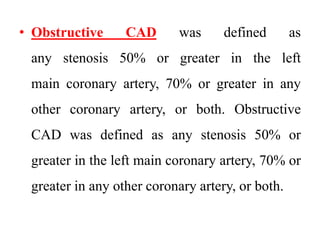
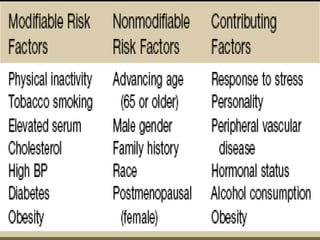
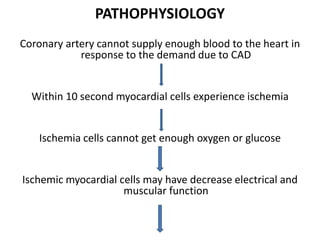
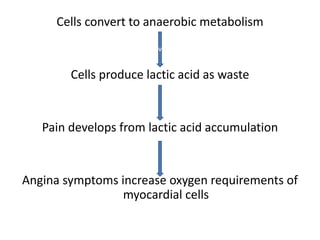
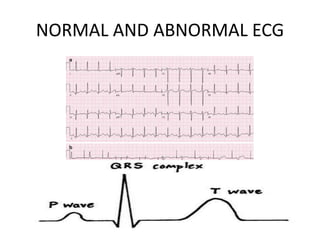
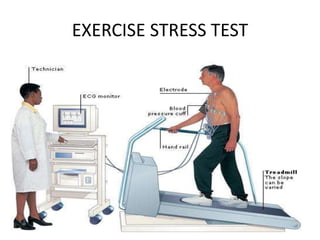
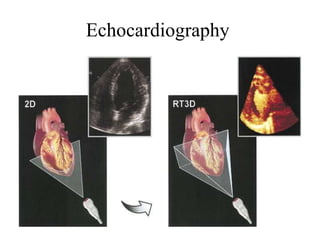
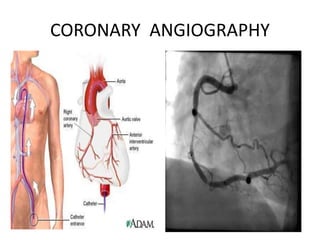
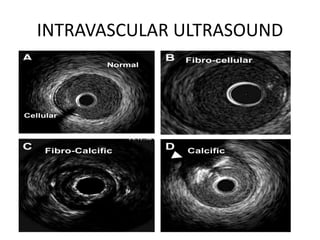
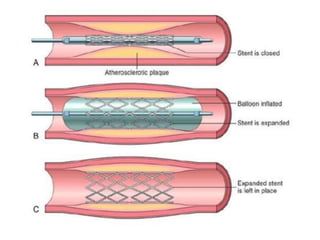
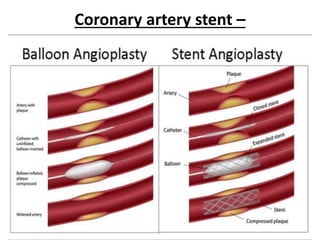
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common type of cardiovascular disease. It is caused by plaque buildup in the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart. This restricts blood flow and oxygen supply to heart muscle. Symptoms include chest pain and discomfort known as angina. Diagnosis involves electrocardiograms, stress tests, imaging like angiography and echocardiograms. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes and medications to control symptoms and risk factors as well as procedures like angioplasty and stents to open blocked arteries. High dose thiamine injections showed promise in curing CAD in one research study. Proper management can help cure angina and allow those with CAD to live long, productive lives