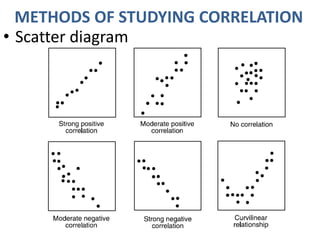
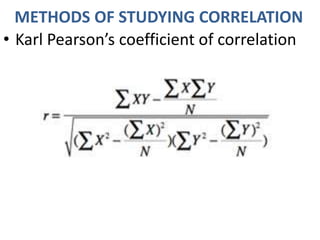
The document discusses different types and methods of studying correlation. It describes positive and negative, linear and non-linear, simple, partial and multiple, and real and spurious correlations. Two main methods of studying correlation mentioned are scatter diagrams and Karl Pearson's coefficient of correlation. Scatter diagrams are simple to understand but don't show the degree of correlation, while Pearson's coefficient measures the closeness of the relationship between -1 and 1 and indicates the direction.