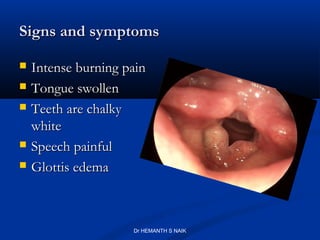
Corrosive poisons are chemicals that damage and destroy surfaces through erosion. Common corrosive poisons include sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, and carbolic acid. When ingested, these chemicals cause severe burning pain and inflammation of tissues in the mouth, throat, and stomach. Victims may experience shock, difficulty swallowing or speaking, and blackened or discolored tissues upon examination. Severe cases can result in coma or death. While some corrosive poisons like carbolic acid also act as narcotics, their primary danger is their corrosive properties which can cause permanent scarring when used in violent acid attacks known as vitriolage.