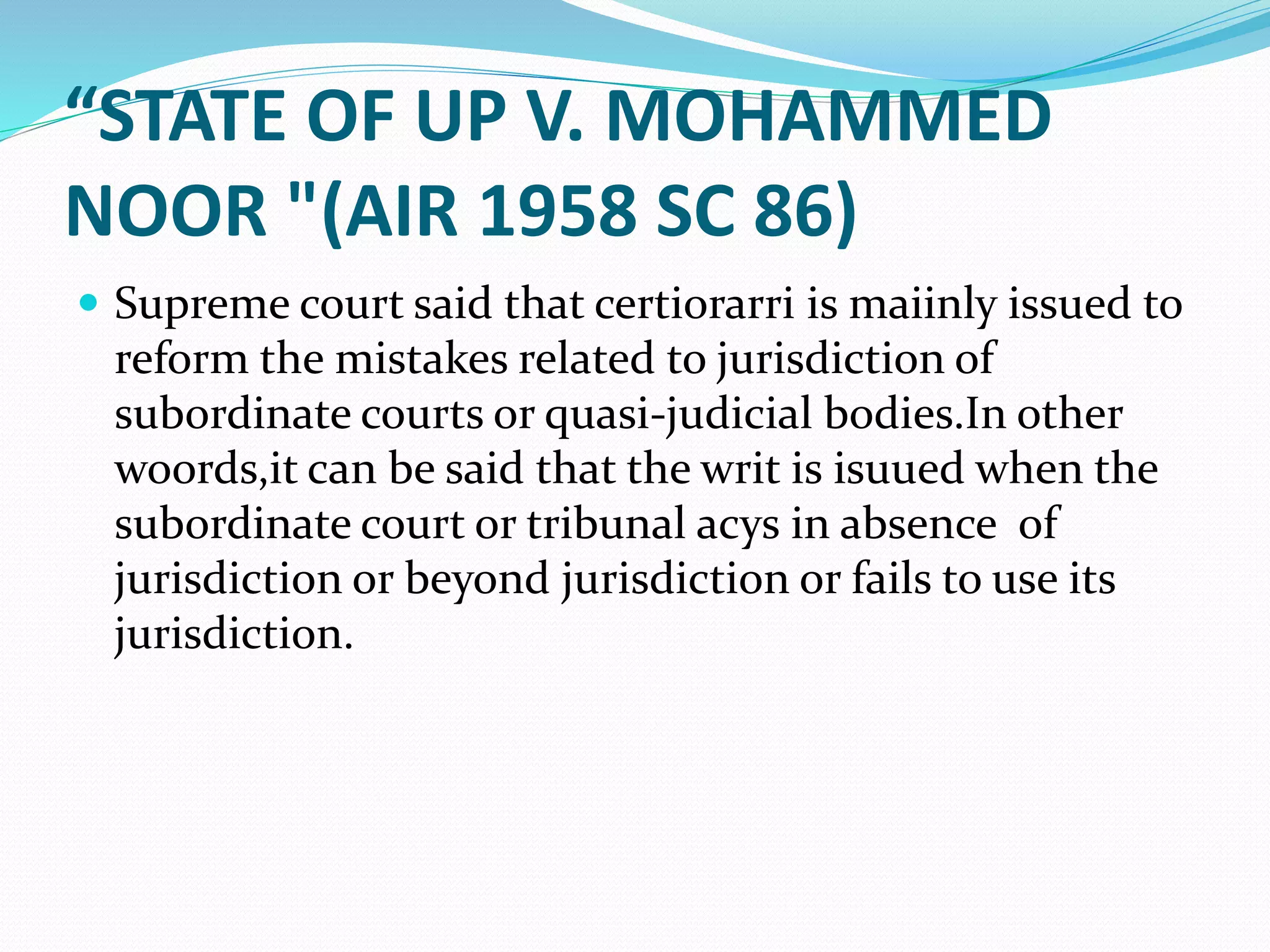
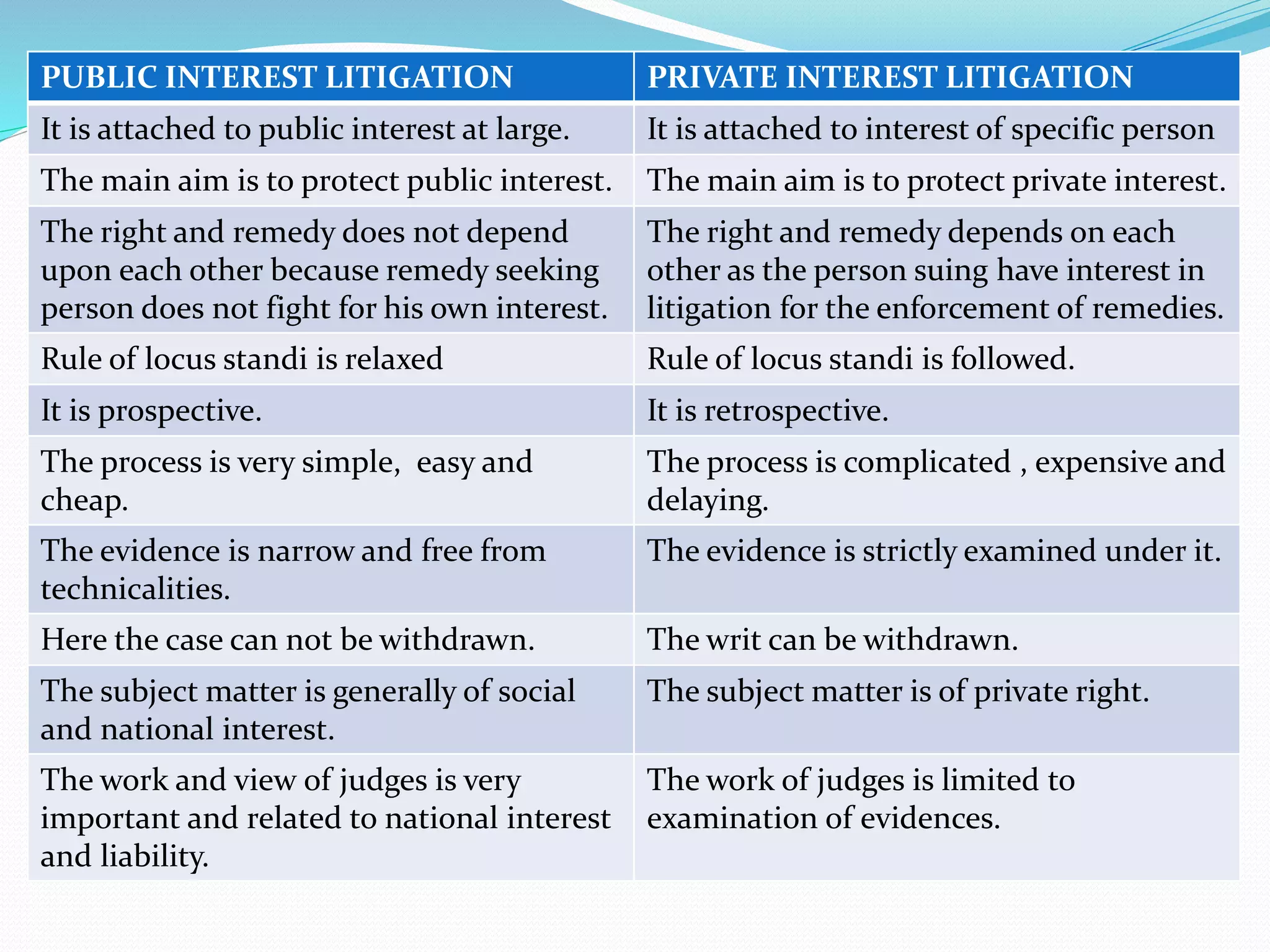
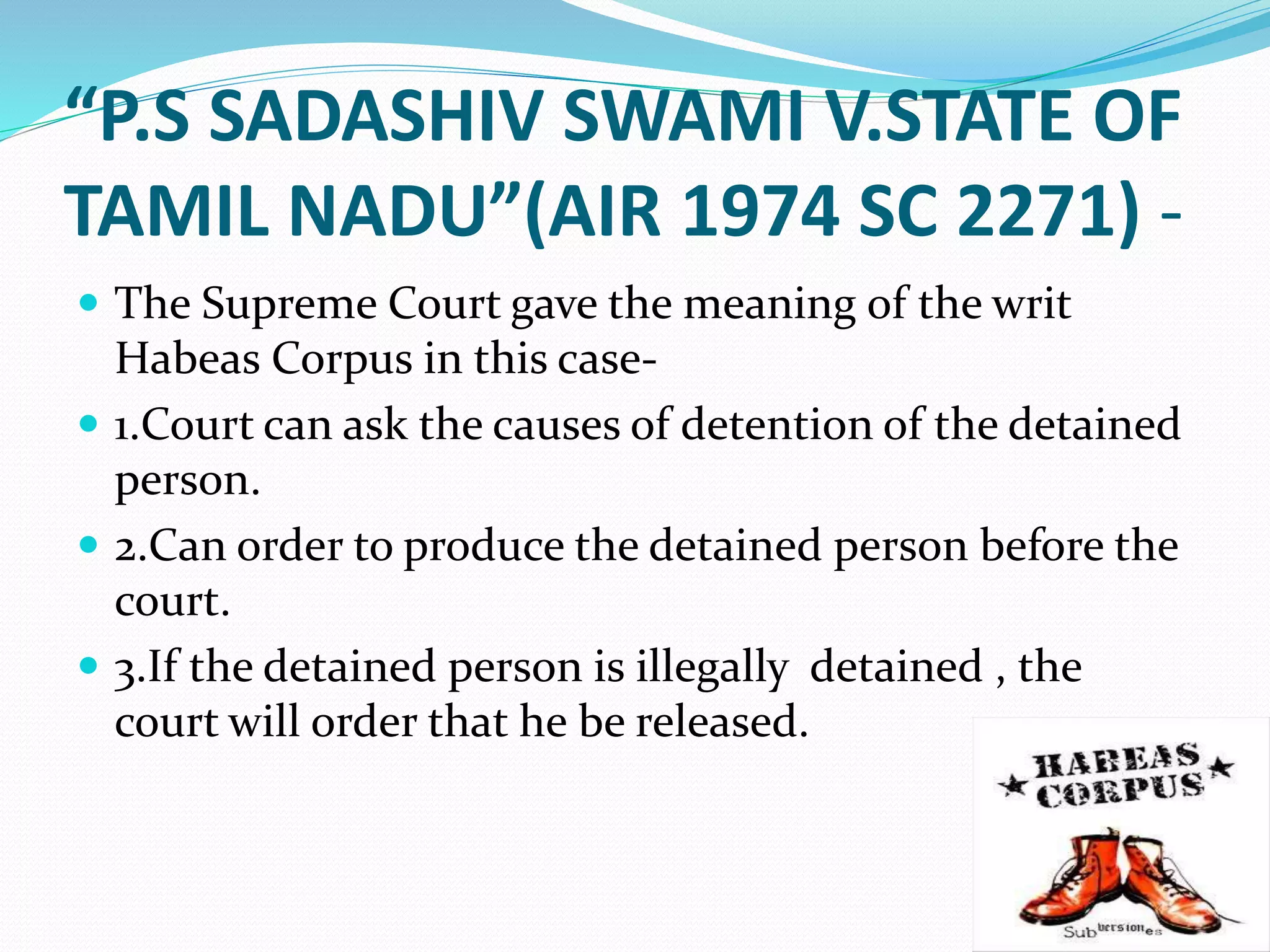
The document explains the concept of writs in Indian law, which are formal orders issued by courts to protect citizens' fundamental rights as per Articles 32 and 226 of the Constitution. It details the five types of writs: habeas corpus, mandamus, prohibition, certiorari, and quo-warranto, along with their definitions and conditions for issuance. Additionally, it contrasts public interest litigation with private interest litigation, highlighting their differences in purpose, process, and involvement.










![“MANI SHOBHREJ JAIN V. STATE
OF HARYANA” [(1977)1 SCC 486]-
Requirement of mandamus writ are described in this
case.According to it,following condition for issue of
mandamus are required to be fulfilled-
Existence of legal right,
Such legal right shall be enforceable by court,
The enforcement of such right imposes responsibility
of performance of any duty over any person , public
authority, corporation or government.
Such duty is of public nature.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typesofwritanddifferencebetweenpublicinterestlitigationandprivateinte0-150926095038-lva1-app6892/75/Types-of-writ-and-difference-between-public-interest-litigation-and-private-inte-0-13-2048.jpg)