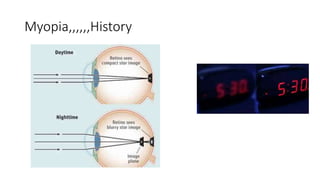
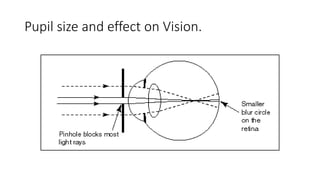
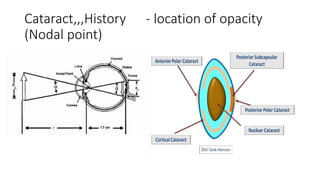
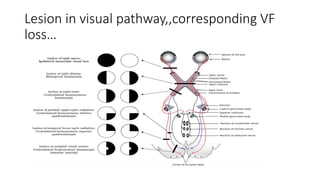
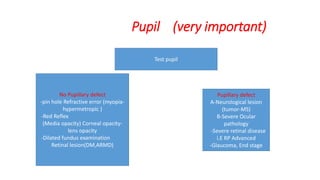
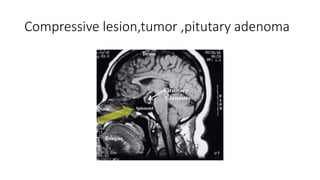
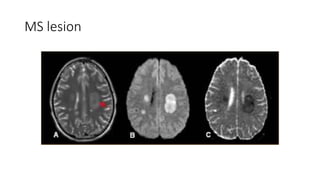
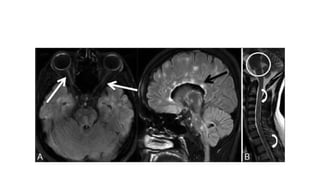
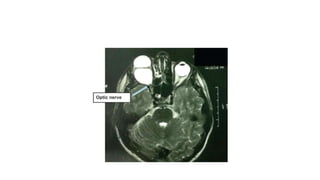
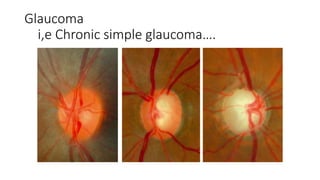
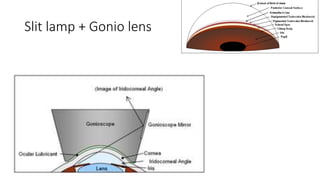
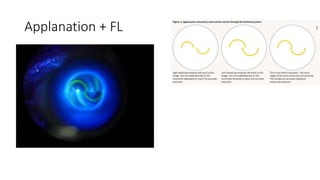
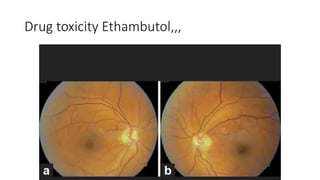
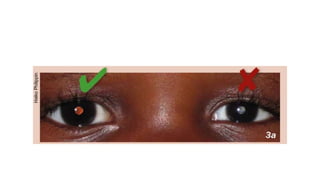
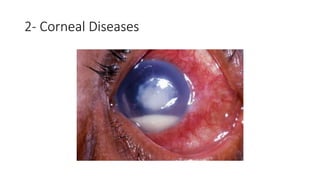
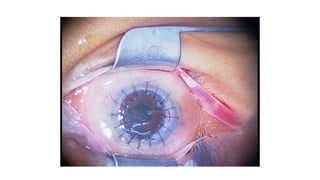
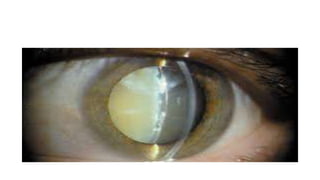
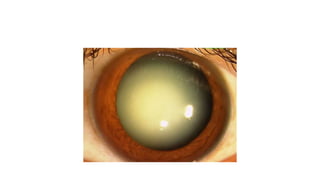
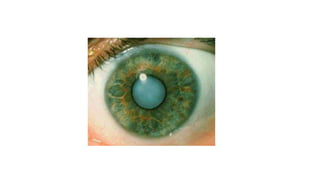
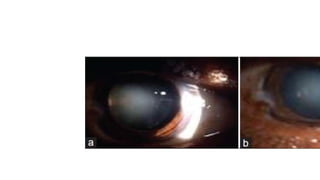
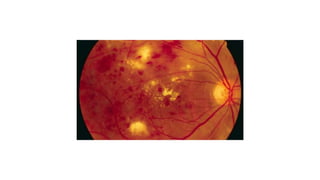
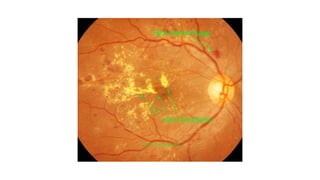
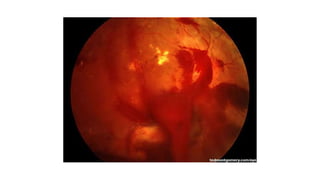
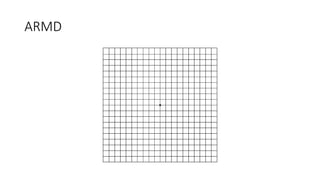
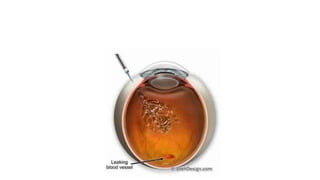
This document discusses the gradual causes of visual loss, including both reversible and irreversible causes. Reversible causes include cataract, refractive error, corneal disease, diabetic macular edema, age-related macular degeneration, and uveitis. Irreversible causes include optic atrophy, multiple sclerosis, end-stage glaucoma, and retinitis pigmentosa. A thorough history and clinical examination focusing on visual acuity, pupil testing, red reflex, fundoscopy, and visual field testing is needed to diagnose the cause. Appropriate management can reverse some conditions, while others may become permanent if not treated.