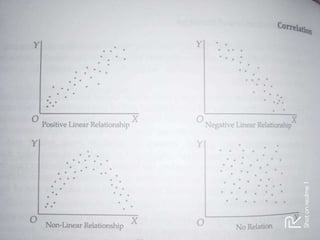
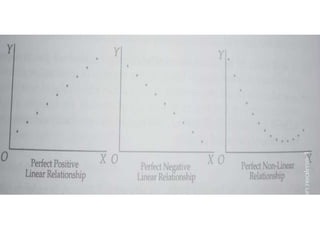
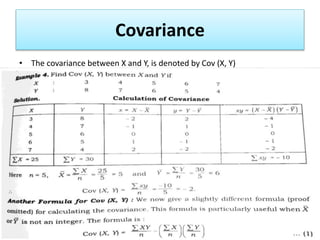
This document discusses simple linear correlation. It defines correlation as the co-variation between two or more variables. The main types of correlation discussed are positive and negative correlation, and linear and non-linear correlation. Positive correlation means that as one variable increases, the other also increases, while negative correlation means one variable increases as the other decreases. Linear correlation means the relationship between the variables is constant, while non-linear means it is not. Methods for studying correlation discussed include scatter diagrams, Pearson's coefficient of correlation, and rank correlation.