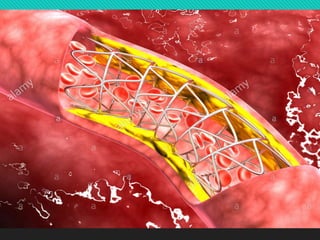
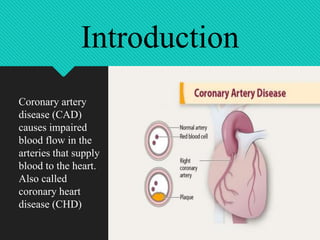
Coronary artery disease is caused by reduced blood flow to the heart due to plaque buildup in the arteries. The most common symptom is angina or chest pain, but other signs include shortness of breath, arm or shoulder pain, sweating, and dizziness. Risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and unhealthy habits. Diagnosis involves tests like an electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, and cardiac catheterization. Treatment options are lifestyle changes, procedures like angioplasty and stents, or bypass surgery.