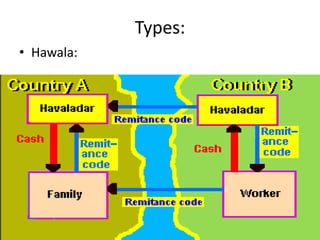
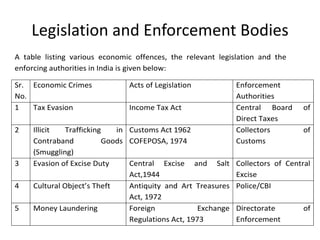
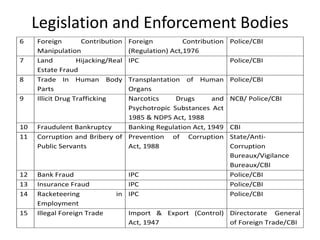
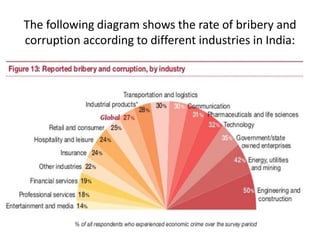
Economic crime refers to wrongful acts committed by an organization to gain money or benefits. Corruption involves using an official position for personal advantage. Money laundering disguises the source of illegal funds. Common economic crimes discussed include insurance fraud, smuggling, cybercrime, trafficking, bribery, and scams like the Indian coal allocation scam. Legislation and enforcement bodies in India that deal with economic offenses are listed, along with steps the Modi government has taken against black money. Rates of bribery and corruption are shown to vary across industries in India. In conclusion, most economic crimes involve cooperation between corrupt politicians, businessmen, and officials. A separate economic offenses code may help counter such crimes more effectively.