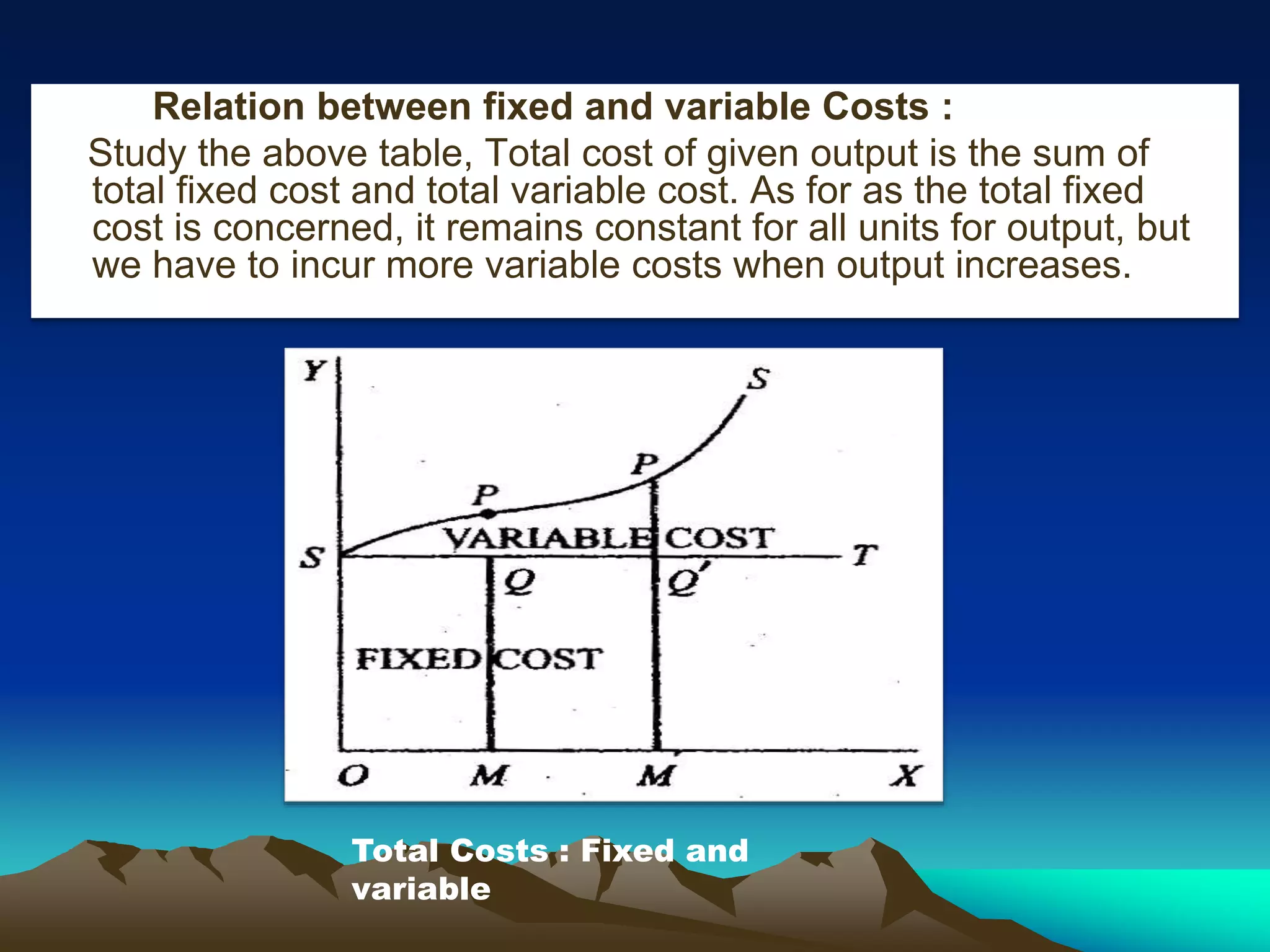
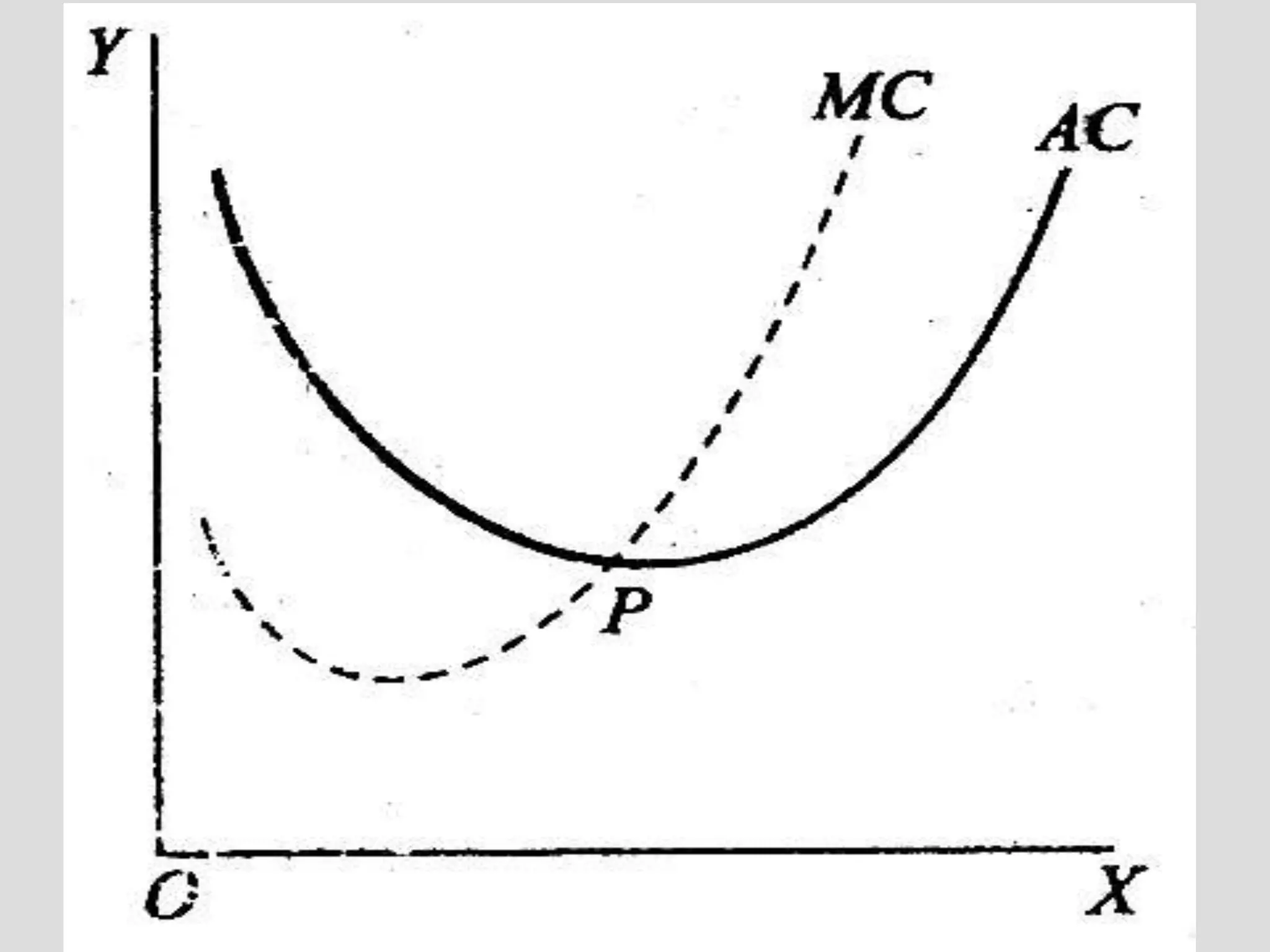
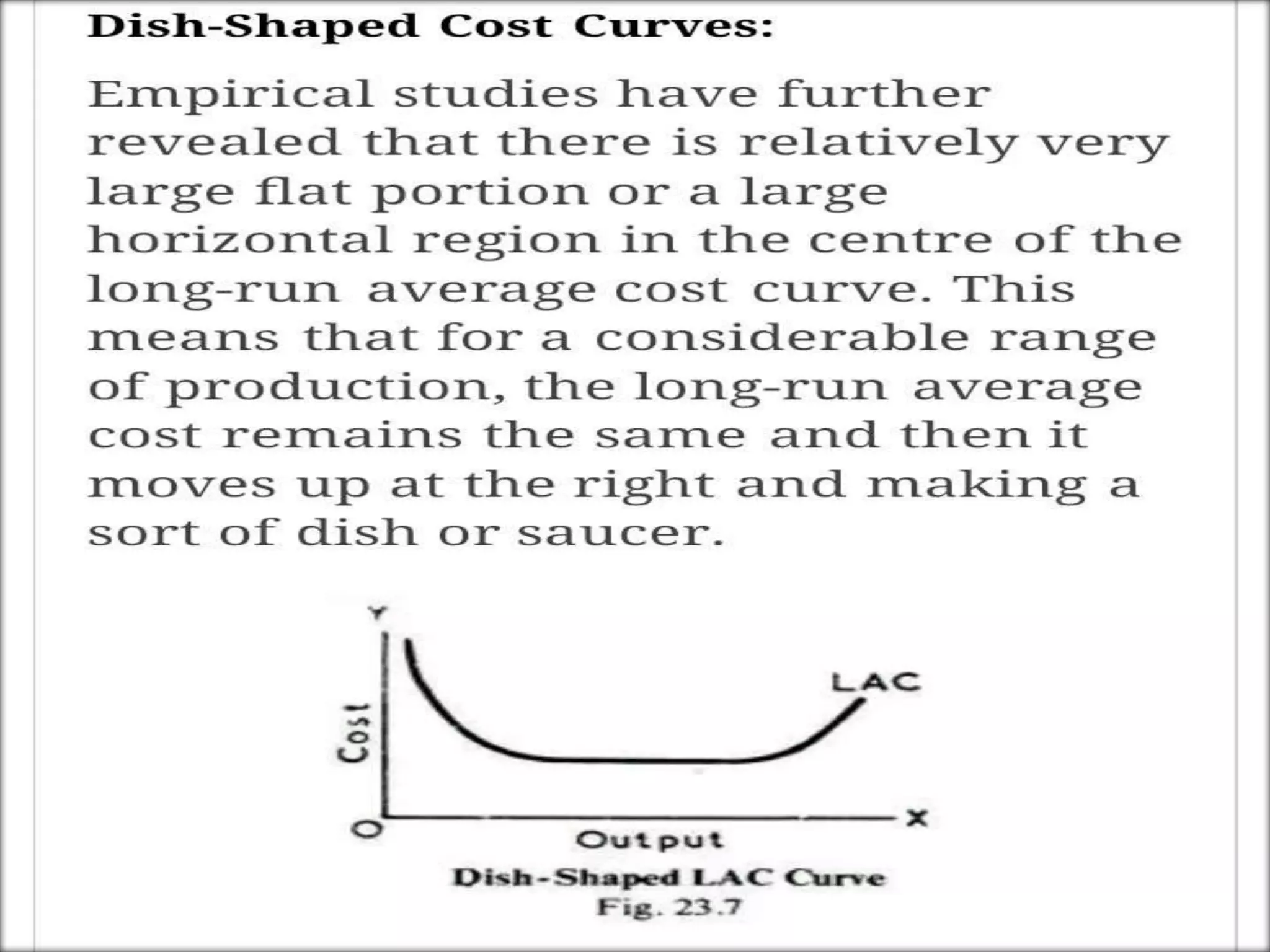
The document discusses the concepts of cost and cost curves in production, distinguishing between nominal costs, real costs, and opportunity costs. It highlights the significance of economic costs, short run versus long run production, and the relationship between fixed and variable costs. Moreover, it addresses limitations of opportunity cost theory while advocating its relevance under current economic considerations.