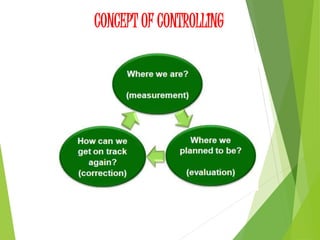
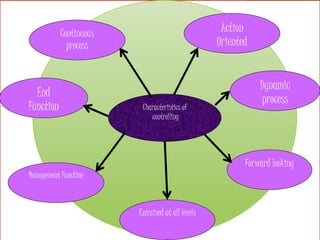
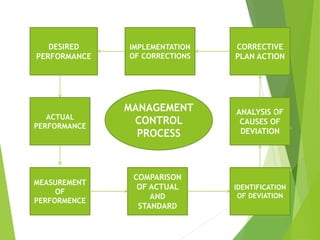
This document discusses the concept and process of controlling. Controlling is defined as monitoring performance and taking action to ensure desired results. It involves establishing standards, measuring performance, comparing actual results to standards, and correcting any deviations. The key aspects of controlling covered include its characteristics as a continuous, dynamic, and action-oriented process exercised at all levels of management. The document also outlines the importance of controlling for adjustment, policy verification, responsibility, coordination, and organizational effectiveness. Finally, it describes the typical steps in the control process of establishing standards, measuring performance, comparing to standards, and correcting deviations.