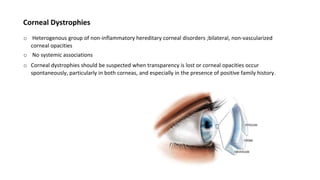
Corneal dystrophies are a group of hereditary corneal disorders characterized by bilateral non-inflammatory corneal opacities. They are classified based on the layer of the cornea involved, which can be the epithelium, stroma, or endothelium. Common types include epithelial basement membrane dystrophy, which causes recurrent corneal erosions, and granular corneal dystrophy type 1, characterized by discrete stromal deposits that increase in size over time. Management depends on the type and severity but may include lubricants, contact lenses, phototherapeutic keratectomy, or corneal transplantation.



![Epithelial Basement membrane dystrophy (Cogan dystrophy) [Map dot fingerprint
dystrophy, anterior basement membrane dystrophy, dystrophic recurrent erosion]
Most commonly encountered anterior corneal
dystrophy
Characterised by recurrent corneal erosions
Onset : usually present in adult life
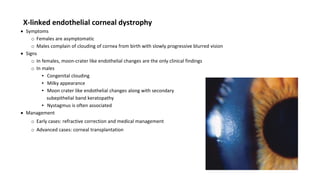
Symptoms
o May be asymptomatic
o Recurrent erosions with pain, lacrimation
and blurred vision
o Irregular astigmatism
o Monocular diplopia
Signs
o Best visualize by retroillumination or scleral
scatter
o Maps: Grey geographical patches
o Dots(Cogan): irregular , round or comma
shaped grey white intraepithelial opacities
o Blebs of Bron and Brown: small clear round
dots in a pebbled glass pattern
o Finger print lines: Parallel, Curvilinear,
refractile, branching lines with club shape
terminations
Recent erosions occur due to lack of
hemidesmosomal connections between
epithelial cells](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cornealdystrophy-230810062345-bd91bd52/85/Corneal-Dystrophy-6-320.jpg)
![ Management:
o Corneal scraping debridement followed by a soft contact lens for 24-48 hours and topical antibiotics and
lubricants
o Conservative therapy with hypertonic sodium chloride
▪ It acts by dehydrating the epithelium allowing it to adhere better
▪ Lubricating eyedrops
o Stromal puncture
▪ 23-25 gauge needle
▪ Anterior stromal puncture by Nd:YAG
o Phototherapeutic Keratectomy
▪ Excimer laser with low pulse energy and low number of pulses
▪ [Shallow ablations with mean ablation depth of 46 microns have been recommended for decreased
complications]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cornealdystrophy-230810062345-bd91bd52/85/Corneal-Dystrophy-7-320.jpg)
![Epithelial recurrent erosion dystrophy (Franceschetti) [Smolandiensis,
Helsinglandica]
o Symptoms :
▪ Onset is usually in the first decade of life
▪ Redness, photophobia, epiphora, ocular pain
▪ Recurrent attacks precipitated by exposure to sunlight, dust, smoke and lack of sleep
▪ Increased sensitivity of eyes
▪ Attacks decline by fourth and fifth decades and cease by 50 years
o Signs
▪ Recurrent corneal erosions spontaneously or after minimal trauma
▪ Diffuse, central, subepithelial opacification with subepithelial fibrosis
▪ Central corneal keloid like opacities seen in Smolandiensis variant
o Management
▪ Keratoplasty
Recurrence after approximately 15 months](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cornealdystrophy-230810062345-bd91bd52/85/Corneal-Dystrophy-8-320.jpg)

![Meesmann corneal dystrophy [Juvenile Hereditary ED; Stocker-Holt]
o It is a rare non progressive abnormality of
corneal epithelial metabolism.
o Bilateral, diffuse involving accumulation of
intracytoplasmic debris in the corneal
epithelium with the formation of epithelial
cysts
o Symptoms :
▪ Onset : early childhood [12 months of age :
clinical signs]
▪ Usually asymptomatic till 4th or 5th decade
▪ Mild visual reduction, glare, light sensitivity
or painful recurrent epithelial erosions
▪ Blurred vision
o Signs:
▪ Tiny intraepithelial cysts of uniform size but
variable density is maximal centrally and
extend towards limbus
▪ Cornea may be slightly thinned and
sensation reduced
o Treatment
▪ Ocular lubricants
▪ Therapeutic contact lenses
▪ Rx for corneal erosions in severe cases](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cornealdystrophy-230810062345-bd91bd52/85/Corneal-Dystrophy-10-320.jpg)

