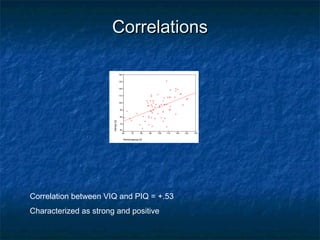
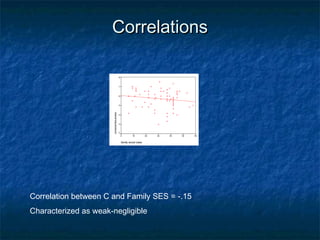
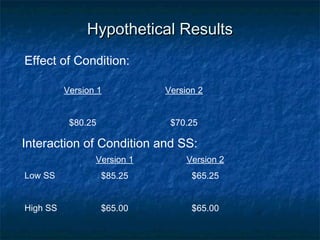
This document discusses different types of research designs used in psychology, including correlational research, quasi-experimental research, and problems to look for in research studies. It provides examples of each type of research design. Correlational research seeks to establish relationships between variables without manipulation. Quasi-experimental research blends correlation and experimental approaches by examining interactions between individual differences and manipulations. Problems to look for include confounds, nonrandom sampling, failure to replicate, and lack of comparison groups.