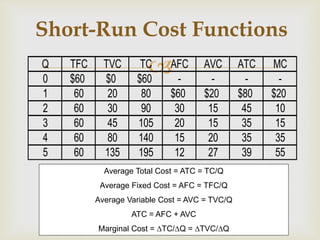
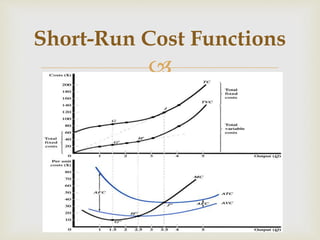
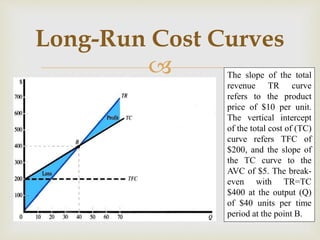
2. In the short-run, costs are classified as fixed, variable, total, average fixed, average variable, and marginal based on their relationship to changing output levels.
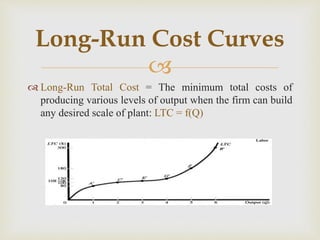
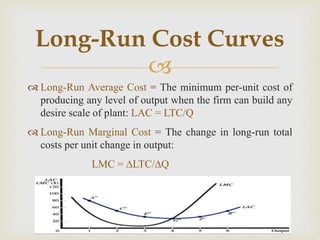
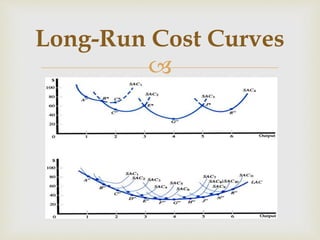
3. In the long-run, all factors are variable and long-run total, average, and marginal cost curves are defined based on minimum cost production at different output scales.








![
Cost Function
Long Run
Marginal
Costs (LMC)
Costs According to Time Period
Short Run Cost Curve Long Run Cost Curve
Total Cost
(TC)
Average
Cost
(AC)
Marginal
Cost (MC)
Long Run
Total Costs
(LTC)
Long Run
Average
Costs (LAC)
Total
Fixed
Costs
(TFC)
Total
Variabl
e
Costs
(TVC)
Averag
e Fixed
Costs
(AFC)
Averag
e
Variabl
e
Costs
(AVC)
[TC =TFC+TVC] [AC = AFC+AVC]
MC = TCn – TCn-1
Or
MC = ΔTC
ΔQ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecopptgroup4-160209081423/85/Economic-Presentation-Cost-Theory-and-Analysis-9-320.jpg)