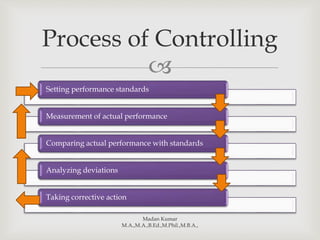
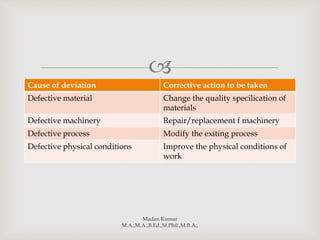
Controlling refers to measuring performance against standards, identifying deviations, and taking corrective actions. It involves setting standards, measuring actual performance, comparing performance to standards, analyzing deviations, and making corrections. Controlling and planning are interrelated functions - planning provides the basis for standards while controlling improves future planning. The process of controlling involves ongoing measurement, evaluation, and adjustment to ensure organizational goals are achieved.