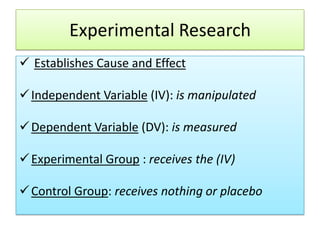
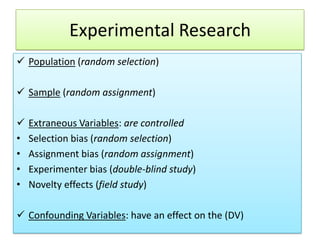
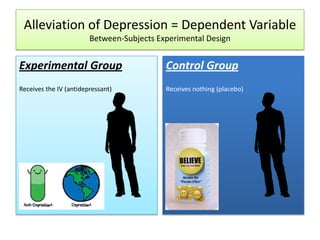
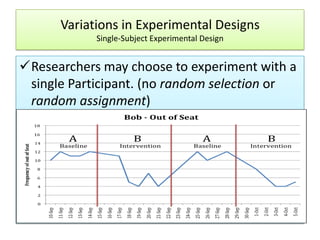
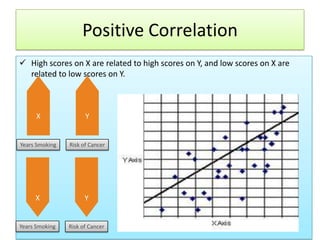
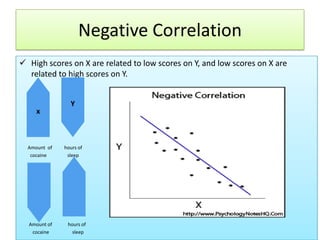
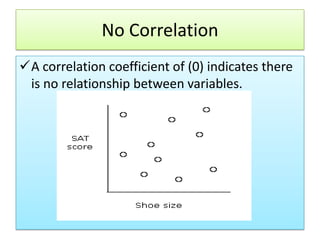
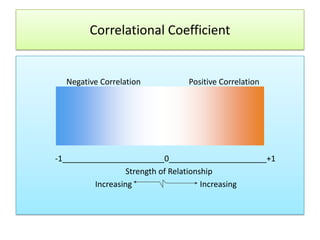
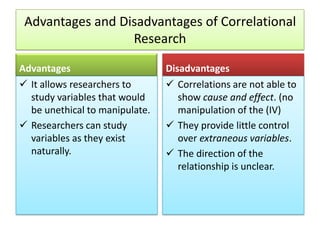
The document outlines the principles and methodologies of psychological research, emphasizing the empirical nature of gathering data through observation to formulate hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships. It describes the steps in scientific research, including hypothesis testing, data collection, and analysis, along with different experimental designs such as between-subjects, within-subjects, and single-subject experiments. Additionally, it covers the advantages and disadvantages of experimental and correlational research approaches, highlighting the importance of controlling variables and understanding the limitations in establishing causal relationships.