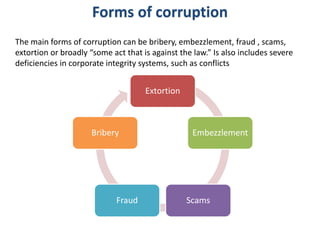
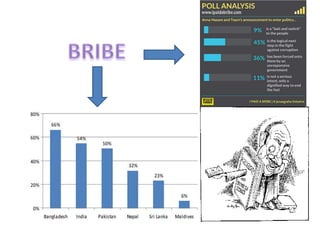
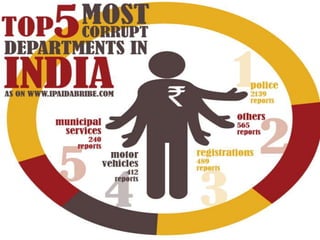
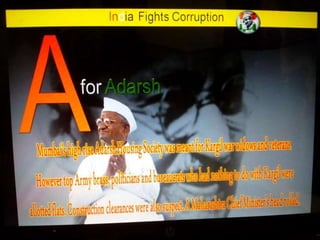
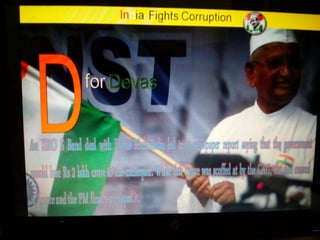
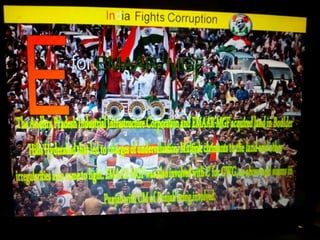
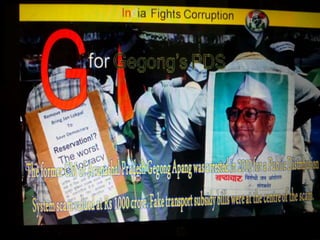
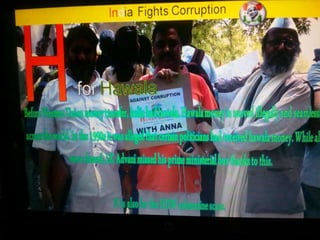
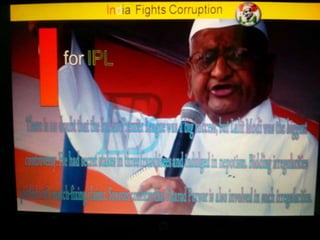
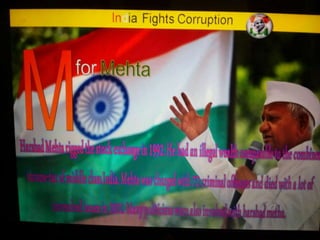
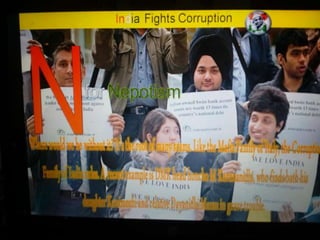
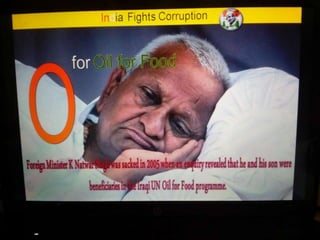
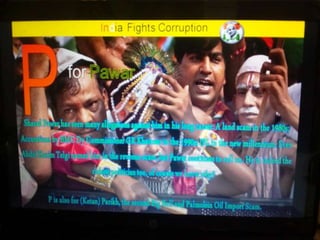
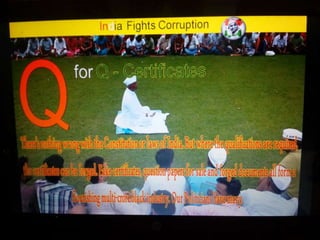
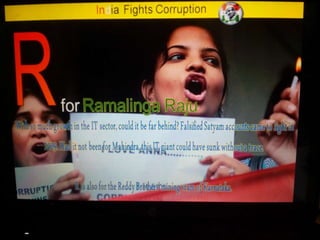
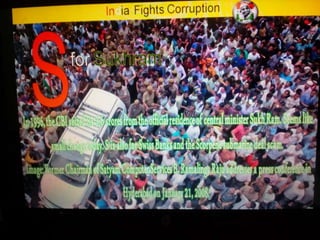
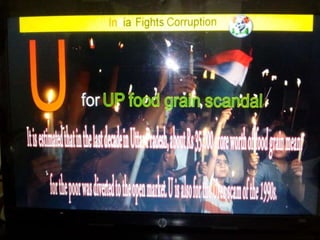
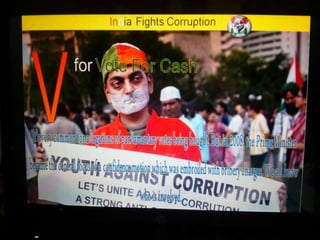
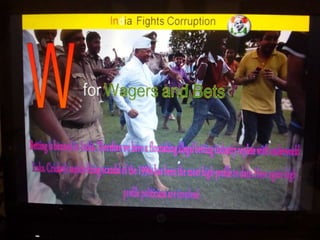
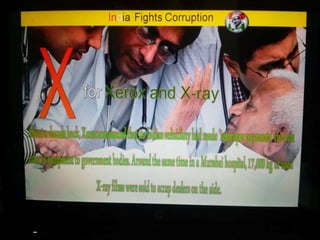
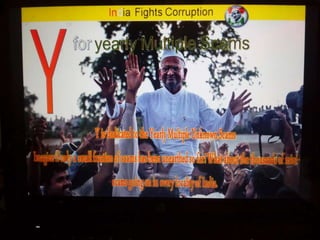
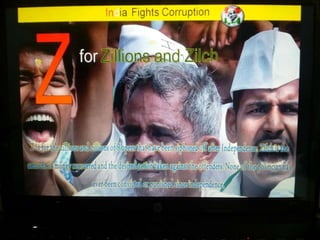
This document summarizes corruption in India, including its definition, causes, forms, types, laws, consequences, and examples of major corruption scams. Corruption is defined as the misuse of public power for private gain. The main causes outlined are lack of management, economic instability, weak leadership, and diminishing social values. Major forms include bribery, embezzlement, fraud, and extortion. Types consist of political, administrative, and professional corruption. Several laws aimed at corruption are also mentioned. The consequences discussed are loss of wealth, hindered development, and increased poverty, crime, and social issues. Examples of significant corruption scams in India involving billions of rupees are also provided.