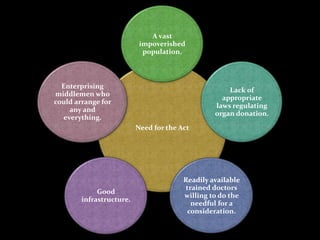
The document discusses organ transplantation in India. It notes that there is a large need for organ transplants but limited availability of organs, resulting in over 100,000 deaths per year. The Transplantation of Human Organs Act was passed in 1994 to regulate organ donation and transplants and prevent commercialization. It established two authorities - the Authorization Committee to approve transplants and the Appropriate Authority to regulate hospitals performing transplants. The Act placed restrictions on organ removal and donation to prevent exploitation and only allow transplants for therapeutic purposes.