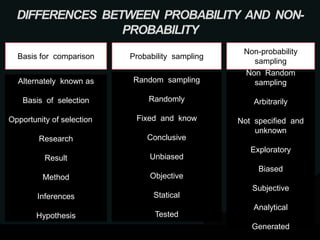
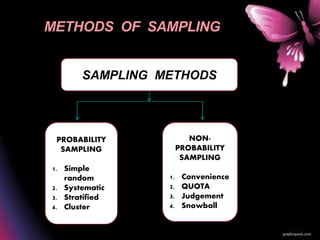
Sampling is the process of selecting a subset of individuals from within a population to estimate characteristics of the whole population, and there are two main types of sampling: probability sampling which gives all individuals an equal chance of being selected, and non-probability sampling which does not. The main difference between these two sampling methods is that probability sampling allows for statistical inferences about the population while non-probability sampling only explores characteristics of the sample. Common sampling methods include simple random, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling for probability sampling and convenience, quota, judgement, and snowball sampling for non-probability sampling.