![Gelatinous drop like corneal dystrophy [subepithelial amyloidosis, primary
familial amyloidosis]
o Symptoms
▪ Onset : 1st-2nd decade
▪ Decreased vision, photophobia, irritation,
redness and lacrimation
o Signs
▪ Clusters of small multiple nodules and acquire a
mulberry configuration
▪ Stromal opacification or larger kumquat like
lesions in advanced stages
▪ Hyperpermeability of corneal epithelium [late
staining of Fluorescein]
▪ Superficial vascularization
o Management
▪ Surgical management may be required for visual
rehabilitation
Superficial Keratectomy
Corneal transplant procedures like lamellar
keratoplasty or penetrating keratoplasty
▪ Recurrence is common [usually after 5 years]
▪ Phototherapeutic keratectomy is useful for
corneal opacities that recur after lamellar grafts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cornealdystrophy-230810062345-bd91bd52/85/Corneal-Dystrophy-12-320.jpg)

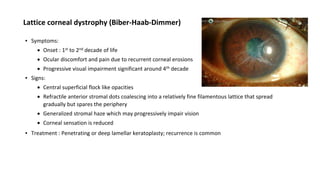
![Familial Amyloidosis [Finnish or Meretoja type] [Gelsolin type LCD]
▪ Systemic condition
▪ Symptoms:
Onset after 20 years
Ocular irritation, late impairment of vision
(6th decade)
Erosions are rare
Bilateral involvement
▪ Signs
Sparse stromal lattice lines spread centrally
from the periphery
Corneal sensation is impaired
▪ Systemic features
Progressive cranial and peripheral
neuropathy
Mask like facies and autonomic features
Dysarthria
Dry and extremely lax itchy skin
Protruding lips with impaired movement
Pendulous ears
Blepharochalasis
▪ Management:
Treatment of recurrent epithelial erosions
Amniotic membrane transplantation may
be done for persistent epithelial defects
Phototherapeutic keratectomy
Corneal transplant (keratoplasty) in cases
with visually significant epithelial scarring
and corneal haze
Recurrence common](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cornealdystrophy-230810062345-bd91bd52/85/Corneal-Dystrophy-17-320.jpg)
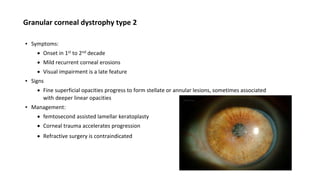
![Granular corneal dystrophy type 1
▪ GCD type 1 [Corneal dystrophy Groenouw type 1]
▪ Symptoms:
Onset in 1st decade
Glare and photophobia
Visual acuity decreases as opacification progresses with age
Recurrent erosions are unknown
▪ Signs:
Discrete white central anterior stromal deposits
Gradual increase in number and size of deposits with deeper and outward spread sparing the limbus
Corneal sensation is impaired
▪ Management:
Penetrating or deep lamellar keratoplasty
Superficial recurrences may require repeated excimer laser keratectomy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cornealdystrophy-230810062345-bd91bd52/85/Corneal-Dystrophy-18-320.jpg)

![Macular corneal dystrophy [Groenouw corneal dystrophy type II, Fehr speckled
dystrophy]
Symptoms
o Onset: childhood
o Slowly progressive course
o Recurrent corneal erosions are common
o Reduced corneal sensitivity
o Visual impairment occur early
Signs:
o Dense but poorly delineated greyish-white
spots centrally in the anterior stroma and
peripherally in the posterior stroma
o Opacities are elevated
o Progression of lesions occur in conjunction
with anterior stromal haze initially
involving the central cornea.Eventual
involvement of full thickness stroma,
extending to the limbus with no clear
zone.
o Thinning of cornea in early stage, with late
thickening due to stromal imbibition of
water from endothelial decompensation
o In advanced stage, Descemet membrane
develop guttate excrescences
o Corneal sensations are reduced
Management : Penetrating keratoplasty;
Recurrence is common](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cornealdystrophy-230810062345-bd91bd52/85/Corneal-Dystrophy-21-320.jpg)


![Congenital stromal corneal dystrophy
▪ Symptoms
Rare, congenital, non-progressive or slowly progressive
Moderate to severe visual loss
Strabismus and glaucoma association seen in some patients
Corneal erosions, photophobia and corneal vascularization are absent
▪ Signs
Bilateral opaque flaky or feathery areas of clouding in the stroma [multiply with age and
eventually preclude visibility of the endothelium]
Corneal stromal thickness increased
▪ Management
Keratoplasty in cases of visually disabling opacities](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cornealdystrophy-230810062345-bd91bd52/85/Corneal-Dystrophy-25-320.jpg)