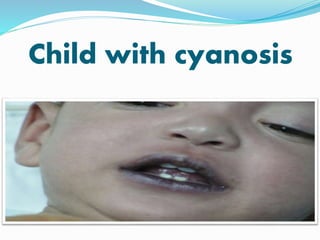
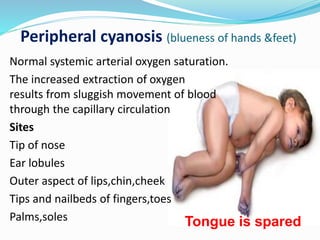
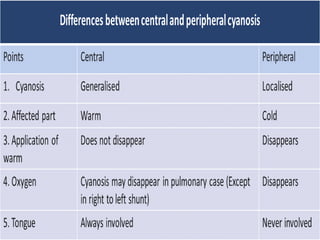
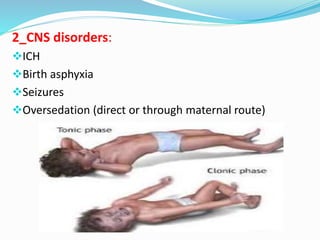
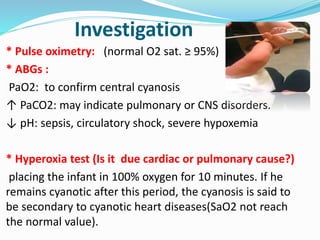
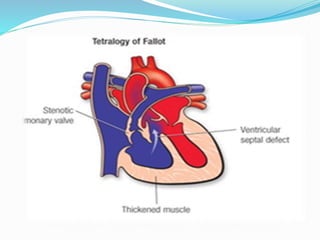
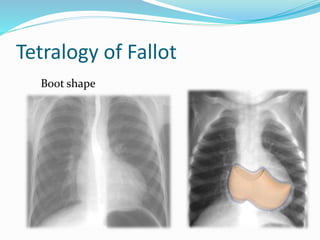
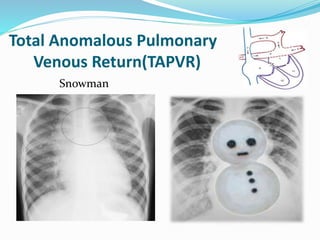
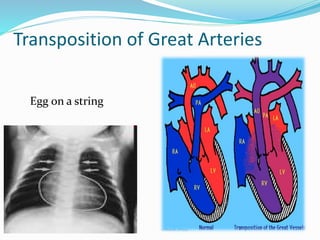
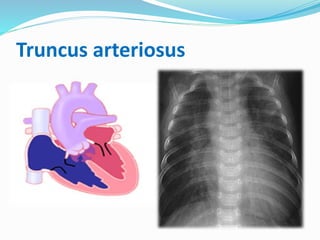
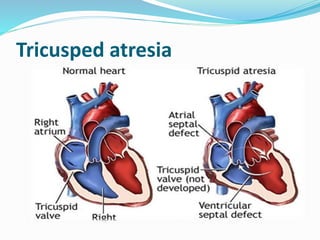
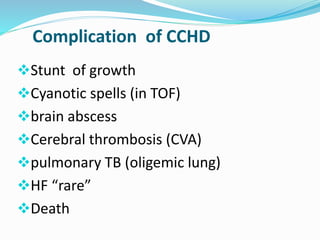
This document discusses cyanosis in children. It defines cyanosis as a bluish discoloration of the skin caused by increased reduced hemoglobin. There are two types: peripheral cyanosis caused by slowed blood flow and central cyanosis caused by low oxygen saturation. Causes of central cyanosis include respiratory disorders like pneumonia, cardiac disorders like congenital heart diseases, and neurological disorders like seizures. Management involves diagnosis of the underlying cause through history, exams, oxygen testing, and imaging like echocardiograms. Treatment depends on the specific condition but may include oxygen, antibiotics for infection, or surgery for heart defects.