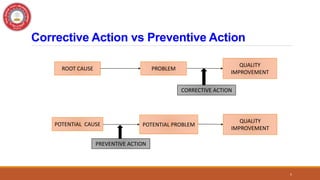
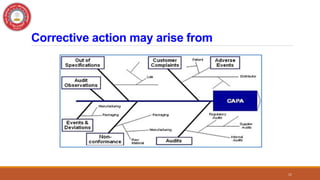
This document discusses Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA), which is a system used in quality management to eliminate causes of nonconformities and prevent their recurrence. CAPA involves both corrective actions, which address existing problems, and preventive actions, which address potential future problems. The document outlines the objectives, processes, differences, steps, benefits, and applications of CAPA for pharmaceutical quality management. It emphasizes that CAPA is an important tool for ensuring quality, compliance, and continuous improvement.