The document discusses the anatomy and clinical examination of the cornea. It contains the following key points:
1) The cornea has 5 layers - an epithelium, Bowman's membrane, a thick stromal layer, Descemet's membrane, and an endothelium. The stroma comprises 90% of the corneal thickness and contains collagen fibrils.
2) The cornea receives its nerve supply from the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve via the nasociliary nerve. Clinical tests like the corneal reflex test examine the integrity of these nerve pathways.
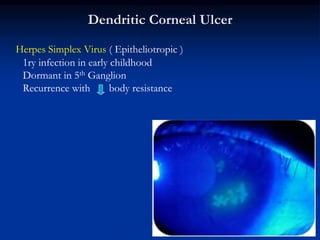
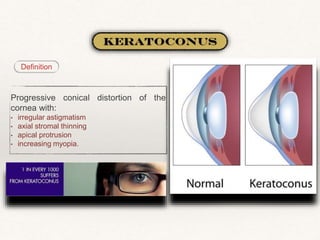
3) Common corneal pathologies include infections like herpes simplex keratitis and acanthamoeba keratitis.